Migrate to new swagger docs generation (#18)
This commit is contained in:
27
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
27
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2012 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
|
||||
met:
|
||||
|
||||
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer
|
||||
in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
|
||||
distribution.
|
||||
* Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its
|
||||
contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
|
||||
this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
|
||||
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
"AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
|
||||
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
|
||||
OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
|
||||
SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
|
||||
DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
|
||||
THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
|
||||
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
|
||||
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
25
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
25
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
# Go's `text/template` package with newline elision
|
||||
|
||||
This is a fork of Go 1.4's [text/template](http://golang.org/pkg/text/template/) package with one addition: a backslash immediately after a closing delimiter will delete all subsequent newlines until a non-newline.
|
||||
|
||||
eg.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{{if true}}\
|
||||
hello
|
||||
{{end}}\
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Will result in:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
hello\n
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Rather than:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
\n
|
||||
hello\n
|
||||
\n
|
||||
```
|
||||
406
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/doc.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
406
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/doc.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,406 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Package template implements data-driven templates for generating textual output.
|
||||
|
||||
To generate HTML output, see package html/template, which has the same interface
|
||||
as this package but automatically secures HTML output against certain attacks.
|
||||
|
||||
Templates are executed by applying them to a data structure. Annotations in the
|
||||
template refer to elements of the data structure (typically a field of a struct
|
||||
or a key in a map) to control execution and derive values to be displayed.
|
||||
Execution of the template walks the structure and sets the cursor, represented
|
||||
by a period '.' and called "dot", to the value at the current location in the
|
||||
structure as execution proceeds.
|
||||
|
||||
The input text for a template is UTF-8-encoded text in any format.
|
||||
"Actions"--data evaluations or control structures--are delimited by
|
||||
"{{" and "}}"; all text outside actions is copied to the output unchanged.
|
||||
Actions may not span newlines, although comments can.
|
||||
|
||||
Once parsed, a template may be executed safely in parallel.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a trivial example that prints "17 items are made of wool".
|
||||
|
||||
type Inventory struct {
|
||||
Material string
|
||||
Count uint
|
||||
}
|
||||
sweaters := Inventory{"wool", 17}
|
||||
tmpl, err := template.New("test").Parse("{{.Count}} items are made of {{.Material}}")
|
||||
if err != nil { panic(err) }
|
||||
err = tmpl.Execute(os.Stdout, sweaters)
|
||||
if err != nil { panic(err) }
|
||||
|
||||
More intricate examples appear below.
|
||||
|
||||
Actions
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the list of actions. "Arguments" and "pipelines" are evaluations of
|
||||
data, defined in detail below.
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
// {{/* a comment */}}
|
||||
// A comment; discarded. May contain newlines.
|
||||
// Comments do not nest and must start and end at the
|
||||
// delimiters, as shown here.
|
||||
/*
|
||||
|
||||
{{pipeline}}
|
||||
The default textual representation of the value of the pipeline
|
||||
is copied to the output.
|
||||
|
||||
{{if pipeline}} T1 {{end}}
|
||||
If the value of the pipeline is empty, no output is generated;
|
||||
otherwise, T1 is executed. The empty values are false, 0, any
|
||||
nil pointer or interface value, and any array, slice, map, or
|
||||
string of length zero.
|
||||
Dot is unaffected.
|
||||
|
||||
{{if pipeline}} T1 {{else}} T0 {{end}}
|
||||
If the value of the pipeline is empty, T0 is executed;
|
||||
otherwise, T1 is executed. Dot is unaffected.
|
||||
|
||||
{{if pipeline}} T1 {{else if pipeline}} T0 {{end}}
|
||||
To simplify the appearance of if-else chains, the else action
|
||||
of an if may include another if directly; the effect is exactly
|
||||
the same as writing
|
||||
{{if pipeline}} T1 {{else}}{{if pipeline}} T0 {{end}}{{end}}
|
||||
|
||||
{{range pipeline}} T1 {{end}}
|
||||
The value of the pipeline must be an array, slice, map, or channel.
|
||||
If the value of the pipeline has length zero, nothing is output;
|
||||
otherwise, dot is set to the successive elements of the array,
|
||||
slice, or map and T1 is executed. If the value is a map and the
|
||||
keys are of basic type with a defined order ("comparable"), the
|
||||
elements will be visited in sorted key order.
|
||||
|
||||
{{range pipeline}} T1 {{else}} T0 {{end}}
|
||||
The value of the pipeline must be an array, slice, map, or channel.
|
||||
If the value of the pipeline has length zero, dot is unaffected and
|
||||
T0 is executed; otherwise, dot is set to the successive elements
|
||||
of the array, slice, or map and T1 is executed.
|
||||
|
||||
{{template "name"}}
|
||||
The template with the specified name is executed with nil data.
|
||||
|
||||
{{template "name" pipeline}}
|
||||
The template with the specified name is executed with dot set
|
||||
to the value of the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
{{with pipeline}} T1 {{end}}
|
||||
If the value of the pipeline is empty, no output is generated;
|
||||
otherwise, dot is set to the value of the pipeline and T1 is
|
||||
executed.
|
||||
|
||||
{{with pipeline}} T1 {{else}} T0 {{end}}
|
||||
If the value of the pipeline is empty, dot is unaffected and T0
|
||||
is executed; otherwise, dot is set to the value of the pipeline
|
||||
and T1 is executed.
|
||||
|
||||
Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
An argument is a simple value, denoted by one of the following.
|
||||
|
||||
- A boolean, string, character, integer, floating-point, imaginary
|
||||
or complex constant in Go syntax. These behave like Go's untyped
|
||||
constants, although raw strings may not span newlines.
|
||||
- The keyword nil, representing an untyped Go nil.
|
||||
- The character '.' (period):
|
||||
.
|
||||
The result is the value of dot.
|
||||
- A variable name, which is a (possibly empty) alphanumeric string
|
||||
preceded by a dollar sign, such as
|
||||
$piOver2
|
||||
or
|
||||
$
|
||||
The result is the value of the variable.
|
||||
Variables are described below.
|
||||
- The name of a field of the data, which must be a struct, preceded
|
||||
by a period, such as
|
||||
.Field
|
||||
The result is the value of the field. Field invocations may be
|
||||
chained:
|
||||
.Field1.Field2
|
||||
Fields can also be evaluated on variables, including chaining:
|
||||
$x.Field1.Field2
|
||||
- The name of a key of the data, which must be a map, preceded
|
||||
by a period, such as
|
||||
.Key
|
||||
The result is the map element value indexed by the key.
|
||||
Key invocations may be chained and combined with fields to any
|
||||
depth:
|
||||
.Field1.Key1.Field2.Key2
|
||||
Although the key must be an alphanumeric identifier, unlike with
|
||||
field names they do not need to start with an upper case letter.
|
||||
Keys can also be evaluated on variables, including chaining:
|
||||
$x.key1.key2
|
||||
- The name of a niladic method of the data, preceded by a period,
|
||||
such as
|
||||
.Method
|
||||
The result is the value of invoking the method with dot as the
|
||||
receiver, dot.Method(). Such a method must have one return value (of
|
||||
any type) or two return values, the second of which is an error.
|
||||
If it has two and the returned error is non-nil, execution terminates
|
||||
and an error is returned to the caller as the value of Execute.
|
||||
Method invocations may be chained and combined with fields and keys
|
||||
to any depth:
|
||||
.Field1.Key1.Method1.Field2.Key2.Method2
|
||||
Methods can also be evaluated on variables, including chaining:
|
||||
$x.Method1.Field
|
||||
- The name of a niladic function, such as
|
||||
fun
|
||||
The result is the value of invoking the function, fun(). The return
|
||||
types and values behave as in methods. Functions and function
|
||||
names are described below.
|
||||
- A parenthesized instance of one the above, for grouping. The result
|
||||
may be accessed by a field or map key invocation.
|
||||
print (.F1 arg1) (.F2 arg2)
|
||||
(.StructValuedMethod "arg").Field
|
||||
|
||||
Arguments may evaluate to any type; if they are pointers the implementation
|
||||
automatically indirects to the base type when required.
|
||||
If an evaluation yields a function value, such as a function-valued
|
||||
field of a struct, the function is not invoked automatically, but it
|
||||
can be used as a truth value for an if action and the like. To invoke
|
||||
it, use the call function, defined below.
|
||||
|
||||
A pipeline is a possibly chained sequence of "commands". A command is a simple
|
||||
value (argument) or a function or method call, possibly with multiple arguments:
|
||||
|
||||
Argument
|
||||
The result is the value of evaluating the argument.
|
||||
.Method [Argument...]
|
||||
The method can be alone or the last element of a chain but,
|
||||
unlike methods in the middle of a chain, it can take arguments.
|
||||
The result is the value of calling the method with the
|
||||
arguments:
|
||||
dot.Method(Argument1, etc.)
|
||||
functionName [Argument...]
|
||||
The result is the value of calling the function associated
|
||||
with the name:
|
||||
function(Argument1, etc.)
|
||||
Functions and function names are described below.
|
||||
|
||||
Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
A pipeline may be "chained" by separating a sequence of commands with pipeline
|
||||
characters '|'. In a chained pipeline, the result of the each command is
|
||||
passed as the last argument of the following command. The output of the final
|
||||
command in the pipeline is the value of the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
The output of a command will be either one value or two values, the second of
|
||||
which has type error. If that second value is present and evaluates to
|
||||
non-nil, execution terminates and the error is returned to the caller of
|
||||
Execute.
|
||||
|
||||
Variables
|
||||
|
||||
A pipeline inside an action may initialize a variable to capture the result.
|
||||
The initialization has syntax
|
||||
|
||||
$variable := pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
where $variable is the name of the variable. An action that declares a
|
||||
variable produces no output.
|
||||
|
||||
If a "range" action initializes a variable, the variable is set to the
|
||||
successive elements of the iteration. Also, a "range" may declare two
|
||||
variables, separated by a comma:
|
||||
|
||||
range $index, $element := pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
in which case $index and $element are set to the successive values of the
|
||||
array/slice index or map key and element, respectively. Note that if there is
|
||||
only one variable, it is assigned the element; this is opposite to the
|
||||
convention in Go range clauses.
|
||||
|
||||
A variable's scope extends to the "end" action of the control structure ("if",
|
||||
"with", or "range") in which it is declared, or to the end of the template if
|
||||
there is no such control structure. A template invocation does not inherit
|
||||
variables from the point of its invocation.
|
||||
|
||||
When execution begins, $ is set to the data argument passed to Execute, that is,
|
||||
to the starting value of dot.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some example one-line templates demonstrating pipelines and variables.
|
||||
All produce the quoted word "output":
|
||||
|
||||
{{"\"output\""}}
|
||||
A string constant.
|
||||
{{`"output"`}}
|
||||
A raw string constant.
|
||||
{{printf "%q" "output"}}
|
||||
A function call.
|
||||
{{"output" | printf "%q"}}
|
||||
A function call whose final argument comes from the previous
|
||||
command.
|
||||
{{printf "%q" (print "out" "put")}}
|
||||
A parenthesized argument.
|
||||
{{"put" | printf "%s%s" "out" | printf "%q"}}
|
||||
A more elaborate call.
|
||||
{{"output" | printf "%s" | printf "%q"}}
|
||||
A longer chain.
|
||||
{{with "output"}}{{printf "%q" .}}{{end}}
|
||||
A with action using dot.
|
||||
{{with $x := "output" | printf "%q"}}{{$x}}{{end}}
|
||||
A with action that creates and uses a variable.
|
||||
{{with $x := "output"}}{{printf "%q" $x}}{{end}}
|
||||
A with action that uses the variable in another action.
|
||||
{{with $x := "output"}}{{$x | printf "%q"}}{{end}}
|
||||
The same, but pipelined.
|
||||
|
||||
Functions
|
||||
|
||||
During execution functions are found in two function maps: first in the
|
||||
template, then in the global function map. By default, no functions are defined
|
||||
in the template but the Funcs method can be used to add them.
|
||||
|
||||
Predefined global functions are named as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
and
|
||||
Returns the boolean AND of its arguments by returning the
|
||||
first empty argument or the last argument, that is,
|
||||
"and x y" behaves as "if x then y else x". All the
|
||||
arguments are evaluated.
|
||||
call
|
||||
Returns the result of calling the first argument, which
|
||||
must be a function, with the remaining arguments as parameters.
|
||||
Thus "call .X.Y 1 2" is, in Go notation, dot.X.Y(1, 2) where
|
||||
Y is a func-valued field, map entry, or the like.
|
||||
The first argument must be the result of an evaluation
|
||||
that yields a value of function type (as distinct from
|
||||
a predefined function such as print). The function must
|
||||
return either one or two result values, the second of which
|
||||
is of type error. If the arguments don't match the function
|
||||
or the returned error value is non-nil, execution stops.
|
||||
html
|
||||
Returns the escaped HTML equivalent of the textual
|
||||
representation of its arguments.
|
||||
index
|
||||
Returns the result of indexing its first argument by the
|
||||
following arguments. Thus "index x 1 2 3" is, in Go syntax,
|
||||
x[1][2][3]. Each indexed item must be a map, slice, or array.
|
||||
js
|
||||
Returns the escaped JavaScript equivalent of the textual
|
||||
representation of its arguments.
|
||||
len
|
||||
Returns the integer length of its argument.
|
||||
not
|
||||
Returns the boolean negation of its single argument.
|
||||
or
|
||||
Returns the boolean OR of its arguments by returning the
|
||||
first non-empty argument or the last argument, that is,
|
||||
"or x y" behaves as "if x then x else y". All the
|
||||
arguments are evaluated.
|
||||
print
|
||||
An alias for fmt.Sprint
|
||||
printf
|
||||
An alias for fmt.Sprintf
|
||||
println
|
||||
An alias for fmt.Sprintln
|
||||
urlquery
|
||||
Returns the escaped value of the textual representation of
|
||||
its arguments in a form suitable for embedding in a URL query.
|
||||
|
||||
The boolean functions take any zero value to be false and a non-zero
|
||||
value to be true.
|
||||
|
||||
There is also a set of binary comparison operators defined as
|
||||
functions:
|
||||
|
||||
eq
|
||||
Returns the boolean truth of arg1 == arg2
|
||||
ne
|
||||
Returns the boolean truth of arg1 != arg2
|
||||
lt
|
||||
Returns the boolean truth of arg1 < arg2
|
||||
le
|
||||
Returns the boolean truth of arg1 <= arg2
|
||||
gt
|
||||
Returns the boolean truth of arg1 > arg2
|
||||
ge
|
||||
Returns the boolean truth of arg1 >= arg2
|
||||
|
||||
For simpler multi-way equality tests, eq (only) accepts two or more
|
||||
arguments and compares the second and subsequent to the first,
|
||||
returning in effect
|
||||
|
||||
arg1==arg2 || arg1==arg3 || arg1==arg4 ...
|
||||
|
||||
(Unlike with || in Go, however, eq is a function call and all the
|
||||
arguments will be evaluated.)
|
||||
|
||||
The comparison functions work on basic types only (or named basic
|
||||
types, such as "type Celsius float32"). They implement the Go rules
|
||||
for comparison of values, except that size and exact type are
|
||||
ignored, so any integer value, signed or unsigned, may be compared
|
||||
with any other integer value. (The arithmetic value is compared,
|
||||
not the bit pattern, so all negative integers are less than all
|
||||
unsigned integers.) However, as usual, one may not compare an int
|
||||
with a float32 and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
Associated templates
|
||||
|
||||
Each template is named by a string specified when it is created. Also, each
|
||||
template is associated with zero or more other templates that it may invoke by
|
||||
name; such associations are transitive and form a name space of templates.
|
||||
|
||||
A template may use a template invocation to instantiate another associated
|
||||
template; see the explanation of the "template" action above. The name must be
|
||||
that of a template associated with the template that contains the invocation.
|
||||
|
||||
Nested template definitions
|
||||
|
||||
When parsing a template, another template may be defined and associated with the
|
||||
template being parsed. Template definitions must appear at the top level of the
|
||||
template, much like global variables in a Go program.
|
||||
|
||||
The syntax of such definitions is to surround each template declaration with a
|
||||
"define" and "end" action.
|
||||
|
||||
The define action names the template being created by providing a string
|
||||
constant. Here is a simple example:
|
||||
|
||||
`{{define "T1"}}ONE{{end}}
|
||||
{{define "T2"}}TWO{{end}}
|
||||
{{define "T3"}}{{template "T1"}} {{template "T2"}}{{end}}
|
||||
{{template "T3"}}`
|
||||
|
||||
This defines two templates, T1 and T2, and a third T3 that invokes the other two
|
||||
when it is executed. Finally it invokes T3. If executed this template will
|
||||
produce the text
|
||||
|
||||
ONE TWO
|
||||
|
||||
By construction, a template may reside in only one association. If it's
|
||||
necessary to have a template addressable from multiple associations, the
|
||||
template definition must be parsed multiple times to create distinct *Template
|
||||
values, or must be copied with the Clone or AddParseTree method.
|
||||
|
||||
Parse may be called multiple times to assemble the various associated templates;
|
||||
see the ParseFiles and ParseGlob functions and methods for simple ways to parse
|
||||
related templates stored in files.
|
||||
|
||||
A template may be executed directly or through ExecuteTemplate, which executes
|
||||
an associated template identified by name. To invoke our example above, we
|
||||
might write,
|
||||
|
||||
err := tmpl.Execute(os.Stdout, "no data needed")
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatalf("execution failed: %s", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
or to invoke a particular template explicitly by name,
|
||||
|
||||
err := tmpl.ExecuteTemplate(os.Stdout, "T2", "no data needed")
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatalf("execution failed: %s", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
package template
|
||||
845
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/exec.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
845
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/exec.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,845 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package template
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
"runtime"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/alecthomas/template/parse"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// state represents the state of an execution. It's not part of the
|
||||
// template so that multiple executions of the same template
|
||||
// can execute in parallel.
|
||||
type state struct {
|
||||
tmpl *Template
|
||||
wr io.Writer
|
||||
node parse.Node // current node, for errors
|
||||
vars []variable // push-down stack of variable values.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// variable holds the dynamic value of a variable such as $, $x etc.
|
||||
type variable struct {
|
||||
name string
|
||||
value reflect.Value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// push pushes a new variable on the stack.
|
||||
func (s *state) push(name string, value reflect.Value) {
|
||||
s.vars = append(s.vars, variable{name, value})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// mark returns the length of the variable stack.
|
||||
func (s *state) mark() int {
|
||||
return len(s.vars)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// pop pops the variable stack up to the mark.
|
||||
func (s *state) pop(mark int) {
|
||||
s.vars = s.vars[0:mark]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// setVar overwrites the top-nth variable on the stack. Used by range iterations.
|
||||
func (s *state) setVar(n int, value reflect.Value) {
|
||||
s.vars[len(s.vars)-n].value = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// varValue returns the value of the named variable.
|
||||
func (s *state) varValue(name string) reflect.Value {
|
||||
for i := s.mark() - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
|
||||
if s.vars[i].name == name {
|
||||
return s.vars[i].value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.errorf("undefined variable: %s", name)
|
||||
return zero
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var zero reflect.Value
|
||||
|
||||
// at marks the state to be on node n, for error reporting.
|
||||
func (s *state) at(node parse.Node) {
|
||||
s.node = node
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// doublePercent returns the string with %'s replaced by %%, if necessary,
|
||||
// so it can be used safely inside a Printf format string.
|
||||
func doublePercent(str string) string {
|
||||
if strings.Contains(str, "%") {
|
||||
str = strings.Replace(str, "%", "%%", -1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// errorf formats the error and terminates processing.
|
||||
func (s *state) errorf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
name := doublePercent(s.tmpl.Name())
|
||||
if s.node == nil {
|
||||
format = fmt.Sprintf("template: %s: %s", name, format)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
location, context := s.tmpl.ErrorContext(s.node)
|
||||
format = fmt.Sprintf("template: %s: executing %q at <%s>: %s", location, name, doublePercent(context), format)
|
||||
}
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf(format, args...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// errRecover is the handler that turns panics into returns from the top
|
||||
// level of Parse.
|
||||
func errRecover(errp *error) {
|
||||
e := recover()
|
||||
if e != nil {
|
||||
switch err := e.(type) {
|
||||
case runtime.Error:
|
||||
panic(e)
|
||||
case error:
|
||||
*errp = err
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic(e)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExecuteTemplate applies the template associated with t that has the given name
|
||||
// to the specified data object and writes the output to wr.
|
||||
// If an error occurs executing the template or writing its output,
|
||||
// execution stops, but partial results may already have been written to
|
||||
// the output writer.
|
||||
// A template may be executed safely in parallel.
|
||||
func (t *Template) ExecuteTemplate(wr io.Writer, name string, data interface{}) error {
|
||||
tmpl := t.tmpl[name]
|
||||
if tmpl == nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("template: no template %q associated with template %q", name, t.name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return tmpl.Execute(wr, data)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Execute applies a parsed template to the specified data object,
|
||||
// and writes the output to wr.
|
||||
// If an error occurs executing the template or writing its output,
|
||||
// execution stops, but partial results may already have been written to
|
||||
// the output writer.
|
||||
// A template may be executed safely in parallel.
|
||||
func (t *Template) Execute(wr io.Writer, data interface{}) (err error) {
|
||||
defer errRecover(&err)
|
||||
value := reflect.ValueOf(data)
|
||||
state := &state{
|
||||
tmpl: t,
|
||||
wr: wr,
|
||||
vars: []variable{{"$", value}},
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.init()
|
||||
if t.Tree == nil || t.Root == nil {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
for name, tmpl := range t.tmpl {
|
||||
if tmpl.Tree == nil || tmpl.Root == nil {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if b.Len() > 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteString(", ")
|
||||
}
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(&b, "%q", name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if b.Len() > 0 {
|
||||
s = "; defined templates are: " + b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
state.errorf("%q is an incomplete or empty template%s", t.Name(), s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
state.walk(value, t.Root)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Walk functions step through the major pieces of the template structure,
|
||||
// generating output as they go.
|
||||
func (s *state) walk(dot reflect.Value, node parse.Node) {
|
||||
s.at(node)
|
||||
switch node := node.(type) {
|
||||
case *parse.ActionNode:
|
||||
// Do not pop variables so they persist until next end.
|
||||
// Also, if the action declares variables, don't print the result.
|
||||
val := s.evalPipeline(dot, node.Pipe)
|
||||
if len(node.Pipe.Decl) == 0 {
|
||||
s.printValue(node, val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case *parse.IfNode:
|
||||
s.walkIfOrWith(parse.NodeIf, dot, node.Pipe, node.List, node.ElseList)
|
||||
case *parse.ListNode:
|
||||
for _, node := range node.Nodes {
|
||||
s.walk(dot, node)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case *parse.RangeNode:
|
||||
s.walkRange(dot, node)
|
||||
case *parse.TemplateNode:
|
||||
s.walkTemplate(dot, node)
|
||||
case *parse.TextNode:
|
||||
if _, err := s.wr.Write(node.Text); err != nil {
|
||||
s.errorf("%s", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case *parse.WithNode:
|
||||
s.walkIfOrWith(parse.NodeWith, dot, node.Pipe, node.List, node.ElseList)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
s.errorf("unknown node: %s", node)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// walkIfOrWith walks an 'if' or 'with' node. The two control structures
|
||||
// are identical in behavior except that 'with' sets dot.
|
||||
func (s *state) walkIfOrWith(typ parse.NodeType, dot reflect.Value, pipe *parse.PipeNode, list, elseList *parse.ListNode) {
|
||||
defer s.pop(s.mark())
|
||||
val := s.evalPipeline(dot, pipe)
|
||||
truth, ok := isTrue(val)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
s.errorf("if/with can't use %v", val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if truth {
|
||||
if typ == parse.NodeWith {
|
||||
s.walk(val, list)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
s.walk(dot, list)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if elseList != nil {
|
||||
s.walk(dot, elseList)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isTrue reports whether the value is 'true', in the sense of not the zero of its type,
|
||||
// and whether the value has a meaningful truth value.
|
||||
func isTrue(val reflect.Value) (truth, ok bool) {
|
||||
if !val.IsValid() {
|
||||
// Something like var x interface{}, never set. It's a form of nil.
|
||||
return false, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch val.Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.Array, reflect.Map, reflect.Slice, reflect.String:
|
||||
truth = val.Len() > 0
|
||||
case reflect.Bool:
|
||||
truth = val.Bool()
|
||||
case reflect.Complex64, reflect.Complex128:
|
||||
truth = val.Complex() != 0
|
||||
case reflect.Chan, reflect.Func, reflect.Ptr, reflect.Interface:
|
||||
truth = !val.IsNil()
|
||||
case reflect.Int, reflect.Int8, reflect.Int16, reflect.Int32, reflect.Int64:
|
||||
truth = val.Int() != 0
|
||||
case reflect.Float32, reflect.Float64:
|
||||
truth = val.Float() != 0
|
||||
case reflect.Uint, reflect.Uint8, reflect.Uint16, reflect.Uint32, reflect.Uint64, reflect.Uintptr:
|
||||
truth = val.Uint() != 0
|
||||
case reflect.Struct:
|
||||
truth = true // Struct values are always true.
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
return truth, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) walkRange(dot reflect.Value, r *parse.RangeNode) {
|
||||
s.at(r)
|
||||
defer s.pop(s.mark())
|
||||
val, _ := indirect(s.evalPipeline(dot, r.Pipe))
|
||||
// mark top of stack before any variables in the body are pushed.
|
||||
mark := s.mark()
|
||||
oneIteration := func(index, elem reflect.Value) {
|
||||
// Set top var (lexically the second if there are two) to the element.
|
||||
if len(r.Pipe.Decl) > 0 {
|
||||
s.setVar(1, elem)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Set next var (lexically the first if there are two) to the index.
|
||||
if len(r.Pipe.Decl) > 1 {
|
||||
s.setVar(2, index)
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.walk(elem, r.List)
|
||||
s.pop(mark)
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch val.Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.Array, reflect.Slice:
|
||||
if val.Len() == 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < val.Len(); i++ {
|
||||
oneIteration(reflect.ValueOf(i), val.Index(i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
case reflect.Map:
|
||||
if val.Len() == 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, key := range sortKeys(val.MapKeys()) {
|
||||
oneIteration(key, val.MapIndex(key))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
case reflect.Chan:
|
||||
if val.IsNil() {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
for ; ; i++ {
|
||||
elem, ok := val.Recv()
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
oneIteration(reflect.ValueOf(i), elem)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i == 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
case reflect.Invalid:
|
||||
break // An invalid value is likely a nil map, etc. and acts like an empty map.
|
||||
default:
|
||||
s.errorf("range can't iterate over %v", val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if r.ElseList != nil {
|
||||
s.walk(dot, r.ElseList)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) walkTemplate(dot reflect.Value, t *parse.TemplateNode) {
|
||||
s.at(t)
|
||||
tmpl := s.tmpl.tmpl[t.Name]
|
||||
if tmpl == nil {
|
||||
s.errorf("template %q not defined", t.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Variables declared by the pipeline persist.
|
||||
dot = s.evalPipeline(dot, t.Pipe)
|
||||
newState := *s
|
||||
newState.tmpl = tmpl
|
||||
// No dynamic scoping: template invocations inherit no variables.
|
||||
newState.vars = []variable{{"$", dot}}
|
||||
newState.walk(dot, tmpl.Root)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Eval functions evaluate pipelines, commands, and their elements and extract
|
||||
// values from the data structure by examining fields, calling methods, and so on.
|
||||
// The printing of those values happens only through walk functions.
|
||||
|
||||
// evalPipeline returns the value acquired by evaluating a pipeline. If the
|
||||
// pipeline has a variable declaration, the variable will be pushed on the
|
||||
// stack. Callers should therefore pop the stack after they are finished
|
||||
// executing commands depending on the pipeline value.
|
||||
func (s *state) evalPipeline(dot reflect.Value, pipe *parse.PipeNode) (value reflect.Value) {
|
||||
if pipe == nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.at(pipe)
|
||||
for _, cmd := range pipe.Cmds {
|
||||
value = s.evalCommand(dot, cmd, value) // previous value is this one's final arg.
|
||||
// If the object has type interface{}, dig down one level to the thing inside.
|
||||
if value.Kind() == reflect.Interface && value.Type().NumMethod() == 0 {
|
||||
value = reflect.ValueOf(value.Interface()) // lovely!
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, variable := range pipe.Decl {
|
||||
s.push(variable.Ident[0], value)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) notAFunction(args []parse.Node, final reflect.Value) {
|
||||
if len(args) > 1 || final.IsValid() {
|
||||
s.errorf("can't give argument to non-function %s", args[0])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) evalCommand(dot reflect.Value, cmd *parse.CommandNode, final reflect.Value) reflect.Value {
|
||||
firstWord := cmd.Args[0]
|
||||
switch n := firstWord.(type) {
|
||||
case *parse.FieldNode:
|
||||
return s.evalFieldNode(dot, n, cmd.Args, final)
|
||||
case *parse.ChainNode:
|
||||
return s.evalChainNode(dot, n, cmd.Args, final)
|
||||
case *parse.IdentifierNode:
|
||||
// Must be a function.
|
||||
return s.evalFunction(dot, n, cmd, cmd.Args, final)
|
||||
case *parse.PipeNode:
|
||||
// Parenthesized pipeline. The arguments are all inside the pipeline; final is ignored.
|
||||
return s.evalPipeline(dot, n)
|
||||
case *parse.VariableNode:
|
||||
return s.evalVariableNode(dot, n, cmd.Args, final)
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.at(firstWord)
|
||||
s.notAFunction(cmd.Args, final)
|
||||
switch word := firstWord.(type) {
|
||||
case *parse.BoolNode:
|
||||
return reflect.ValueOf(word.True)
|
||||
case *parse.DotNode:
|
||||
return dot
|
||||
case *parse.NilNode:
|
||||
s.errorf("nil is not a command")
|
||||
case *parse.NumberNode:
|
||||
return s.idealConstant(word)
|
||||
case *parse.StringNode:
|
||||
return reflect.ValueOf(word.Text)
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.errorf("can't evaluate command %q", firstWord)
|
||||
panic("not reached")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// idealConstant is called to return the value of a number in a context where
|
||||
// we don't know the type. In that case, the syntax of the number tells us
|
||||
// its type, and we use Go rules to resolve. Note there is no such thing as
|
||||
// a uint ideal constant in this situation - the value must be of int type.
|
||||
func (s *state) idealConstant(constant *parse.NumberNode) reflect.Value {
|
||||
// These are ideal constants but we don't know the type
|
||||
// and we have no context. (If it was a method argument,
|
||||
// we'd know what we need.) The syntax guides us to some extent.
|
||||
s.at(constant)
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case constant.IsComplex:
|
||||
return reflect.ValueOf(constant.Complex128) // incontrovertible.
|
||||
case constant.IsFloat && !isHexConstant(constant.Text) && strings.IndexAny(constant.Text, ".eE") >= 0:
|
||||
return reflect.ValueOf(constant.Float64)
|
||||
case constant.IsInt:
|
||||
n := int(constant.Int64)
|
||||
if int64(n) != constant.Int64 {
|
||||
s.errorf("%s overflows int", constant.Text)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return reflect.ValueOf(n)
|
||||
case constant.IsUint:
|
||||
s.errorf("%s overflows int", constant.Text)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return zero
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func isHexConstant(s string) bool {
|
||||
return len(s) > 2 && s[0] == '0' && (s[1] == 'x' || s[1] == 'X')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) evalFieldNode(dot reflect.Value, field *parse.FieldNode, args []parse.Node, final reflect.Value) reflect.Value {
|
||||
s.at(field)
|
||||
return s.evalFieldChain(dot, dot, field, field.Ident, args, final)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) evalChainNode(dot reflect.Value, chain *parse.ChainNode, args []parse.Node, final reflect.Value) reflect.Value {
|
||||
s.at(chain)
|
||||
// (pipe).Field1.Field2 has pipe as .Node, fields as .Field. Eval the pipeline, then the fields.
|
||||
pipe := s.evalArg(dot, nil, chain.Node)
|
||||
if len(chain.Field) == 0 {
|
||||
s.errorf("internal error: no fields in evalChainNode")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.evalFieldChain(dot, pipe, chain, chain.Field, args, final)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) evalVariableNode(dot reflect.Value, variable *parse.VariableNode, args []parse.Node, final reflect.Value) reflect.Value {
|
||||
// $x.Field has $x as the first ident, Field as the second. Eval the var, then the fields.
|
||||
s.at(variable)
|
||||
value := s.varValue(variable.Ident[0])
|
||||
if len(variable.Ident) == 1 {
|
||||
s.notAFunction(args, final)
|
||||
return value
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.evalFieldChain(dot, value, variable, variable.Ident[1:], args, final)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// evalFieldChain evaluates .X.Y.Z possibly followed by arguments.
|
||||
// dot is the environment in which to evaluate arguments, while
|
||||
// receiver is the value being walked along the chain.
|
||||
func (s *state) evalFieldChain(dot, receiver reflect.Value, node parse.Node, ident []string, args []parse.Node, final reflect.Value) reflect.Value {
|
||||
n := len(ident)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n-1; i++ {
|
||||
receiver = s.evalField(dot, ident[i], node, nil, zero, receiver)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Now if it's a method, it gets the arguments.
|
||||
return s.evalField(dot, ident[n-1], node, args, final, receiver)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) evalFunction(dot reflect.Value, node *parse.IdentifierNode, cmd parse.Node, args []parse.Node, final reflect.Value) reflect.Value {
|
||||
s.at(node)
|
||||
name := node.Ident
|
||||
function, ok := findFunction(name, s.tmpl)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
s.errorf("%q is not a defined function", name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.evalCall(dot, function, cmd, name, args, final)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// evalField evaluates an expression like (.Field) or (.Field arg1 arg2).
|
||||
// The 'final' argument represents the return value from the preceding
|
||||
// value of the pipeline, if any.
|
||||
func (s *state) evalField(dot reflect.Value, fieldName string, node parse.Node, args []parse.Node, final, receiver reflect.Value) reflect.Value {
|
||||
if !receiver.IsValid() {
|
||||
return zero
|
||||
}
|
||||
typ := receiver.Type()
|
||||
receiver, _ = indirect(receiver)
|
||||
// Unless it's an interface, need to get to a value of type *T to guarantee
|
||||
// we see all methods of T and *T.
|
||||
ptr := receiver
|
||||
if ptr.Kind() != reflect.Interface && ptr.CanAddr() {
|
||||
ptr = ptr.Addr()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if method := ptr.MethodByName(fieldName); method.IsValid() {
|
||||
return s.evalCall(dot, method, node, fieldName, args, final)
|
||||
}
|
||||
hasArgs := len(args) > 1 || final.IsValid()
|
||||
// It's not a method; must be a field of a struct or an element of a map. The receiver must not be nil.
|
||||
receiver, isNil := indirect(receiver)
|
||||
if isNil {
|
||||
s.errorf("nil pointer evaluating %s.%s", typ, fieldName)
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch receiver.Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.Struct:
|
||||
tField, ok := receiver.Type().FieldByName(fieldName)
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
field := receiver.FieldByIndex(tField.Index)
|
||||
if tField.PkgPath != "" { // field is unexported
|
||||
s.errorf("%s is an unexported field of struct type %s", fieldName, typ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// If it's a function, we must call it.
|
||||
if hasArgs {
|
||||
s.errorf("%s has arguments but cannot be invoked as function", fieldName)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return field
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.errorf("%s is not a field of struct type %s", fieldName, typ)
|
||||
case reflect.Map:
|
||||
// If it's a map, attempt to use the field name as a key.
|
||||
nameVal := reflect.ValueOf(fieldName)
|
||||
if nameVal.Type().AssignableTo(receiver.Type().Key()) {
|
||||
if hasArgs {
|
||||
s.errorf("%s is not a method but has arguments", fieldName)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return receiver.MapIndex(nameVal)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.errorf("can't evaluate field %s in type %s", fieldName, typ)
|
||||
panic("not reached")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
errorType = reflect.TypeOf((*error)(nil)).Elem()
|
||||
fmtStringerType = reflect.TypeOf((*fmt.Stringer)(nil)).Elem()
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// evalCall executes a function or method call. If it's a method, fun already has the receiver bound, so
|
||||
// it looks just like a function call. The arg list, if non-nil, includes (in the manner of the shell), arg[0]
|
||||
// as the function itself.
|
||||
func (s *state) evalCall(dot, fun reflect.Value, node parse.Node, name string, args []parse.Node, final reflect.Value) reflect.Value {
|
||||
if args != nil {
|
||||
args = args[1:] // Zeroth arg is function name/node; not passed to function.
|
||||
}
|
||||
typ := fun.Type()
|
||||
numIn := len(args)
|
||||
if final.IsValid() {
|
||||
numIn++
|
||||
}
|
||||
numFixed := len(args)
|
||||
if typ.IsVariadic() {
|
||||
numFixed = typ.NumIn() - 1 // last arg is the variadic one.
|
||||
if numIn < numFixed {
|
||||
s.errorf("wrong number of args for %s: want at least %d got %d", name, typ.NumIn()-1, len(args))
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if numIn < typ.NumIn()-1 || !typ.IsVariadic() && numIn != typ.NumIn() {
|
||||
s.errorf("wrong number of args for %s: want %d got %d", name, typ.NumIn(), len(args))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !goodFunc(typ) {
|
||||
// TODO: This could still be a confusing error; maybe goodFunc should provide info.
|
||||
s.errorf("can't call method/function %q with %d results", name, typ.NumOut())
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Build the arg list.
|
||||
argv := make([]reflect.Value, numIn)
|
||||
// Args must be evaluated. Fixed args first.
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
for ; i < numFixed && i < len(args); i++ {
|
||||
argv[i] = s.evalArg(dot, typ.In(i), args[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Now the ... args.
|
||||
if typ.IsVariadic() {
|
||||
argType := typ.In(typ.NumIn() - 1).Elem() // Argument is a slice.
|
||||
for ; i < len(args); i++ {
|
||||
argv[i] = s.evalArg(dot, argType, args[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Add final value if necessary.
|
||||
if final.IsValid() {
|
||||
t := typ.In(typ.NumIn() - 1)
|
||||
if typ.IsVariadic() {
|
||||
t = t.Elem()
|
||||
}
|
||||
argv[i] = s.validateType(final, t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
result := fun.Call(argv)
|
||||
// If we have an error that is not nil, stop execution and return that error to the caller.
|
||||
if len(result) == 2 && !result[1].IsNil() {
|
||||
s.at(node)
|
||||
s.errorf("error calling %s: %s", name, result[1].Interface().(error))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// canBeNil reports whether an untyped nil can be assigned to the type. See reflect.Zero.
|
||||
func canBeNil(typ reflect.Type) bool {
|
||||
switch typ.Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.Chan, reflect.Func, reflect.Interface, reflect.Map, reflect.Ptr, reflect.Slice:
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// validateType guarantees that the value is valid and assignable to the type.
|
||||
func (s *state) validateType(value reflect.Value, typ reflect.Type) reflect.Value {
|
||||
if !value.IsValid() {
|
||||
if typ == nil || canBeNil(typ) {
|
||||
// An untyped nil interface{}. Accept as a proper nil value.
|
||||
return reflect.Zero(typ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.errorf("invalid value; expected %s", typ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if typ != nil && !value.Type().AssignableTo(typ) {
|
||||
if value.Kind() == reflect.Interface && !value.IsNil() {
|
||||
value = value.Elem()
|
||||
if value.Type().AssignableTo(typ) {
|
||||
return value
|
||||
}
|
||||
// fallthrough
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Does one dereference or indirection work? We could do more, as we
|
||||
// do with method receivers, but that gets messy and method receivers
|
||||
// are much more constrained, so it makes more sense there than here.
|
||||
// Besides, one is almost always all you need.
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case value.Kind() == reflect.Ptr && value.Type().Elem().AssignableTo(typ):
|
||||
value = value.Elem()
|
||||
if !value.IsValid() {
|
||||
s.errorf("dereference of nil pointer of type %s", typ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case reflect.PtrTo(value.Type()).AssignableTo(typ) && value.CanAddr():
|
||||
value = value.Addr()
|
||||
default:
|
||||
s.errorf("wrong type for value; expected %s; got %s", typ, value.Type())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) evalArg(dot reflect.Value, typ reflect.Type, n parse.Node) reflect.Value {
|
||||
s.at(n)
|
||||
switch arg := n.(type) {
|
||||
case *parse.DotNode:
|
||||
return s.validateType(dot, typ)
|
||||
case *parse.NilNode:
|
||||
if canBeNil(typ) {
|
||||
return reflect.Zero(typ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.errorf("cannot assign nil to %s", typ)
|
||||
case *parse.FieldNode:
|
||||
return s.validateType(s.evalFieldNode(dot, arg, []parse.Node{n}, zero), typ)
|
||||
case *parse.VariableNode:
|
||||
return s.validateType(s.evalVariableNode(dot, arg, nil, zero), typ)
|
||||
case *parse.PipeNode:
|
||||
return s.validateType(s.evalPipeline(dot, arg), typ)
|
||||
case *parse.IdentifierNode:
|
||||
return s.evalFunction(dot, arg, arg, nil, zero)
|
||||
case *parse.ChainNode:
|
||||
return s.validateType(s.evalChainNode(dot, arg, nil, zero), typ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch typ.Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.Bool:
|
||||
return s.evalBool(typ, n)
|
||||
case reflect.Complex64, reflect.Complex128:
|
||||
return s.evalComplex(typ, n)
|
||||
case reflect.Float32, reflect.Float64:
|
||||
return s.evalFloat(typ, n)
|
||||
case reflect.Int, reflect.Int8, reflect.Int16, reflect.Int32, reflect.Int64:
|
||||
return s.evalInteger(typ, n)
|
||||
case reflect.Interface:
|
||||
if typ.NumMethod() == 0 {
|
||||
return s.evalEmptyInterface(dot, n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case reflect.String:
|
||||
return s.evalString(typ, n)
|
||||
case reflect.Uint, reflect.Uint8, reflect.Uint16, reflect.Uint32, reflect.Uint64, reflect.Uintptr:
|
||||
return s.evalUnsignedInteger(typ, n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.errorf("can't handle %s for arg of type %s", n, typ)
|
||||
panic("not reached")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) evalBool(typ reflect.Type, n parse.Node) reflect.Value {
|
||||
s.at(n)
|
||||
if n, ok := n.(*parse.BoolNode); ok {
|
||||
value := reflect.New(typ).Elem()
|
||||
value.SetBool(n.True)
|
||||
return value
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.errorf("expected bool; found %s", n)
|
||||
panic("not reached")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) evalString(typ reflect.Type, n parse.Node) reflect.Value {
|
||||
s.at(n)
|
||||
if n, ok := n.(*parse.StringNode); ok {
|
||||
value := reflect.New(typ).Elem()
|
||||
value.SetString(n.Text)
|
||||
return value
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.errorf("expected string; found %s", n)
|
||||
panic("not reached")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) evalInteger(typ reflect.Type, n parse.Node) reflect.Value {
|
||||
s.at(n)
|
||||
if n, ok := n.(*parse.NumberNode); ok && n.IsInt {
|
||||
value := reflect.New(typ).Elem()
|
||||
value.SetInt(n.Int64)
|
||||
return value
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.errorf("expected integer; found %s", n)
|
||||
panic("not reached")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) evalUnsignedInteger(typ reflect.Type, n parse.Node) reflect.Value {
|
||||
s.at(n)
|
||||
if n, ok := n.(*parse.NumberNode); ok && n.IsUint {
|
||||
value := reflect.New(typ).Elem()
|
||||
value.SetUint(n.Uint64)
|
||||
return value
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.errorf("expected unsigned integer; found %s", n)
|
||||
panic("not reached")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) evalFloat(typ reflect.Type, n parse.Node) reflect.Value {
|
||||
s.at(n)
|
||||
if n, ok := n.(*parse.NumberNode); ok && n.IsFloat {
|
||||
value := reflect.New(typ).Elem()
|
||||
value.SetFloat(n.Float64)
|
||||
return value
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.errorf("expected float; found %s", n)
|
||||
panic("not reached")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) evalComplex(typ reflect.Type, n parse.Node) reflect.Value {
|
||||
if n, ok := n.(*parse.NumberNode); ok && n.IsComplex {
|
||||
value := reflect.New(typ).Elem()
|
||||
value.SetComplex(n.Complex128)
|
||||
return value
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.errorf("expected complex; found %s", n)
|
||||
panic("not reached")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *state) evalEmptyInterface(dot reflect.Value, n parse.Node) reflect.Value {
|
||||
s.at(n)
|
||||
switch n := n.(type) {
|
||||
case *parse.BoolNode:
|
||||
return reflect.ValueOf(n.True)
|
||||
case *parse.DotNode:
|
||||
return dot
|
||||
case *parse.FieldNode:
|
||||
return s.evalFieldNode(dot, n, nil, zero)
|
||||
case *parse.IdentifierNode:
|
||||
return s.evalFunction(dot, n, n, nil, zero)
|
||||
case *parse.NilNode:
|
||||
// NilNode is handled in evalArg, the only place that calls here.
|
||||
s.errorf("evalEmptyInterface: nil (can't happen)")
|
||||
case *parse.NumberNode:
|
||||
return s.idealConstant(n)
|
||||
case *parse.StringNode:
|
||||
return reflect.ValueOf(n.Text)
|
||||
case *parse.VariableNode:
|
||||
return s.evalVariableNode(dot, n, nil, zero)
|
||||
case *parse.PipeNode:
|
||||
return s.evalPipeline(dot, n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.errorf("can't handle assignment of %s to empty interface argument", n)
|
||||
panic("not reached")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// indirect returns the item at the end of indirection, and a bool to indicate if it's nil.
|
||||
// We indirect through pointers and empty interfaces (only) because
|
||||
// non-empty interfaces have methods we might need.
|
||||
func indirect(v reflect.Value) (rv reflect.Value, isNil bool) {
|
||||
for ; v.Kind() == reflect.Ptr || v.Kind() == reflect.Interface; v = v.Elem() {
|
||||
if v.IsNil() {
|
||||
return v, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
if v.Kind() == reflect.Interface && v.NumMethod() > 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// printValue writes the textual representation of the value to the output of
|
||||
// the template.
|
||||
func (s *state) printValue(n parse.Node, v reflect.Value) {
|
||||
s.at(n)
|
||||
iface, ok := printableValue(v)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
s.errorf("can't print %s of type %s", n, v.Type())
|
||||
}
|
||||
fmt.Fprint(s.wr, iface)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// printableValue returns the, possibly indirected, interface value inside v that
|
||||
// is best for a call to formatted printer.
|
||||
func printableValue(v reflect.Value) (interface{}, bool) {
|
||||
if v.Kind() == reflect.Ptr {
|
||||
v, _ = indirect(v) // fmt.Fprint handles nil.
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !v.IsValid() {
|
||||
return "<no value>", true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if !v.Type().Implements(errorType) && !v.Type().Implements(fmtStringerType) {
|
||||
if v.CanAddr() && (reflect.PtrTo(v.Type()).Implements(errorType) || reflect.PtrTo(v.Type()).Implements(fmtStringerType)) {
|
||||
v = v.Addr()
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
switch v.Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.Chan, reflect.Func:
|
||||
return nil, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v.Interface(), true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Types to help sort the keys in a map for reproducible output.
|
||||
|
||||
type rvs []reflect.Value
|
||||
|
||||
func (x rvs) Len() int { return len(x) }
|
||||
func (x rvs) Swap(i, j int) { x[i], x[j] = x[j], x[i] }
|
||||
|
||||
type rvInts struct{ rvs }
|
||||
|
||||
func (x rvInts) Less(i, j int) bool { return x.rvs[i].Int() < x.rvs[j].Int() }
|
||||
|
||||
type rvUints struct{ rvs }
|
||||
|
||||
func (x rvUints) Less(i, j int) bool { return x.rvs[i].Uint() < x.rvs[j].Uint() }
|
||||
|
||||
type rvFloats struct{ rvs }
|
||||
|
||||
func (x rvFloats) Less(i, j int) bool { return x.rvs[i].Float() < x.rvs[j].Float() }
|
||||
|
||||
type rvStrings struct{ rvs }
|
||||
|
||||
func (x rvStrings) Less(i, j int) bool { return x.rvs[i].String() < x.rvs[j].String() }
|
||||
|
||||
// sortKeys sorts (if it can) the slice of reflect.Values, which is a slice of map keys.
|
||||
func sortKeys(v []reflect.Value) []reflect.Value {
|
||||
if len(v) <= 1 {
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch v[0].Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.Float32, reflect.Float64:
|
||||
sort.Sort(rvFloats{v})
|
||||
case reflect.Int, reflect.Int8, reflect.Int16, reflect.Int32, reflect.Int64:
|
||||
sort.Sort(rvInts{v})
|
||||
case reflect.String:
|
||||
sort.Sort(rvStrings{v})
|
||||
case reflect.Uint, reflect.Uint8, reflect.Uint16, reflect.Uint32, reflect.Uint64, reflect.Uintptr:
|
||||
sort.Sort(rvUints{v})
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
598
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/funcs.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
598
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/funcs.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,598 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package template
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"net/url"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// FuncMap is the type of the map defining the mapping from names to functions.
|
||||
// Each function must have either a single return value, or two return values of
|
||||
// which the second has type error. In that case, if the second (error)
|
||||
// return value evaluates to non-nil during execution, execution terminates and
|
||||
// Execute returns that error.
|
||||
type FuncMap map[string]interface{}
|
||||
|
||||
var builtins = FuncMap{
|
||||
"and": and,
|
||||
"call": call,
|
||||
"html": HTMLEscaper,
|
||||
"index": index,
|
||||
"js": JSEscaper,
|
||||
"len": length,
|
||||
"not": not,
|
||||
"or": or,
|
||||
"print": fmt.Sprint,
|
||||
"printf": fmt.Sprintf,
|
||||
"println": fmt.Sprintln,
|
||||
"urlquery": URLQueryEscaper,
|
||||
|
||||
// Comparisons
|
||||
"eq": eq, // ==
|
||||
"ge": ge, // >=
|
||||
"gt": gt, // >
|
||||
"le": le, // <=
|
||||
"lt": lt, // <
|
||||
"ne": ne, // !=
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var builtinFuncs = createValueFuncs(builtins)
|
||||
|
||||
// createValueFuncs turns a FuncMap into a map[string]reflect.Value
|
||||
func createValueFuncs(funcMap FuncMap) map[string]reflect.Value {
|
||||
m := make(map[string]reflect.Value)
|
||||
addValueFuncs(m, funcMap)
|
||||
return m
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// addValueFuncs adds to values the functions in funcs, converting them to reflect.Values.
|
||||
func addValueFuncs(out map[string]reflect.Value, in FuncMap) {
|
||||
for name, fn := range in {
|
||||
v := reflect.ValueOf(fn)
|
||||
if v.Kind() != reflect.Func {
|
||||
panic("value for " + name + " not a function")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !goodFunc(v.Type()) {
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf("can't install method/function %q with %d results", name, v.Type().NumOut()))
|
||||
}
|
||||
out[name] = v
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// addFuncs adds to values the functions in funcs. It does no checking of the input -
|
||||
// call addValueFuncs first.
|
||||
func addFuncs(out, in FuncMap) {
|
||||
for name, fn := range in {
|
||||
out[name] = fn
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// goodFunc checks that the function or method has the right result signature.
|
||||
func goodFunc(typ reflect.Type) bool {
|
||||
// We allow functions with 1 result or 2 results where the second is an error.
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case typ.NumOut() == 1:
|
||||
return true
|
||||
case typ.NumOut() == 2 && typ.Out(1) == errorType:
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// findFunction looks for a function in the template, and global map.
|
||||
func findFunction(name string, tmpl *Template) (reflect.Value, bool) {
|
||||
if tmpl != nil && tmpl.common != nil {
|
||||
if fn := tmpl.execFuncs[name]; fn.IsValid() {
|
||||
return fn, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if fn := builtinFuncs[name]; fn.IsValid() {
|
||||
return fn, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return reflect.Value{}, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Indexing.
|
||||
|
||||
// index returns the result of indexing its first argument by the following
|
||||
// arguments. Thus "index x 1 2 3" is, in Go syntax, x[1][2][3]. Each
|
||||
// indexed item must be a map, slice, or array.
|
||||
func index(item interface{}, indices ...interface{}) (interface{}, error) {
|
||||
v := reflect.ValueOf(item)
|
||||
for _, i := range indices {
|
||||
index := reflect.ValueOf(i)
|
||||
var isNil bool
|
||||
if v, isNil = indirect(v); isNil {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("index of nil pointer")
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch v.Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.Array, reflect.Slice, reflect.String:
|
||||
var x int64
|
||||
switch index.Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.Int, reflect.Int8, reflect.Int16, reflect.Int32, reflect.Int64:
|
||||
x = index.Int()
|
||||
case reflect.Uint, reflect.Uint8, reflect.Uint16, reflect.Uint32, reflect.Uint64, reflect.Uintptr:
|
||||
x = int64(index.Uint())
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot index slice/array with type %s", index.Type())
|
||||
}
|
||||
if x < 0 || x >= int64(v.Len()) {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("index out of range: %d", x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
v = v.Index(int(x))
|
||||
case reflect.Map:
|
||||
if !index.IsValid() {
|
||||
index = reflect.Zero(v.Type().Key())
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !index.Type().AssignableTo(v.Type().Key()) {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("%s is not index type for %s", index.Type(), v.Type())
|
||||
}
|
||||
if x := v.MapIndex(index); x.IsValid() {
|
||||
v = x
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
v = reflect.Zero(v.Type().Elem())
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("can't index item of type %s", v.Type())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v.Interface(), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Length
|
||||
|
||||
// length returns the length of the item, with an error if it has no defined length.
|
||||
func length(item interface{}) (int, error) {
|
||||
v, isNil := indirect(reflect.ValueOf(item))
|
||||
if isNil {
|
||||
return 0, fmt.Errorf("len of nil pointer")
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch v.Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.Array, reflect.Chan, reflect.Map, reflect.Slice, reflect.String:
|
||||
return v.Len(), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0, fmt.Errorf("len of type %s", v.Type())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Function invocation
|
||||
|
||||
// call returns the result of evaluating the first argument as a function.
|
||||
// The function must return 1 result, or 2 results, the second of which is an error.
|
||||
func call(fn interface{}, args ...interface{}) (interface{}, error) {
|
||||
v := reflect.ValueOf(fn)
|
||||
typ := v.Type()
|
||||
if typ.Kind() != reflect.Func {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("non-function of type %s", typ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !goodFunc(typ) {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("function called with %d args; should be 1 or 2", typ.NumOut())
|
||||
}
|
||||
numIn := typ.NumIn()
|
||||
var dddType reflect.Type
|
||||
if typ.IsVariadic() {
|
||||
if len(args) < numIn-1 {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("wrong number of args: got %d want at least %d", len(args), numIn-1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
dddType = typ.In(numIn - 1).Elem()
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if len(args) != numIn {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("wrong number of args: got %d want %d", len(args), numIn)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
argv := make([]reflect.Value, len(args))
|
||||
for i, arg := range args {
|
||||
value := reflect.ValueOf(arg)
|
||||
// Compute the expected type. Clumsy because of variadics.
|
||||
var argType reflect.Type
|
||||
if !typ.IsVariadic() || i < numIn-1 {
|
||||
argType = typ.In(i)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
argType = dddType
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !value.IsValid() && canBeNil(argType) {
|
||||
value = reflect.Zero(argType)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !value.Type().AssignableTo(argType) {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("arg %d has type %s; should be %s", i, value.Type(), argType)
|
||||
}
|
||||
argv[i] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
result := v.Call(argv)
|
||||
if len(result) == 2 && !result[1].IsNil() {
|
||||
return result[0].Interface(), result[1].Interface().(error)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result[0].Interface(), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Boolean logic.
|
||||
|
||||
func truth(a interface{}) bool {
|
||||
t, _ := isTrue(reflect.ValueOf(a))
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// and computes the Boolean AND of its arguments, returning
|
||||
// the first false argument it encounters, or the last argument.
|
||||
func and(arg0 interface{}, args ...interface{}) interface{} {
|
||||
if !truth(arg0) {
|
||||
return arg0
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := range args {
|
||||
arg0 = args[i]
|
||||
if !truth(arg0) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return arg0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// or computes the Boolean OR of its arguments, returning
|
||||
// the first true argument it encounters, or the last argument.
|
||||
func or(arg0 interface{}, args ...interface{}) interface{} {
|
||||
if truth(arg0) {
|
||||
return arg0
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := range args {
|
||||
arg0 = args[i]
|
||||
if truth(arg0) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return arg0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// not returns the Boolean negation of its argument.
|
||||
func not(arg interface{}) (truth bool) {
|
||||
truth, _ = isTrue(reflect.ValueOf(arg))
|
||||
return !truth
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Comparison.
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: Perhaps allow comparison between signed and unsigned integers.
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
errBadComparisonType = errors.New("invalid type for comparison")
|
||||
errBadComparison = errors.New("incompatible types for comparison")
|
||||
errNoComparison = errors.New("missing argument for comparison")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type kind int
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
invalidKind kind = iota
|
||||
boolKind
|
||||
complexKind
|
||||
intKind
|
||||
floatKind
|
||||
integerKind
|
||||
stringKind
|
||||
uintKind
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func basicKind(v reflect.Value) (kind, error) {
|
||||
switch v.Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.Bool:
|
||||
return boolKind, nil
|
||||
case reflect.Int, reflect.Int8, reflect.Int16, reflect.Int32, reflect.Int64:
|
||||
return intKind, nil
|
||||
case reflect.Uint, reflect.Uint8, reflect.Uint16, reflect.Uint32, reflect.Uint64, reflect.Uintptr:
|
||||
return uintKind, nil
|
||||
case reflect.Float32, reflect.Float64:
|
||||
return floatKind, nil
|
||||
case reflect.Complex64, reflect.Complex128:
|
||||
return complexKind, nil
|
||||
case reflect.String:
|
||||
return stringKind, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return invalidKind, errBadComparisonType
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// eq evaluates the comparison a == b || a == c || ...
|
||||
func eq(arg1 interface{}, arg2 ...interface{}) (bool, error) {
|
||||
v1 := reflect.ValueOf(arg1)
|
||||
k1, err := basicKind(v1)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(arg2) == 0 {
|
||||
return false, errNoComparison
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, arg := range arg2 {
|
||||
v2 := reflect.ValueOf(arg)
|
||||
k2, err := basicKind(v2)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
truth := false
|
||||
if k1 != k2 {
|
||||
// Special case: Can compare integer values regardless of type's sign.
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case k1 == intKind && k2 == uintKind:
|
||||
truth = v1.Int() >= 0 && uint64(v1.Int()) == v2.Uint()
|
||||
case k1 == uintKind && k2 == intKind:
|
||||
truth = v2.Int() >= 0 && v1.Uint() == uint64(v2.Int())
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return false, errBadComparison
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
switch k1 {
|
||||
case boolKind:
|
||||
truth = v1.Bool() == v2.Bool()
|
||||
case complexKind:
|
||||
truth = v1.Complex() == v2.Complex()
|
||||
case floatKind:
|
||||
truth = v1.Float() == v2.Float()
|
||||
case intKind:
|
||||
truth = v1.Int() == v2.Int()
|
||||
case stringKind:
|
||||
truth = v1.String() == v2.String()
|
||||
case uintKind:
|
||||
truth = v1.Uint() == v2.Uint()
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("invalid kind")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if truth {
|
||||
return true, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ne evaluates the comparison a != b.
|
||||
func ne(arg1, arg2 interface{}) (bool, error) {
|
||||
// != is the inverse of ==.
|
||||
equal, err := eq(arg1, arg2)
|
||||
return !equal, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lt evaluates the comparison a < b.
|
||||
func lt(arg1, arg2 interface{}) (bool, error) {
|
||||
v1 := reflect.ValueOf(arg1)
|
||||
k1, err := basicKind(v1)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
v2 := reflect.ValueOf(arg2)
|
||||
k2, err := basicKind(v2)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
truth := false
|
||||
if k1 != k2 {
|
||||
// Special case: Can compare integer values regardless of type's sign.
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case k1 == intKind && k2 == uintKind:
|
||||
truth = v1.Int() < 0 || uint64(v1.Int()) < v2.Uint()
|
||||
case k1 == uintKind && k2 == intKind:
|
||||
truth = v2.Int() >= 0 && v1.Uint() < uint64(v2.Int())
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return false, errBadComparison
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
switch k1 {
|
||||
case boolKind, complexKind:
|
||||
return false, errBadComparisonType
|
||||
case floatKind:
|
||||
truth = v1.Float() < v2.Float()
|
||||
case intKind:
|
||||
truth = v1.Int() < v2.Int()
|
||||
case stringKind:
|
||||
truth = v1.String() < v2.String()
|
||||
case uintKind:
|
||||
truth = v1.Uint() < v2.Uint()
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("invalid kind")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return truth, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// le evaluates the comparison <= b.
|
||||
func le(arg1, arg2 interface{}) (bool, error) {
|
||||
// <= is < or ==.
|
||||
lessThan, err := lt(arg1, arg2)
|
||||
if lessThan || err != nil {
|
||||
return lessThan, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return eq(arg1, arg2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// gt evaluates the comparison a > b.
|
||||
func gt(arg1, arg2 interface{}) (bool, error) {
|
||||
// > is the inverse of <=.
|
||||
lessOrEqual, err := le(arg1, arg2)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return !lessOrEqual, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ge evaluates the comparison a >= b.
|
||||
func ge(arg1, arg2 interface{}) (bool, error) {
|
||||
// >= is the inverse of <.
|
||||
lessThan, err := lt(arg1, arg2)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return !lessThan, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HTML escaping.
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
htmlQuot = []byte(""") // shorter than """
|
||||
htmlApos = []byte("'") // shorter than "'" and apos was not in HTML until HTML5
|
||||
htmlAmp = []byte("&")
|
||||
htmlLt = []byte("<")
|
||||
htmlGt = []byte(">")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// HTMLEscape writes to w the escaped HTML equivalent of the plain text data b.
|
||||
func HTMLEscape(w io.Writer, b []byte) {
|
||||
last := 0
|
||||
for i, c := range b {
|
||||
var html []byte
|
||||
switch c {
|
||||
case '"':
|
||||
html = htmlQuot
|
||||
case '\'':
|
||||
html = htmlApos
|
||||
case '&':
|
||||
html = htmlAmp
|
||||
case '<':
|
||||
html = htmlLt
|
||||
case '>':
|
||||
html = htmlGt
|
||||
default:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.Write(b[last:i])
|
||||
w.Write(html)
|
||||
last = i + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.Write(b[last:])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HTMLEscapeString returns the escaped HTML equivalent of the plain text data s.
|
||||
func HTMLEscapeString(s string) string {
|
||||
// Avoid allocation if we can.
|
||||
if strings.IndexAny(s, `'"&<>`) < 0 {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
HTMLEscape(&b, []byte(s))
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HTMLEscaper returns the escaped HTML equivalent of the textual
|
||||
// representation of its arguments.
|
||||
func HTMLEscaper(args ...interface{}) string {
|
||||
return HTMLEscapeString(evalArgs(args))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// JavaScript escaping.
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
jsLowUni = []byte(`\u00`)
|
||||
hex = []byte("0123456789ABCDEF")
|
||||
|
||||
jsBackslash = []byte(`\\`)
|
||||
jsApos = []byte(`\'`)
|
||||
jsQuot = []byte(`\"`)
|
||||
jsLt = []byte(`\x3C`)
|
||||
jsGt = []byte(`\x3E`)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// JSEscape writes to w the escaped JavaScript equivalent of the plain text data b.
|
||||
func JSEscape(w io.Writer, b []byte) {
|
||||
last := 0
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(b); i++ {
|
||||
c := b[i]
|
||||
|
||||
if !jsIsSpecial(rune(c)) {
|
||||
// fast path: nothing to do
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.Write(b[last:i])
|
||||
|
||||
if c < utf8.RuneSelf {
|
||||
// Quotes, slashes and angle brackets get quoted.
|
||||
// Control characters get written as \u00XX.
|
||||
switch c {
|
||||
case '\\':
|
||||
w.Write(jsBackslash)
|
||||
case '\'':
|
||||
w.Write(jsApos)
|
||||
case '"':
|
||||
w.Write(jsQuot)
|
||||
case '<':
|
||||
w.Write(jsLt)
|
||||
case '>':
|
||||
w.Write(jsGt)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
w.Write(jsLowUni)
|
||||
t, b := c>>4, c&0x0f
|
||||
w.Write(hex[t : t+1])
|
||||
w.Write(hex[b : b+1])
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Unicode rune.
|
||||
r, size := utf8.DecodeRune(b[i:])
|
||||
if unicode.IsPrint(r) {
|
||||
w.Write(b[i : i+size])
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(w, "\\u%04X", r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
i += size - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
last = i + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.Write(b[last:])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// JSEscapeString returns the escaped JavaScript equivalent of the plain text data s.
|
||||
func JSEscapeString(s string) string {
|
||||
// Avoid allocation if we can.
|
||||
if strings.IndexFunc(s, jsIsSpecial) < 0 {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
JSEscape(&b, []byte(s))
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func jsIsSpecial(r rune) bool {
|
||||
switch r {
|
||||
case '\\', '\'', '"', '<', '>':
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r < ' ' || utf8.RuneSelf <= r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// JSEscaper returns the escaped JavaScript equivalent of the textual
|
||||
// representation of its arguments.
|
||||
func JSEscaper(args ...interface{}) string {
|
||||
return JSEscapeString(evalArgs(args))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// URLQueryEscaper returns the escaped value of the textual representation of
|
||||
// its arguments in a form suitable for embedding in a URL query.
|
||||
func URLQueryEscaper(args ...interface{}) string {
|
||||
return url.QueryEscape(evalArgs(args))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// evalArgs formats the list of arguments into a string. It is therefore equivalent to
|
||||
// fmt.Sprint(args...)
|
||||
// except that each argument is indirected (if a pointer), as required,
|
||||
// using the same rules as the default string evaluation during template
|
||||
// execution.
|
||||
func evalArgs(args []interface{}) string {
|
||||
ok := false
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
// Fast path for simple common case.
|
||||
if len(args) == 1 {
|
||||
s, ok = args[0].(string)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
for i, arg := range args {
|
||||
a, ok := printableValue(reflect.ValueOf(arg))
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
args[i] = a
|
||||
} // else left fmt do its thing
|
||||
}
|
||||
s = fmt.Sprint(args...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
108
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/helper.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
108
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/helper.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Helper functions to make constructing templates easier.
|
||||
|
||||
package template
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Functions and methods to parse templates.
|
||||
|
||||
// Must is a helper that wraps a call to a function returning (*Template, error)
|
||||
// and panics if the error is non-nil. It is intended for use in variable
|
||||
// initializations such as
|
||||
// var t = template.Must(template.New("name").Parse("text"))
|
||||
func Must(t *Template, err error) *Template {
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
panic(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseFiles creates a new Template and parses the template definitions from
|
||||
// the named files. The returned template's name will have the (base) name and
|
||||
// (parsed) contents of the first file. There must be at least one file.
|
||||
// If an error occurs, parsing stops and the returned *Template is nil.
|
||||
func ParseFiles(filenames ...string) (*Template, error) {
|
||||
return parseFiles(nil, filenames...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseFiles parses the named files and associates the resulting templates with
|
||||
// t. If an error occurs, parsing stops and the returned template is nil;
|
||||
// otherwise it is t. There must be at least one file.
|
||||
func (t *Template) ParseFiles(filenames ...string) (*Template, error) {
|
||||
return parseFiles(t, filenames...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// parseFiles is the helper for the method and function. If the argument
|
||||
// template is nil, it is created from the first file.
|
||||
func parseFiles(t *Template, filenames ...string) (*Template, error) {
|
||||
if len(filenames) == 0 {
|
||||
// Not really a problem, but be consistent.
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("template: no files named in call to ParseFiles")
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, filename := range filenames {
|
||||
b, err := ioutil.ReadFile(filename)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
s := string(b)
|
||||
name := filepath.Base(filename)
|
||||
// First template becomes return value if not already defined,
|
||||
// and we use that one for subsequent New calls to associate
|
||||
// all the templates together. Also, if this file has the same name
|
||||
// as t, this file becomes the contents of t, so
|
||||
// t, err := New(name).Funcs(xxx).ParseFiles(name)
|
||||
// works. Otherwise we create a new template associated with t.
|
||||
var tmpl *Template
|
||||
if t == nil {
|
||||
t = New(name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if name == t.Name() {
|
||||
tmpl = t
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
tmpl = t.New(name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
_, err = tmpl.Parse(s)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseGlob creates a new Template and parses the template definitions from the
|
||||
// files identified by the pattern, which must match at least one file. The
|
||||
// returned template will have the (base) name and (parsed) contents of the
|
||||
// first file matched by the pattern. ParseGlob is equivalent to calling
|
||||
// ParseFiles with the list of files matched by the pattern.
|
||||
func ParseGlob(pattern string) (*Template, error) {
|
||||
return parseGlob(nil, pattern)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseGlob parses the template definitions in the files identified by the
|
||||
// pattern and associates the resulting templates with t. The pattern is
|
||||
// processed by filepath.Glob and must match at least one file. ParseGlob is
|
||||
// equivalent to calling t.ParseFiles with the list of files matched by the
|
||||
// pattern.
|
||||
func (t *Template) ParseGlob(pattern string) (*Template, error) {
|
||||
return parseGlob(t, pattern)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// parseGlob is the implementation of the function and method ParseGlob.
|
||||
func parseGlob(t *Template, pattern string) (*Template, error) {
|
||||
filenames, err := filepath.Glob(pattern)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(filenames) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("template: pattern matches no files: %#q", pattern)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parseFiles(t, filenames...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
556
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/parse/lex.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
556
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/parse/lex.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,556 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package parse
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// item represents a token or text string returned from the scanner.
|
||||
type item struct {
|
||||
typ itemType // The type of this item.
|
||||
pos Pos // The starting position, in bytes, of this item in the input string.
|
||||
val string // The value of this item.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (i item) String() string {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case i.typ == itemEOF:
|
||||
return "EOF"
|
||||
case i.typ == itemError:
|
||||
return i.val
|
||||
case i.typ > itemKeyword:
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("<%s>", i.val)
|
||||
case len(i.val) > 10:
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%.10q...", i.val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%q", i.val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// itemType identifies the type of lex items.
|
||||
type itemType int
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
itemError itemType = iota // error occurred; value is text of error
|
||||
itemBool // boolean constant
|
||||
itemChar // printable ASCII character; grab bag for comma etc.
|
||||
itemCharConstant // character constant
|
||||
itemComplex // complex constant (1+2i); imaginary is just a number
|
||||
itemColonEquals // colon-equals (':=') introducing a declaration
|
||||
itemEOF
|
||||
itemField // alphanumeric identifier starting with '.'
|
||||
itemIdentifier // alphanumeric identifier not starting with '.'
|
||||
itemLeftDelim // left action delimiter
|
||||
itemLeftParen // '(' inside action
|
||||
itemNumber // simple number, including imaginary
|
||||
itemPipe // pipe symbol
|
||||
itemRawString // raw quoted string (includes quotes)
|
||||
itemRightDelim // right action delimiter
|
||||
itemElideNewline // elide newline after right delim
|
||||
itemRightParen // ')' inside action
|
||||
itemSpace // run of spaces separating arguments
|
||||
itemString // quoted string (includes quotes)
|
||||
itemText // plain text
|
||||
itemVariable // variable starting with '$', such as '$' or '$1' or '$hello'
|
||||
// Keywords appear after all the rest.
|
||||
itemKeyword // used only to delimit the keywords
|
||||
itemDot // the cursor, spelled '.'
|
||||
itemDefine // define keyword
|
||||
itemElse // else keyword
|
||||
itemEnd // end keyword
|
||||
itemIf // if keyword
|
||||
itemNil // the untyped nil constant, easiest to treat as a keyword
|
||||
itemRange // range keyword
|
||||
itemTemplate // template keyword
|
||||
itemWith // with keyword
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var key = map[string]itemType{
|
||||
".": itemDot,
|
||||
"define": itemDefine,
|
||||
"else": itemElse,
|
||||
"end": itemEnd,
|
||||
"if": itemIf,
|
||||
"range": itemRange,
|
||||
"nil": itemNil,
|
||||
"template": itemTemplate,
|
||||
"with": itemWith,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const eof = -1
|
||||
|
||||
// stateFn represents the state of the scanner as a function that returns the next state.
|
||||
type stateFn func(*lexer) stateFn
|
||||
|
||||
// lexer holds the state of the scanner.
|
||||
type lexer struct {
|
||||
name string // the name of the input; used only for error reports
|
||||
input string // the string being scanned
|
||||
leftDelim string // start of action
|
||||
rightDelim string // end of action
|
||||
state stateFn // the next lexing function to enter
|
||||
pos Pos // current position in the input
|
||||
start Pos // start position of this item
|
||||
width Pos // width of last rune read from input
|
||||
lastPos Pos // position of most recent item returned by nextItem
|
||||
items chan item // channel of scanned items
|
||||
parenDepth int // nesting depth of ( ) exprs
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// next returns the next rune in the input.
|
||||
func (l *lexer) next() rune {
|
||||
if int(l.pos) >= len(l.input) {
|
||||
l.width = 0
|
||||
return eof
|
||||
}
|
||||
r, w := utf8.DecodeRuneInString(l.input[l.pos:])
|
||||
l.width = Pos(w)
|
||||
l.pos += l.width
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// peek returns but does not consume the next rune in the input.
|
||||
func (l *lexer) peek() rune {
|
||||
r := l.next()
|
||||
l.backup()
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// backup steps back one rune. Can only be called once per call of next.
|
||||
func (l *lexer) backup() {
|
||||
l.pos -= l.width
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// emit passes an item back to the client.
|
||||
func (l *lexer) emit(t itemType) {
|
||||
l.items <- item{t, l.start, l.input[l.start:l.pos]}
|
||||
l.start = l.pos
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ignore skips over the pending input before this point.
|
||||
func (l *lexer) ignore() {
|
||||
l.start = l.pos
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// accept consumes the next rune if it's from the valid set.
|
||||
func (l *lexer) accept(valid string) bool {
|
||||
if strings.IndexRune(valid, l.next()) >= 0 {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.backup()
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// acceptRun consumes a run of runes from the valid set.
|
||||
func (l *lexer) acceptRun(valid string) {
|
||||
for strings.IndexRune(valid, l.next()) >= 0 {
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.backup()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lineNumber reports which line we're on, based on the position of
|
||||
// the previous item returned by nextItem. Doing it this way
|
||||
// means we don't have to worry about peek double counting.
|
||||
func (l *lexer) lineNumber() int {
|
||||
return 1 + strings.Count(l.input[:l.lastPos], "\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// errorf returns an error token and terminates the scan by passing
|
||||
// back a nil pointer that will be the next state, terminating l.nextItem.
|
||||
func (l *lexer) errorf(format string, args ...interface{}) stateFn {
|
||||
l.items <- item{itemError, l.start, fmt.Sprintf(format, args...)}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// nextItem returns the next item from the input.
|
||||
func (l *lexer) nextItem() item {
|
||||
item := <-l.items
|
||||
l.lastPos = item.pos
|
||||
return item
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lex creates a new scanner for the input string.
|
||||
func lex(name, input, left, right string) *lexer {
|
||||
if left == "" {
|
||||
left = leftDelim
|
||||
}
|
||||
if right == "" {
|
||||
right = rightDelim
|
||||
}
|
||||
l := &lexer{
|
||||
name: name,
|
||||
input: input,
|
||||
leftDelim: left,
|
||||
rightDelim: right,
|
||||
items: make(chan item),
|
||||
}
|
||||
go l.run()
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// run runs the state machine for the lexer.
|
||||
func (l *lexer) run() {
|
||||
for l.state = lexText; l.state != nil; {
|
||||
l.state = l.state(l)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// state functions
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
leftDelim = "{{"
|
||||
rightDelim = "}}"
|
||||
leftComment = "/*"
|
||||
rightComment = "*/"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// lexText scans until an opening action delimiter, "{{".
|
||||
func lexText(l *lexer) stateFn {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
if strings.HasPrefix(l.input[l.pos:], l.leftDelim) {
|
||||
if l.pos > l.start {
|
||||
l.emit(itemText)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return lexLeftDelim
|
||||
}
|
||||
if l.next() == eof {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Correctly reached EOF.
|
||||
if l.pos > l.start {
|
||||
l.emit(itemText)
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.emit(itemEOF)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lexLeftDelim scans the left delimiter, which is known to be present.
|
||||
func lexLeftDelim(l *lexer) stateFn {
|
||||
l.pos += Pos(len(l.leftDelim))
|
||||
if strings.HasPrefix(l.input[l.pos:], leftComment) {
|
||||
return lexComment
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.emit(itemLeftDelim)
|
||||
l.parenDepth = 0
|
||||
return lexInsideAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lexComment scans a comment. The left comment marker is known to be present.
|
||||
func lexComment(l *lexer) stateFn {
|
||||
l.pos += Pos(len(leftComment))
|
||||
i := strings.Index(l.input[l.pos:], rightComment)
|
||||
if i < 0 {
|
||||
return l.errorf("unclosed comment")
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.pos += Pos(i + len(rightComment))
|
||||
if !strings.HasPrefix(l.input[l.pos:], l.rightDelim) {
|
||||
return l.errorf("comment ends before closing delimiter")
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.pos += Pos(len(l.rightDelim))
|
||||
l.ignore()
|
||||
return lexText
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lexRightDelim scans the right delimiter, which is known to be present.
|
||||
func lexRightDelim(l *lexer) stateFn {
|
||||
l.pos += Pos(len(l.rightDelim))
|
||||
l.emit(itemRightDelim)
|
||||
if l.peek() == '\\' {
|
||||
l.pos++
|
||||
l.emit(itemElideNewline)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return lexText
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lexInsideAction scans the elements inside action delimiters.
|
||||
func lexInsideAction(l *lexer) stateFn {
|
||||
// Either number, quoted string, or identifier.
|
||||
// Spaces separate arguments; runs of spaces turn into itemSpace.
|
||||
// Pipe symbols separate and are emitted.
|
||||
if strings.HasPrefix(l.input[l.pos:], l.rightDelim+"\\") || strings.HasPrefix(l.input[l.pos:], l.rightDelim) {
|
||||
if l.parenDepth == 0 {
|
||||
return lexRightDelim
|
||||
}
|
||||
return l.errorf("unclosed left paren")
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch r := l.next(); {
|
||||
case r == eof || isEndOfLine(r):
|
||||
return l.errorf("unclosed action")
|
||||
case isSpace(r):
|
||||
return lexSpace
|
||||
case r == ':':
|
||||
if l.next() != '=' {
|
||||
return l.errorf("expected :=")
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.emit(itemColonEquals)
|
||||
case r == '|':
|
||||
l.emit(itemPipe)
|
||||
case r == '"':
|
||||
return lexQuote
|
||||
case r == '`':
|
||||
return lexRawQuote
|
||||
case r == '$':
|
||||
return lexVariable
|
||||
case r == '\'':
|
||||
return lexChar
|
||||
case r == '.':
|
||||
// special look-ahead for ".field" so we don't break l.backup().
|
||||
if l.pos < Pos(len(l.input)) {
|
||||
r := l.input[l.pos]
|
||||
if r < '0' || '9' < r {
|
||||
return lexField
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
fallthrough // '.' can start a number.
|
||||
case r == '+' || r == '-' || ('0' <= r && r <= '9'):
|
||||
l.backup()
|
||||
return lexNumber
|
||||
case isAlphaNumeric(r):
|
||||
l.backup()
|
||||
return lexIdentifier
|
||||
case r == '(':
|
||||
l.emit(itemLeftParen)
|
||||
l.parenDepth++
|
||||
return lexInsideAction
|
||||
case r == ')':
|
||||
l.emit(itemRightParen)
|
||||
l.parenDepth--
|
||||
if l.parenDepth < 0 {
|
||||
return l.errorf("unexpected right paren %#U", r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return lexInsideAction
|
||||
case r <= unicode.MaxASCII && unicode.IsPrint(r):
|
||||
l.emit(itemChar)
|
||||
return lexInsideAction
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return l.errorf("unrecognized character in action: %#U", r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return lexInsideAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lexSpace scans a run of space characters.
|
||||
// One space has already been seen.
|
||||
func lexSpace(l *lexer) stateFn {
|
||||
for isSpace(l.peek()) {
|
||||
l.next()
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.emit(itemSpace)
|
||||
return lexInsideAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lexIdentifier scans an alphanumeric.
|
||||
func lexIdentifier(l *lexer) stateFn {
|
||||
Loop:
|
||||
for {
|
||||
switch r := l.next(); {
|
||||
case isAlphaNumeric(r):
|
||||
// absorb.
|
||||
default:
|
||||
l.backup()
|
||||
word := l.input[l.start:l.pos]
|
||||
if !l.atTerminator() {
|
||||
return l.errorf("bad character %#U", r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case key[word] > itemKeyword:
|
||||
l.emit(key[word])
|
||||
case word[0] == '.':
|
||||
l.emit(itemField)
|
||||
case word == "true", word == "false":
|
||||
l.emit(itemBool)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
l.emit(itemIdentifier)
|
||||
}
|
||||
break Loop
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return lexInsideAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lexField scans a field: .Alphanumeric.
|
||||
// The . has been scanned.
|
||||
func lexField(l *lexer) stateFn {
|
||||
return lexFieldOrVariable(l, itemField)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lexVariable scans a Variable: $Alphanumeric.
|
||||
// The $ has been scanned.
|
||||
func lexVariable(l *lexer) stateFn {
|
||||
if l.atTerminator() { // Nothing interesting follows -> "$".
|
||||
l.emit(itemVariable)
|
||||
return lexInsideAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
return lexFieldOrVariable(l, itemVariable)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lexVariable scans a field or variable: [.$]Alphanumeric.
|
||||
// The . or $ has been scanned.
|
||||
func lexFieldOrVariable(l *lexer, typ itemType) stateFn {
|
||||
if l.atTerminator() { // Nothing interesting follows -> "." or "$".
|
||||
if typ == itemVariable {
|
||||
l.emit(itemVariable)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
l.emit(itemDot)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return lexInsideAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
var r rune
|
||||
for {
|
||||
r = l.next()
|
||||
if !isAlphaNumeric(r) {
|
||||
l.backup()
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !l.atTerminator() {
|
||||
return l.errorf("bad character %#U", r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.emit(typ)
|
||||
return lexInsideAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// atTerminator reports whether the input is at valid termination character to
|
||||
// appear after an identifier. Breaks .X.Y into two pieces. Also catches cases
|
||||
// like "$x+2" not being acceptable without a space, in case we decide one
|
||||
// day to implement arithmetic.
|
||||
func (l *lexer) atTerminator() bool {
|
||||
r := l.peek()
|
||||
if isSpace(r) || isEndOfLine(r) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch r {
|
||||
case eof, '.', ',', '|', ':', ')', '(':
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Does r start the delimiter? This can be ambiguous (with delim=="//", $x/2 will
|
||||
// succeed but should fail) but only in extremely rare cases caused by willfully
|
||||
// bad choice of delimiter.
|
||||
if rd, _ := utf8.DecodeRuneInString(l.rightDelim); rd == r {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lexChar scans a character constant. The initial quote is already
|
||||
// scanned. Syntax checking is done by the parser.
|
||||
func lexChar(l *lexer) stateFn {
|
||||
Loop:
|
||||
for {
|
||||
switch l.next() {
|
||||
case '\\':
|
||||
if r := l.next(); r != eof && r != '\n' {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case eof, '\n':
|
||||
return l.errorf("unterminated character constant")
|
||||
case '\'':
|
||||
break Loop
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.emit(itemCharConstant)
|
||||
return lexInsideAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lexNumber scans a number: decimal, octal, hex, float, or imaginary. This
|
||||
// isn't a perfect number scanner - for instance it accepts "." and "0x0.2"
|
||||
// and "089" - but when it's wrong the input is invalid and the parser (via
|
||||
// strconv) will notice.
|
||||
func lexNumber(l *lexer) stateFn {
|
||||
if !l.scanNumber() {
|
||||
return l.errorf("bad number syntax: %q", l.input[l.start:l.pos])
|
||||
}
|
||||
if sign := l.peek(); sign == '+' || sign == '-' {
|
||||
// Complex: 1+2i. No spaces, must end in 'i'.
|
||||
if !l.scanNumber() || l.input[l.pos-1] != 'i' {
|
||||
return l.errorf("bad number syntax: %q", l.input[l.start:l.pos])
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.emit(itemComplex)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
l.emit(itemNumber)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return lexInsideAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *lexer) scanNumber() bool {
|
||||
// Optional leading sign.
|
||||
l.accept("+-")
|
||||
// Is it hex?
|
||||
digits := "0123456789"
|
||||
if l.accept("0") && l.accept("xX") {
|
||||
digits = "0123456789abcdefABCDEF"
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.acceptRun(digits)
|
||||
if l.accept(".") {
|
||||
l.acceptRun(digits)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if l.accept("eE") {
|
||||
l.accept("+-")
|
||||
l.acceptRun("0123456789")
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Is it imaginary?
|
||||
l.accept("i")
|
||||
// Next thing mustn't be alphanumeric.
|
||||
if isAlphaNumeric(l.peek()) {
|
||||
l.next()
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lexQuote scans a quoted string.
|
||||
func lexQuote(l *lexer) stateFn {
|
||||
Loop:
|
||||
for {
|
||||
switch l.next() {
|
||||
case '\\':
|
||||
if r := l.next(); r != eof && r != '\n' {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case eof, '\n':
|
||||
return l.errorf("unterminated quoted string")
|
||||
case '"':
|
||||
break Loop
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.emit(itemString)
|
||||
return lexInsideAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lexRawQuote scans a raw quoted string.
|
||||
func lexRawQuote(l *lexer) stateFn {
|
||||
Loop:
|
||||
for {
|
||||
switch l.next() {
|
||||
case eof, '\n':
|
||||
return l.errorf("unterminated raw quoted string")
|
||||
case '`':
|
||||
break Loop
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.emit(itemRawString)
|
||||
return lexInsideAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isSpace reports whether r is a space character.
|
||||
func isSpace(r rune) bool {
|
||||
return r == ' ' || r == '\t'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isEndOfLine reports whether r is an end-of-line character.
|
||||
func isEndOfLine(r rune) bool {
|
||||
return r == '\r' || r == '\n'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// isAlphaNumeric reports whether r is an alphabetic, digit, or underscore.
|
||||
func isAlphaNumeric(r rune) bool {
|
||||
return r == '_' || unicode.IsLetter(r) || unicode.IsDigit(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
834
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/parse/node.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
834
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/parse/node.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,834 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
package parse
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var textFormat = "%s" // Changed to "%q" in tests for better error messages.
|
||||
|
||||
// A Node is an element in the parse tree. The interface is trivial.
|
||||
// The interface contains an unexported method so that only
|
||||
// types local to this package can satisfy it.
|
||||
type Node interface {
|
||||
Type() NodeType
|
||||
String() string
|
||||
// Copy does a deep copy of the Node and all its components.
|
||||
// To avoid type assertions, some XxxNodes also have specialized
|
||||
// CopyXxx methods that return *XxxNode.
|
||||
Copy() Node
|
||||
Position() Pos // byte position of start of node in full original input string
|
||||
// tree returns the containing *Tree.
|
||||
// It is unexported so all implementations of Node are in this package.
|
||||
tree() *Tree
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NodeType identifies the type of a parse tree node.
|
||||
type NodeType int
|
||||
|
||||
// Pos represents a byte position in the original input text from which
|
||||
// this template was parsed.
|
||||
type Pos int
|
||||
|
||||
func (p Pos) Position() Pos {
|
||||
return p
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Type returns itself and provides an easy default implementation
|
||||
// for embedding in a Node. Embedded in all non-trivial Nodes.
|
||||
func (t NodeType) Type() NodeType {
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
NodeText NodeType = iota // Plain text.
|
||||
NodeAction // A non-control action such as a field evaluation.
|
||||
NodeBool // A boolean constant.
|
||||
NodeChain // A sequence of field accesses.
|
||||
NodeCommand // An element of a pipeline.
|
||||
NodeDot // The cursor, dot.
|
||||
nodeElse // An else action. Not added to tree.
|
||||
nodeEnd // An end action. Not added to tree.
|
||||
NodeField // A field or method name.
|
||||
NodeIdentifier // An identifier; always a function name.
|
||||
NodeIf // An if action.
|
||||
NodeList // A list of Nodes.
|
||||
NodeNil // An untyped nil constant.
|
||||
NodeNumber // A numerical constant.
|
||||
NodePipe // A pipeline of commands.
|
||||
NodeRange // A range action.
|
||||
NodeString // A string constant.
|
||||
NodeTemplate // A template invocation action.
|
||||
NodeVariable // A $ variable.
|
||||
NodeWith // A with action.
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
// ListNode holds a sequence of nodes.
|
||||
type ListNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
Nodes []Node // The element nodes in lexical order.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newList(pos Pos) *ListNode {
|
||||
return &ListNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeList, Pos: pos}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *ListNode) append(n Node) {
|
||||
l.Nodes = append(l.Nodes, n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *ListNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return l.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *ListNode) String() string {
|
||||
b := new(bytes.Buffer)
|
||||
for _, n := range l.Nodes {
|
||||
fmt.Fprint(b, n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *ListNode) CopyList() *ListNode {
|
||||
if l == nil {
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
n := l.tr.newList(l.Pos)
|
||||
for _, elem := range l.Nodes {
|
||||
n.append(elem.Copy())
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *ListNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return l.CopyList()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TextNode holds plain text.
|
||||
type TextNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
Text []byte // The text; may span newlines.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newText(pos Pos, text string) *TextNode {
|
||||
return &TextNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeText, Pos: pos, Text: []byte(text)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *TextNode) String() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf(textFormat, t.Text)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *TextNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return t.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *TextNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return &TextNode{tr: t.tr, NodeType: NodeText, Pos: t.Pos, Text: append([]byte{}, t.Text...)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PipeNode holds a pipeline with optional declaration
|
||||
type PipeNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
Line int // The line number in the input (deprecated; kept for compatibility)
|
||||
Decl []*VariableNode // Variable declarations in lexical order.
|
||||
Cmds []*CommandNode // The commands in lexical order.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newPipeline(pos Pos, line int, decl []*VariableNode) *PipeNode {
|
||||
return &PipeNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodePipe, Pos: pos, Line: line, Decl: decl}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *PipeNode) append(command *CommandNode) {
|
||||
p.Cmds = append(p.Cmds, command)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *PipeNode) String() string {
|
||||
s := ""
|
||||
if len(p.Decl) > 0 {
|
||||
for i, v := range p.Decl {
|
||||
if i > 0 {
|
||||
s += ", "
|
||||
}
|
||||
s += v.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
s += " := "
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i, c := range p.Cmds {
|
||||
if i > 0 {
|
||||
s += " | "
|
||||
}
|
||||
s += c.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *PipeNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return p.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *PipeNode) CopyPipe() *PipeNode {
|
||||
if p == nil {
|
||||
return p
|
||||
}
|
||||
var decl []*VariableNode
|
||||
for _, d := range p.Decl {
|
||||
decl = append(decl, d.Copy().(*VariableNode))
|
||||
}
|
||||
n := p.tr.newPipeline(p.Pos, p.Line, decl)
|
||||
for _, c := range p.Cmds {
|
||||
n.append(c.Copy().(*CommandNode))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *PipeNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return p.CopyPipe()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ActionNode holds an action (something bounded by delimiters).
|
||||
// Control actions have their own nodes; ActionNode represents simple
|
||||
// ones such as field evaluations and parenthesized pipelines.
|
||||
type ActionNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
Line int // The line number in the input (deprecated; kept for compatibility)
|
||||
Pipe *PipeNode // The pipeline in the action.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newAction(pos Pos, line int, pipe *PipeNode) *ActionNode {
|
||||
return &ActionNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeAction, Pos: pos, Line: line, Pipe: pipe}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *ActionNode) String() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("{{%s}}", a.Pipe)
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *ActionNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return a.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *ActionNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return a.tr.newAction(a.Pos, a.Line, a.Pipe.CopyPipe())
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CommandNode holds a command (a pipeline inside an evaluating action).
|
||||
type CommandNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
Args []Node // Arguments in lexical order: Identifier, field, or constant.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newCommand(pos Pos) *CommandNode {
|
||||
return &CommandNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeCommand, Pos: pos}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *CommandNode) append(arg Node) {
|
||||
c.Args = append(c.Args, arg)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *CommandNode) String() string {
|
||||
s := ""
|
||||
for i, arg := range c.Args {
|
||||
if i > 0 {
|
||||
s += " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
if arg, ok := arg.(*PipeNode); ok {
|
||||
s += "(" + arg.String() + ")"
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
s += arg.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *CommandNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return c.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *CommandNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
if c == nil {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
n := c.tr.newCommand(c.Pos)
|
||||
for _, c := range c.Args {
|
||||
n.append(c.Copy())
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IdentifierNode holds an identifier.
|
||||
type IdentifierNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
Ident string // The identifier's name.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewIdentifier returns a new IdentifierNode with the given identifier name.
|
||||
func NewIdentifier(ident string) *IdentifierNode {
|
||||
return &IdentifierNode{NodeType: NodeIdentifier, Ident: ident}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetPos sets the position. NewIdentifier is a public method so we can't modify its signature.
|
||||
// Chained for convenience.
|
||||
// TODO: fix one day?
|
||||
func (i *IdentifierNode) SetPos(pos Pos) *IdentifierNode {
|
||||
i.Pos = pos
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetTree sets the parent tree for the node. NewIdentifier is a public method so we can't modify its signature.
|
||||
// Chained for convenience.
|
||||
// TODO: fix one day?
|
||||
func (i *IdentifierNode) SetTree(t *Tree) *IdentifierNode {
|
||||
i.tr = t
|
||||
return i
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (i *IdentifierNode) String() string {
|
||||
return i.Ident
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (i *IdentifierNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return i.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (i *IdentifierNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return NewIdentifier(i.Ident).SetTree(i.tr).SetPos(i.Pos)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VariableNode holds a list of variable names, possibly with chained field
|
||||
// accesses. The dollar sign is part of the (first) name.
|
||||
type VariableNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
Ident []string // Variable name and fields in lexical order.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newVariable(pos Pos, ident string) *VariableNode {
|
||||
return &VariableNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeVariable, Pos: pos, Ident: strings.Split(ident, ".")}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (v *VariableNode) String() string {
|
||||
s := ""
|
||||
for i, id := range v.Ident {
|
||||
if i > 0 {
|
||||
s += "."
|
||||
}
|
||||
s += id
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (v *VariableNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return v.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (v *VariableNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return &VariableNode{tr: v.tr, NodeType: NodeVariable, Pos: v.Pos, Ident: append([]string{}, v.Ident...)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DotNode holds the special identifier '.'.
|
||||
type DotNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newDot(pos Pos) *DotNode {
|
||||
return &DotNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeDot, Pos: pos}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *DotNode) Type() NodeType {
|
||||
// Override method on embedded NodeType for API compatibility.
|
||||
// TODO: Not really a problem; could change API without effect but
|
||||
// api tool complains.
|
||||
return NodeDot
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *DotNode) String() string {
|
||||
return "."
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *DotNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return d.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d *DotNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return d.tr.newDot(d.Pos)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NilNode holds the special identifier 'nil' representing an untyped nil constant.
|
||||
type NilNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newNil(pos Pos) *NilNode {
|
||||
return &NilNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeNil, Pos: pos}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (n *NilNode) Type() NodeType {
|
||||
// Override method on embedded NodeType for API compatibility.
|
||||
// TODO: Not really a problem; could change API without effect but
|
||||
// api tool complains.
|
||||
return NodeNil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (n *NilNode) String() string {
|
||||
return "nil"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (n *NilNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return n.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (n *NilNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return n.tr.newNil(n.Pos)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// FieldNode holds a field (identifier starting with '.').
|
||||
// The names may be chained ('.x.y').
|
||||
// The period is dropped from each ident.
|
||||
type FieldNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
Ident []string // The identifiers in lexical order.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newField(pos Pos, ident string) *FieldNode {
|
||||
return &FieldNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeField, Pos: pos, Ident: strings.Split(ident[1:], ".")} // [1:] to drop leading period
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *FieldNode) String() string {
|
||||
s := ""
|
||||
for _, id := range f.Ident {
|
||||
s += "." + id
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *FieldNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return f.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *FieldNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return &FieldNode{tr: f.tr, NodeType: NodeField, Pos: f.Pos, Ident: append([]string{}, f.Ident...)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ChainNode holds a term followed by a chain of field accesses (identifier starting with '.').
|
||||
// The names may be chained ('.x.y').
|
||||
// The periods are dropped from each ident.
|
||||
type ChainNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
Node Node
|
||||
Field []string // The identifiers in lexical order.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newChain(pos Pos, node Node) *ChainNode {
|
||||
return &ChainNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeChain, Pos: pos, Node: node}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add adds the named field (which should start with a period) to the end of the chain.
|
||||
func (c *ChainNode) Add(field string) {
|
||||
if len(field) == 0 || field[0] != '.' {
|
||||
panic("no dot in field")
|
||||
}
|
||||
field = field[1:] // Remove leading dot.
|
||||
if field == "" {
|
||||
panic("empty field")
|
||||
}
|
||||
c.Field = append(c.Field, field)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *ChainNode) String() string {
|
||||
s := c.Node.String()
|
||||
if _, ok := c.Node.(*PipeNode); ok {
|
||||
s = "(" + s + ")"
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, field := range c.Field {
|
||||
s += "." + field
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *ChainNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return c.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *ChainNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return &ChainNode{tr: c.tr, NodeType: NodeChain, Pos: c.Pos, Node: c.Node, Field: append([]string{}, c.Field...)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BoolNode holds a boolean constant.
|
||||
type BoolNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
True bool // The value of the boolean constant.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newBool(pos Pos, true bool) *BoolNode {
|
||||
return &BoolNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeBool, Pos: pos, True: true}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *BoolNode) String() string {
|
||||
if b.True {
|
||||
return "true"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "false"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *BoolNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return b.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *BoolNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return b.tr.newBool(b.Pos, b.True)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NumberNode holds a number: signed or unsigned integer, float, or complex.
|
||||
// The value is parsed and stored under all the types that can represent the value.
|
||||
// This simulates in a small amount of code the behavior of Go's ideal constants.
|
||||
type NumberNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
IsInt bool // Number has an integral value.
|
||||
IsUint bool // Number has an unsigned integral value.
|
||||
IsFloat bool // Number has a floating-point value.
|
||||
IsComplex bool // Number is complex.
|
||||
Int64 int64 // The signed integer value.
|
||||
Uint64 uint64 // The unsigned integer value.
|
||||
Float64 float64 // The floating-point value.
|
||||
Complex128 complex128 // The complex value.
|
||||
Text string // The original textual representation from the input.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newNumber(pos Pos, text string, typ itemType) (*NumberNode, error) {
|
||||
n := &NumberNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeNumber, Pos: pos, Text: text}
|
||||
switch typ {
|
||||
case itemCharConstant:
|
||||
rune, _, tail, err := strconv.UnquoteChar(text[1:], text[0])
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if tail != "'" {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("malformed character constant: %s", text)
|
||||
}
|
||||
n.Int64 = int64(rune)
|
||||
n.IsInt = true
|
||||
n.Uint64 = uint64(rune)
|
||||
n.IsUint = true
|
||||
n.Float64 = float64(rune) // odd but those are the rules.
|
||||
n.IsFloat = true
|
||||
return n, nil
|
||||
case itemComplex:
|
||||
// fmt.Sscan can parse the pair, so let it do the work.
|
||||
if _, err := fmt.Sscan(text, &n.Complex128); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
n.IsComplex = true
|
||||
n.simplifyComplex()
|
||||
return n, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Imaginary constants can only be complex unless they are zero.
|
||||
if len(text) > 0 && text[len(text)-1] == 'i' {
|
||||
f, err := strconv.ParseFloat(text[:len(text)-1], 64)
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
n.IsComplex = true
|
||||
n.Complex128 = complex(0, f)
|
||||
n.simplifyComplex()
|
||||
return n, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Do integer test first so we get 0x123 etc.
|
||||
u, err := strconv.ParseUint(text, 0, 64) // will fail for -0; fixed below.
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
n.IsUint = true
|
||||
n.Uint64 = u
|
||||
}
|
||||
i, err := strconv.ParseInt(text, 0, 64)
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
n.IsInt = true
|
||||
n.Int64 = i
|
||||
if i == 0 {
|
||||
n.IsUint = true // in case of -0.
|
||||
n.Uint64 = u
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// If an integer extraction succeeded, promote the float.
|
||||
if n.IsInt {
|
||||
n.IsFloat = true
|
||||
n.Float64 = float64(n.Int64)
|
||||
} else if n.IsUint {
|
||||
n.IsFloat = true
|
||||
n.Float64 = float64(n.Uint64)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
f, err := strconv.ParseFloat(text, 64)
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
n.IsFloat = true
|
||||
n.Float64 = f
|
||||
// If a floating-point extraction succeeded, extract the int if needed.
|
||||
if !n.IsInt && float64(int64(f)) == f {
|
||||
n.IsInt = true
|
||||
n.Int64 = int64(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !n.IsUint && float64(uint64(f)) == f {
|
||||
n.IsUint = true
|
||||
n.Uint64 = uint64(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !n.IsInt && !n.IsUint && !n.IsFloat {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("illegal number syntax: %q", text)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// simplifyComplex pulls out any other types that are represented by the complex number.
|
||||
// These all require that the imaginary part be zero.
|
||||
func (n *NumberNode) simplifyComplex() {
|
||||
n.IsFloat = imag(n.Complex128) == 0
|
||||
if n.IsFloat {
|
||||
n.Float64 = real(n.Complex128)
|
||||
n.IsInt = float64(int64(n.Float64)) == n.Float64
|
||||
if n.IsInt {
|
||||
n.Int64 = int64(n.Float64)
|
||||
}
|
||||
n.IsUint = float64(uint64(n.Float64)) == n.Float64
|
||||
if n.IsUint {
|
||||
n.Uint64 = uint64(n.Float64)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (n *NumberNode) String() string {
|
||||
return n.Text
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (n *NumberNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return n.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (n *NumberNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
nn := new(NumberNode)
|
||||
*nn = *n // Easy, fast, correct.
|
||||
return nn
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StringNode holds a string constant. The value has been "unquoted".
|
||||
type StringNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
Quoted string // The original text of the string, with quotes.
|
||||
Text string // The string, after quote processing.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newString(pos Pos, orig, text string) *StringNode {
|
||||
return &StringNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeString, Pos: pos, Quoted: orig, Text: text}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *StringNode) String() string {
|
||||
return s.Quoted
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *StringNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return s.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *StringNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return s.tr.newString(s.Pos, s.Quoted, s.Text)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// endNode represents an {{end}} action.
|
||||
// It does not appear in the final parse tree.
|
||||
type endNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newEnd(pos Pos) *endNode {
|
||||
return &endNode{tr: t, NodeType: nodeEnd, Pos: pos}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *endNode) String() string {
|
||||
return "{{end}}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *endNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return e.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *endNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return e.tr.newEnd(e.Pos)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// elseNode represents an {{else}} action. Does not appear in the final tree.
|
||||
type elseNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
Line int // The line number in the input (deprecated; kept for compatibility)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newElse(pos Pos, line int) *elseNode {
|
||||
return &elseNode{tr: t, NodeType: nodeElse, Pos: pos, Line: line}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *elseNode) Type() NodeType {
|
||||
return nodeElse
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *elseNode) String() string {
|
||||
return "{{else}}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *elseNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return e.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *elseNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return e.tr.newElse(e.Pos, e.Line)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BranchNode is the common representation of if, range, and with.
|
||||
type BranchNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
Line int // The line number in the input (deprecated; kept for compatibility)
|
||||
Pipe *PipeNode // The pipeline to be evaluated.
|
||||
List *ListNode // What to execute if the value is non-empty.
|
||||
ElseList *ListNode // What to execute if the value is empty (nil if absent).
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *BranchNode) String() string {
|
||||
name := ""
|
||||
switch b.NodeType {
|
||||
case NodeIf:
|
||||
name = "if"
|
||||
case NodeRange:
|
||||
name = "range"
|
||||
case NodeWith:
|
||||
name = "with"
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("unknown branch type")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if b.ElseList != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("{{%s %s}}%s{{else}}%s{{end}}", name, b.Pipe, b.List, b.ElseList)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("{{%s %s}}%s{{end}}", name, b.Pipe, b.List)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *BranchNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return b.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *BranchNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
switch b.NodeType {
|
||||
case NodeIf:
|
||||
return b.tr.newIf(b.Pos, b.Line, b.Pipe, b.List, b.ElseList)
|
||||
case NodeRange:
|
||||
return b.tr.newRange(b.Pos, b.Line, b.Pipe, b.List, b.ElseList)
|
||||
case NodeWith:
|
||||
return b.tr.newWith(b.Pos, b.Line, b.Pipe, b.List, b.ElseList)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("unknown branch type")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IfNode represents an {{if}} action and its commands.
|
||||
type IfNode struct {
|
||||
BranchNode
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newIf(pos Pos, line int, pipe *PipeNode, list, elseList *ListNode) *IfNode {
|
||||
return &IfNode{BranchNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeIf, Pos: pos, Line: line, Pipe: pipe, List: list, ElseList: elseList}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (i *IfNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return i.tr.newIf(i.Pos, i.Line, i.Pipe.CopyPipe(), i.List.CopyList(), i.ElseList.CopyList())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RangeNode represents a {{range}} action and its commands.
|
||||
type RangeNode struct {
|
||||
BranchNode
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newRange(pos Pos, line int, pipe *PipeNode, list, elseList *ListNode) *RangeNode {
|
||||
return &RangeNode{BranchNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeRange, Pos: pos, Line: line, Pipe: pipe, List: list, ElseList: elseList}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (r *RangeNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return r.tr.newRange(r.Pos, r.Line, r.Pipe.CopyPipe(), r.List.CopyList(), r.ElseList.CopyList())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithNode represents a {{with}} action and its commands.
|
||||
type WithNode struct {
|
||||
BranchNode
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newWith(pos Pos, line int, pipe *PipeNode, list, elseList *ListNode) *WithNode {
|
||||
return &WithNode{BranchNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeWith, Pos: pos, Line: line, Pipe: pipe, List: list, ElseList: elseList}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *WithNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return w.tr.newWith(w.Pos, w.Line, w.Pipe.CopyPipe(), w.List.CopyList(), w.ElseList.CopyList())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TemplateNode represents a {{template}} action.
|
||||
type TemplateNode struct {
|
||||
NodeType
|
||||
Pos
|
||||
tr *Tree
|
||||
Line int // The line number in the input (deprecated; kept for compatibility)
|
||||
Name string // The name of the template (unquoted).
|
||||
Pipe *PipeNode // The command to evaluate as dot for the template.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) newTemplate(pos Pos, line int, name string, pipe *PipeNode) *TemplateNode {
|
||||
return &TemplateNode{tr: t, NodeType: NodeTemplate, Pos: pos, Line: line, Name: name, Pipe: pipe}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *TemplateNode) String() string {
|
||||
if t.Pipe == nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("{{template %q}}", t.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("{{template %q %s}}", t.Name, t.Pipe)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *TemplateNode) tree() *Tree {
|
||||
return t.tr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *TemplateNode) Copy() Node {
|
||||
return t.tr.newTemplate(t.Pos, t.Line, t.Name, t.Pipe.CopyPipe())
|
||||
}
|
||||
700
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/parse/parse.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
700
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/parse/parse.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,700 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package parse builds parse trees for templates as defined by text/template
|
||||
// and html/template. Clients should use those packages to construct templates
|
||||
// rather than this one, which provides shared internal data structures not
|
||||
// intended for general use.
|
||||
package parse
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"runtime"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Tree is the representation of a single parsed template.
|
||||
type Tree struct {
|
||||
Name string // name of the template represented by the tree.
|
||||
ParseName string // name of the top-level template during parsing, for error messages.
|
||||
Root *ListNode // top-level root of the tree.
|
||||
text string // text parsed to create the template (or its parent)
|
||||
// Parsing only; cleared after parse.
|
||||
funcs []map[string]interface{}
|
||||
lex *lexer
|
||||
token [3]item // three-token lookahead for parser.
|
||||
peekCount int
|
||||
vars []string // variables defined at the moment.
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Copy returns a copy of the Tree. Any parsing state is discarded.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) Copy() *Tree {
|
||||
if t == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return &Tree{
|
||||
Name: t.Name,
|
||||
ParseName: t.ParseName,
|
||||
Root: t.Root.CopyList(),
|
||||
text: t.text,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse returns a map from template name to parse.Tree, created by parsing the
|
||||
// templates described in the argument string. The top-level template will be
|
||||
// given the specified name. If an error is encountered, parsing stops and an
|
||||
// empty map is returned with the error.
|
||||
func Parse(name, text, leftDelim, rightDelim string, funcs ...map[string]interface{}) (treeSet map[string]*Tree, err error) {
|
||||
treeSet = make(map[string]*Tree)
|
||||
t := New(name)
|
||||
t.text = text
|
||||
_, err = t.Parse(text, leftDelim, rightDelim, treeSet, funcs...)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// next returns the next token.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) next() item {
|
||||
if t.peekCount > 0 {
|
||||
t.peekCount--
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
t.token[0] = t.lex.nextItem()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t.token[t.peekCount]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// backup backs the input stream up one token.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) backup() {
|
||||
t.peekCount++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// backup2 backs the input stream up two tokens.
|
||||
// The zeroth token is already there.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) backup2(t1 item) {
|
||||
t.token[1] = t1
|
||||
t.peekCount = 2
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// backup3 backs the input stream up three tokens
|
||||
// The zeroth token is already there.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) backup3(t2, t1 item) { // Reverse order: we're pushing back.
|
||||
t.token[1] = t1
|
||||
t.token[2] = t2
|
||||
t.peekCount = 3
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// peek returns but does not consume the next token.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) peek() item {
|
||||
if t.peekCount > 0 {
|
||||
return t.token[t.peekCount-1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.peekCount = 1
|
||||
t.token[0] = t.lex.nextItem()
|
||||
return t.token[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// nextNonSpace returns the next non-space token.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) nextNonSpace() (token item) {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
token = t.next()
|
||||
if token.typ != itemSpace {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return token
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// peekNonSpace returns but does not consume the next non-space token.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) peekNonSpace() (token item) {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
token = t.next()
|
||||
if token.typ != itemSpace {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.backup()
|
||||
return token
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parsing.
|
||||
|
||||
// New allocates a new parse tree with the given name.
|
||||
func New(name string, funcs ...map[string]interface{}) *Tree {
|
||||
return &Tree{
|
||||
Name: name,
|
||||
funcs: funcs,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ErrorContext returns a textual representation of the location of the node in the input text.
|
||||
// The receiver is only used when the node does not have a pointer to the tree inside,
|
||||
// which can occur in old code.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) ErrorContext(n Node) (location, context string) {
|
||||
pos := int(n.Position())
|
||||
tree := n.tree()
|
||||
if tree == nil {
|
||||
tree = t
|
||||
}
|
||||
text := tree.text[:pos]
|
||||
byteNum := strings.LastIndex(text, "\n")
|
||||
if byteNum == -1 {
|
||||
byteNum = pos // On first line.
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
byteNum++ // After the newline.
|
||||
byteNum = pos - byteNum
|
||||
}
|
||||
lineNum := 1 + strings.Count(text, "\n")
|
||||
context = n.String()
|
||||
if len(context) > 20 {
|
||||
context = fmt.Sprintf("%.20s...", context)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d:%d", tree.ParseName, lineNum, byteNum), context
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// errorf formats the error and terminates processing.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) errorf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
t.Root = nil
|
||||
format = fmt.Sprintf("template: %s:%d: %s", t.ParseName, t.lex.lineNumber(), format)
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf(format, args...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// error terminates processing.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) error(err error) {
|
||||
t.errorf("%s", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// expect consumes the next token and guarantees it has the required type.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) expect(expected itemType, context string) item {
|
||||
token := t.nextNonSpace()
|
||||
if token.typ != expected {
|
||||
t.unexpected(token, context)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return token
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// expectOneOf consumes the next token and guarantees it has one of the required types.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) expectOneOf(expected1, expected2 itemType, context string) item {
|
||||
token := t.nextNonSpace()
|
||||
if token.typ != expected1 && token.typ != expected2 {
|
||||
t.unexpected(token, context)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return token
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// unexpected complains about the token and terminates processing.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) unexpected(token item, context string) {
|
||||
t.errorf("unexpected %s in %s", token, context)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// recover is the handler that turns panics into returns from the top level of Parse.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) recover(errp *error) {
|
||||
e := recover()
|
||||
if e != nil {
|
||||
if _, ok := e.(runtime.Error); ok {
|
||||
panic(e)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t != nil {
|
||||
t.stopParse()
|
||||
}
|
||||
*errp = e.(error)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// startParse initializes the parser, using the lexer.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) startParse(funcs []map[string]interface{}, lex *lexer) {
|
||||
t.Root = nil
|
||||
t.lex = lex
|
||||
t.vars = []string{"$"}
|
||||
t.funcs = funcs
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// stopParse terminates parsing.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) stopParse() {
|
||||
t.lex = nil
|
||||
t.vars = nil
|
||||
t.funcs = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse parses the template definition string to construct a representation of
|
||||
// the template for execution. If either action delimiter string is empty, the
|
||||
// default ("{{" or "}}") is used. Embedded template definitions are added to
|
||||
// the treeSet map.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) Parse(text, leftDelim, rightDelim string, treeSet map[string]*Tree, funcs ...map[string]interface{}) (tree *Tree, err error) {
|
||||
defer t.recover(&err)
|
||||
t.ParseName = t.Name
|
||||
t.startParse(funcs, lex(t.Name, text, leftDelim, rightDelim))
|
||||
t.text = text
|
||||
t.parse(treeSet)
|
||||
t.add(treeSet)
|
||||
t.stopParse()
|
||||
return t, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// add adds tree to the treeSet.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) add(treeSet map[string]*Tree) {
|
||||
tree := treeSet[t.Name]
|
||||
if tree == nil || IsEmptyTree(tree.Root) {
|
||||
treeSet[t.Name] = t
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !IsEmptyTree(t.Root) {
|
||||
t.errorf("template: multiple definition of template %q", t.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsEmptyTree reports whether this tree (node) is empty of everything but space.
|
||||
func IsEmptyTree(n Node) bool {
|
||||
switch n := n.(type) {
|
||||
case nil:
|
||||
return true
|
||||
case *ActionNode:
|
||||
case *IfNode:
|
||||
case *ListNode:
|
||||
for _, node := range n.Nodes {
|
||||
if !IsEmptyTree(node) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
case *RangeNode:
|
||||
case *TemplateNode:
|
||||
case *TextNode:
|
||||
return len(bytes.TrimSpace(n.Text)) == 0
|
||||
case *WithNode:
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic("unknown node: " + n.String())
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// parse is the top-level parser for a template, essentially the same
|
||||
// as itemList except it also parses {{define}} actions.
|
||||
// It runs to EOF.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) parse(treeSet map[string]*Tree) (next Node) {
|
||||
t.Root = t.newList(t.peek().pos)
|
||||
for t.peek().typ != itemEOF {
|
||||
if t.peek().typ == itemLeftDelim {
|
||||
delim := t.next()
|
||||
if t.nextNonSpace().typ == itemDefine {
|
||||
newT := New("definition") // name will be updated once we know it.
|
||||
newT.text = t.text
|
||||
newT.ParseName = t.ParseName
|
||||
newT.startParse(t.funcs, t.lex)
|
||||
newT.parseDefinition(treeSet)
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.backup2(delim)
|
||||
}
|
||||
n := t.textOrAction()
|
||||
if n.Type() == nodeEnd {
|
||||
t.errorf("unexpected %s", n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.Root.append(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// parseDefinition parses a {{define}} ... {{end}} template definition and
|
||||
// installs the definition in the treeSet map. The "define" keyword has already
|
||||
// been scanned.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) parseDefinition(treeSet map[string]*Tree) {
|
||||
const context = "define clause"
|
||||
name := t.expectOneOf(itemString, itemRawString, context)
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
t.Name, err = strconv.Unquote(name.val)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
t.error(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.expect(itemRightDelim, context)
|
||||
var end Node
|
||||
t.Root, end = t.itemList()
|
||||
if end.Type() != nodeEnd {
|
||||
t.errorf("unexpected %s in %s", end, context)
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.add(treeSet)
|
||||
t.stopParse()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// itemList:
|
||||
// textOrAction*
|
||||
// Terminates at {{end}} or {{else}}, returned separately.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) itemList() (list *ListNode, next Node) {
|
||||
list = t.newList(t.peekNonSpace().pos)
|
||||
for t.peekNonSpace().typ != itemEOF {
|
||||
n := t.textOrAction()
|
||||
switch n.Type() {
|
||||
case nodeEnd, nodeElse:
|
||||
return list, n
|
||||
}
|
||||
list.append(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.errorf("unexpected EOF")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// textOrAction:
|
||||
// text | action
|
||||
func (t *Tree) textOrAction() Node {
|
||||
switch token := t.nextNonSpace(); token.typ {
|
||||
case itemElideNewline:
|
||||
return t.elideNewline()
|
||||
case itemText:
|
||||
return t.newText(token.pos, token.val)
|
||||
case itemLeftDelim:
|
||||
return t.action()
|
||||
default:
|
||||
t.unexpected(token, "input")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// elideNewline:
|
||||
// Remove newlines trailing rightDelim if \\ is present.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) elideNewline() Node {
|
||||
token := t.peek()
|
||||
if token.typ != itemText {
|
||||
t.unexpected(token, "input")
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
t.next()
|
||||
stripped := strings.TrimLeft(token.val, "\n\r")
|
||||
diff := len(token.val) - len(stripped)
|
||||
if diff > 0 {
|
||||
// This is a bit nasty. We mutate the token in-place to remove
|
||||
// preceding newlines.
|
||||
token.pos += Pos(diff)
|
||||
token.val = stripped
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t.newText(token.pos, token.val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Action:
|
||||
// control
|
||||
// command ("|" command)*
|
||||
// Left delim is past. Now get actions.
|
||||
// First word could be a keyword such as range.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) action() (n Node) {
|
||||
switch token := t.nextNonSpace(); token.typ {
|
||||
case itemElse:
|
||||
return t.elseControl()
|
||||
case itemEnd:
|
||||
return t.endControl()
|
||||
case itemIf:
|
||||
return t.ifControl()
|
||||
case itemRange:
|
||||
return t.rangeControl()
|
||||
case itemTemplate:
|
||||
return t.templateControl()
|
||||
case itemWith:
|
||||
return t.withControl()
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.backup()
|
||||
// Do not pop variables; they persist until "end".
|
||||
return t.newAction(t.peek().pos, t.lex.lineNumber(), t.pipeline("command"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Pipeline:
|
||||
// declarations? command ('|' command)*
|
||||
func (t *Tree) pipeline(context string) (pipe *PipeNode) {
|
||||
var decl []*VariableNode
|
||||
pos := t.peekNonSpace().pos
|
||||
// Are there declarations?
|
||||
for {
|
||||
if v := t.peekNonSpace(); v.typ == itemVariable {
|
||||
t.next()
|
||||
// Since space is a token, we need 3-token look-ahead here in the worst case:
|
||||
// in "$x foo" we need to read "foo" (as opposed to ":=") to know that $x is an
|
||||
// argument variable rather than a declaration. So remember the token
|
||||
// adjacent to the variable so we can push it back if necessary.
|
||||
tokenAfterVariable := t.peek()
|
||||
if next := t.peekNonSpace(); next.typ == itemColonEquals || (next.typ == itemChar && next.val == ",") {
|
||||
t.nextNonSpace()
|
||||
variable := t.newVariable(v.pos, v.val)
|
||||
decl = append(decl, variable)
|
||||
t.vars = append(t.vars, v.val)
|
||||
if next.typ == itemChar && next.val == "," {
|
||||
if context == "range" && len(decl) < 2 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.errorf("too many declarations in %s", context)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if tokenAfterVariable.typ == itemSpace {
|
||||
t.backup3(v, tokenAfterVariable)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
t.backup2(v)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
pipe = t.newPipeline(pos, t.lex.lineNumber(), decl)
|
||||
for {
|
||||
switch token := t.nextNonSpace(); token.typ {
|
||||
case itemRightDelim, itemRightParen:
|
||||
if len(pipe.Cmds) == 0 {
|
||||
t.errorf("missing value for %s", context)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if token.typ == itemRightParen {
|
||||
t.backup()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
case itemBool, itemCharConstant, itemComplex, itemDot, itemField, itemIdentifier,
|
||||
itemNumber, itemNil, itemRawString, itemString, itemVariable, itemLeftParen:
|
||||
t.backup()
|
||||
pipe.append(t.command())
|
||||
default:
|
||||
t.unexpected(token, context)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Tree) parseControl(allowElseIf bool, context string) (pos Pos, line int, pipe *PipeNode, list, elseList *ListNode) {
|
||||
defer t.popVars(len(t.vars))
|
||||
line = t.lex.lineNumber()
|
||||
pipe = t.pipeline(context)
|
||||
var next Node
|
||||
list, next = t.itemList()
|
||||
switch next.Type() {
|
||||
case nodeEnd: //done
|
||||
case nodeElse:
|
||||
if allowElseIf {
|
||||
// Special case for "else if". If the "else" is followed immediately by an "if",
|
||||
// the elseControl will have left the "if" token pending. Treat
|
||||
// {{if a}}_{{else if b}}_{{end}}
|
||||
// as
|
||||
// {{if a}}_{{else}}{{if b}}_{{end}}{{end}}.
|
||||
// To do this, parse the if as usual and stop at it {{end}}; the subsequent{{end}}
|
||||
// is assumed. This technique works even for long if-else-if chains.
|
||||
// TODO: Should we allow else-if in with and range?
|
||||
if t.peek().typ == itemIf {
|
||||
t.next() // Consume the "if" token.
|
||||
elseList = t.newList(next.Position())
|
||||
elseList.append(t.ifControl())
|
||||
// Do not consume the next item - only one {{end}} required.
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
elseList, next = t.itemList()
|
||||
if next.Type() != nodeEnd {
|
||||
t.errorf("expected end; found %s", next)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return pipe.Position(), line, pipe, list, elseList
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If:
|
||||
// {{if pipeline}} itemList {{end}}
|
||||
// {{if pipeline}} itemList {{else}} itemList {{end}}
|
||||
// If keyword is past.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) ifControl() Node {
|
||||
return t.newIf(t.parseControl(true, "if"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Range:
|
||||
// {{range pipeline}} itemList {{end}}
|
||||
// {{range pipeline}} itemList {{else}} itemList {{end}}
|
||||
// Range keyword is past.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) rangeControl() Node {
|
||||
return t.newRange(t.parseControl(false, "range"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// With:
|
||||
// {{with pipeline}} itemList {{end}}
|
||||
// {{with pipeline}} itemList {{else}} itemList {{end}}
|
||||
// If keyword is past.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) withControl() Node {
|
||||
return t.newWith(t.parseControl(false, "with"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// End:
|
||||
// {{end}}
|
||||
// End keyword is past.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) endControl() Node {
|
||||
return t.newEnd(t.expect(itemRightDelim, "end").pos)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Else:
|
||||
// {{else}}
|
||||
// Else keyword is past.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) elseControl() Node {
|
||||
// Special case for "else if".
|
||||
peek := t.peekNonSpace()
|
||||
if peek.typ == itemIf {
|
||||
// We see "{{else if ... " but in effect rewrite it to {{else}}{{if ... ".
|
||||
return t.newElse(peek.pos, t.lex.lineNumber())
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t.newElse(t.expect(itemRightDelim, "else").pos, t.lex.lineNumber())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Template:
|
||||
// {{template stringValue pipeline}}
|
||||
// Template keyword is past. The name must be something that can evaluate
|
||||
// to a string.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) templateControl() Node {
|
||||
var name string
|
||||
token := t.nextNonSpace()
|
||||
switch token.typ {
|
||||
case itemString, itemRawString:
|
||||
s, err := strconv.Unquote(token.val)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
t.error(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
name = s
|
||||
default:
|
||||
t.unexpected(token, "template invocation")
|
||||
}
|
||||
var pipe *PipeNode
|
||||
if t.nextNonSpace().typ != itemRightDelim {
|
||||
t.backup()
|
||||
// Do not pop variables; they persist until "end".
|
||||
pipe = t.pipeline("template")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t.newTemplate(token.pos, t.lex.lineNumber(), name, pipe)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// command:
|
||||
// operand (space operand)*
|
||||
// space-separated arguments up to a pipeline character or right delimiter.
|
||||
// we consume the pipe character but leave the right delim to terminate the action.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) command() *CommandNode {
|
||||
cmd := t.newCommand(t.peekNonSpace().pos)
|
||||
for {
|
||||
t.peekNonSpace() // skip leading spaces.
|
||||
operand := t.operand()
|
||||
if operand != nil {
|
||||
cmd.append(operand)
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch token := t.next(); token.typ {
|
||||
case itemSpace:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
case itemError:
|
||||
t.errorf("%s", token.val)
|
||||
case itemRightDelim, itemRightParen:
|
||||
t.backup()
|
||||
case itemPipe:
|
||||
default:
|
||||
t.errorf("unexpected %s in operand; missing space?", token)
|
||||
}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(cmd.Args) == 0 {
|
||||
t.errorf("empty command")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return cmd
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// operand:
|
||||
// term .Field*
|
||||
// An operand is a space-separated component of a command,
|
||||
// a term possibly followed by field accesses.
|
||||
// A nil return means the next item is not an operand.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) operand() Node {
|
||||
node := t.term()
|
||||
if node == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t.peek().typ == itemField {
|
||||
chain := t.newChain(t.peek().pos, node)
|
||||
for t.peek().typ == itemField {
|
||||
chain.Add(t.next().val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Compatibility with original API: If the term is of type NodeField
|
||||
// or NodeVariable, just put more fields on the original.
|
||||
// Otherwise, keep the Chain node.
|
||||
// TODO: Switch to Chains always when we can.
|
||||
switch node.Type() {
|
||||
case NodeField:
|
||||
node = t.newField(chain.Position(), chain.String())
|
||||
case NodeVariable:
|
||||
node = t.newVariable(chain.Position(), chain.String())
|
||||
default:
|
||||
node = chain
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return node
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// term:
|
||||
// literal (number, string, nil, boolean)
|
||||
// function (identifier)
|
||||
// .
|
||||
// .Field
|
||||
// $
|
||||
// '(' pipeline ')'
|
||||
// A term is a simple "expression".
|
||||
// A nil return means the next item is not a term.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) term() Node {
|
||||
switch token := t.nextNonSpace(); token.typ {
|
||||
case itemError:
|
||||
t.errorf("%s", token.val)
|
||||
case itemIdentifier:
|
||||
if !t.hasFunction(token.val) {
|
||||
t.errorf("function %q not defined", token.val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return NewIdentifier(token.val).SetTree(t).SetPos(token.pos)
|
||||
case itemDot:
|
||||
return t.newDot(token.pos)
|
||||
case itemNil:
|
||||
return t.newNil(token.pos)
|
||||
case itemVariable:
|
||||
return t.useVar(token.pos, token.val)
|
||||
case itemField:
|
||||
return t.newField(token.pos, token.val)
|
||||
case itemBool:
|
||||
return t.newBool(token.pos, token.val == "true")
|
||||
case itemCharConstant, itemComplex, itemNumber:
|
||||
number, err := t.newNumber(token.pos, token.val, token.typ)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
t.error(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return number
|
||||
case itemLeftParen:
|
||||
pipe := t.pipeline("parenthesized pipeline")
|
||||
if token := t.next(); token.typ != itemRightParen {
|
||||
t.errorf("unclosed right paren: unexpected %s", token)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return pipe
|
||||
case itemString, itemRawString:
|
||||
s, err := strconv.Unquote(token.val)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
t.error(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t.newString(token.pos, token.val, s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.backup()
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// hasFunction reports if a function name exists in the Tree's maps.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) hasFunction(name string) bool {
|
||||
for _, funcMap := range t.funcs {
|
||||
if funcMap == nil {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if funcMap[name] != nil {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// popVars trims the variable list to the specified length
|
||||
func (t *Tree) popVars(n int) {
|
||||
t.vars = t.vars[:n]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// useVar returns a node for a variable reference. It errors if the
|
||||
// variable is not defined.
|
||||
func (t *Tree) useVar(pos Pos, name string) Node {
|
||||
v := t.newVariable(pos, name)
|
||||
for _, varName := range t.vars {
|
||||
if varName == v.Ident[0] {
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.errorf("undefined variable %q", v.Ident[0])
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
218
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/template.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
218
vendor/github.com/alecthomas/template/template.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,218 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package template
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/alecthomas/template/parse"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// common holds the information shared by related templates.
|
||||
type common struct {
|
||||
tmpl map[string]*Template
|
||||
// We use two maps, one for parsing and one for execution.
|
||||
// This separation makes the API cleaner since it doesn't
|
||||
// expose reflection to the client.
|
||||
parseFuncs FuncMap
|
||||
execFuncs map[string]reflect.Value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Template is the representation of a parsed template. The *parse.Tree
|
||||
// field is exported only for use by html/template and should be treated
|
||||
// as unexported by all other clients.
|
||||
type Template struct {
|
||||
name string
|
||||
*parse.Tree
|
||||
*common
|
||||
leftDelim string
|
||||
rightDelim string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// New allocates a new template with the given name.
|
||||
func New(name string) *Template {
|
||||
return &Template{
|
||||
name: name,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Name returns the name of the template.
|
||||
func (t *Template) Name() string {
|
||||
return t.name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// New allocates a new template associated with the given one and with the same
|
||||
// delimiters. The association, which is transitive, allows one template to
|
||||
// invoke another with a {{template}} action.
|
||||
func (t *Template) New(name string) *Template {
|
||||
t.init()
|
||||
return &Template{
|
||||
name: name,
|
||||
common: t.common,
|
||||
leftDelim: t.leftDelim,
|
||||
rightDelim: t.rightDelim,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Template) init() {
|
||||
if t.common == nil {
|
||||
t.common = new(common)
|
||||
t.tmpl = make(map[string]*Template)
|
||||
t.parseFuncs = make(FuncMap)
|
||||
t.execFuncs = make(map[string]reflect.Value)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a duplicate of the template, including all associated
|
||||
// templates. The actual representation is not copied, but the name space of
|
||||
// associated templates is, so further calls to Parse in the copy will add
|
||||
// templates to the copy but not to the original. Clone can be used to prepare
|
||||
// common templates and use them with variant definitions for other templates
|
||||
// by adding the variants after the clone is made.
|
||||
func (t *Template) Clone() (*Template, error) {
|
||||
nt := t.copy(nil)
|
||||
nt.init()
|
||||
nt.tmpl[t.name] = nt
|
||||
for k, v := range t.tmpl {
|
||||
if k == t.name { // Already installed.
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
// The associated templates share nt's common structure.
|
||||
tmpl := v.copy(nt.common)
|
||||
nt.tmpl[k] = tmpl
|
||||
}
|
||||
for k, v := range t.parseFuncs {
|
||||
nt.parseFuncs[k] = v
|
||||
}
|
||||
for k, v := range t.execFuncs {
|
||||
nt.execFuncs[k] = v
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nt, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// copy returns a shallow copy of t, with common set to the argument.
|
||||
func (t *Template) copy(c *common) *Template {
|
||||
nt := New(t.name)
|
||||
nt.Tree = t.Tree
|
||||
nt.common = c
|
||||
nt.leftDelim = t.leftDelim
|
||||
nt.rightDelim = t.rightDelim
|
||||
return nt
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddParseTree creates a new template with the name and parse tree
|
||||
// and associates it with t.
|
||||
func (t *Template) AddParseTree(name string, tree *parse.Tree) (*Template, error) {
|
||||
if t.common != nil && t.tmpl[name] != nil {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("template: redefinition of template %q", name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
nt := t.New(name)
|
||||
nt.Tree = tree
|
||||
t.tmpl[name] = nt
|
||||
return nt, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Templates returns a slice of the templates associated with t, including t
|
||||
// itself.
|
||||
func (t *Template) Templates() []*Template {
|
||||
if t.common == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Return a slice so we don't expose the map.
|
||||
m := make([]*Template, 0, len(t.tmpl))
|
||||
for _, v := range t.tmpl {
|
||||
m = append(m, v)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return m
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Delims sets the action delimiters to the specified strings, to be used in
|
||||
// subsequent calls to Parse, ParseFiles, or ParseGlob. Nested template
|
||||
// definitions will inherit the settings. An empty delimiter stands for the
|
||||
// corresponding default: {{ or }}.
|
||||
// The return value is the template, so calls can be chained.
|
||||
func (t *Template) Delims(left, right string) *Template {
|
||||
t.leftDelim = left
|
||||
t.rightDelim = right
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Funcs adds the elements of the argument map to the template's function map.
|
||||
// It panics if a value in the map is not a function with appropriate return
|
||||
// type. However, it is legal to overwrite elements of the map. The return
|
||||
// value is the template, so calls can be chained.
|
||||
func (t *Template) Funcs(funcMap FuncMap) *Template {
|
||||
t.init()
|
||||
addValueFuncs(t.execFuncs, funcMap)
|
||||
addFuncs(t.parseFuncs, funcMap)
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Lookup returns the template with the given name that is associated with t,
|
||||
// or nil if there is no such template.
|
||||
func (t *Template) Lookup(name string) *Template {
|
||||
if t.common == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t.tmpl[name]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse parses a string into a template. Nested template definitions will be
|
||||
// associated with the top-level template t. Parse may be called multiple times
|
||||
// to parse definitions of templates to associate with t. It is an error if a
|
||||
// resulting template is non-empty (contains content other than template
|
||||
// definitions) and would replace a non-empty template with the same name.
|
||||
// (In multiple calls to Parse with the same receiver template, only one call
|
||||
// can contain text other than space, comments, and template definitions.)
|
||||
func (t *Template) Parse(text string) (*Template, error) {
|
||||
t.init()
|
||||
trees, err := parse.Parse(t.name, text, t.leftDelim, t.rightDelim, t.parseFuncs, builtins)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Add the newly parsed trees, including the one for t, into our common structure.
|
||||
for name, tree := range trees {
|
||||
// If the name we parsed is the name of this template, overwrite this template.
|
||||
// The associate method checks it's not a redefinition.
|
||||
tmpl := t
|
||||
if name != t.name {
|
||||
tmpl = t.New(name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Even if t == tmpl, we need to install it in the common.tmpl map.
|
||||
if replace, err := t.associate(tmpl, tree); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
} else if replace {
|
||||
tmpl.Tree = tree
|
||||
}
|
||||
tmpl.leftDelim = t.leftDelim
|
||||
tmpl.rightDelim = t.rightDelim
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// associate installs the new template into the group of templates associated
|
||||
// with t. It is an error to reuse a name except to overwrite an empty
|
||||
// template. The two are already known to share the common structure.
|
||||
// The boolean return value reports wither to store this tree as t.Tree.
|
||||
func (t *Template) associate(new *Template, tree *parse.Tree) (bool, error) {
|
||||
if new.common != t.common {
|
||||
panic("internal error: associate not common")
|
||||
}
|
||||
name := new.name
|
||||
if old := t.tmpl[name]; old != nil {
|
||||
oldIsEmpty := parse.IsEmptyTree(old.Root)
|
||||
newIsEmpty := parse.IsEmptyTree(tree.Root)
|
||||
if newIsEmpty {
|
||||
// Whether old is empty or not, new is empty; no reason to replace old.
|
||||
return false, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !oldIsEmpty {
|
||||
return false, fmt.Errorf("template: redefinition of template %q", name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.tmpl[name] = new
|
||||
return true, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
20
vendor/github.com/ghodss/yaml/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
20
vendor/github.com/ghodss/yaml/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
# OSX leaves these everywhere on SMB shares
|
||||
._*
|
||||
|
||||
# Eclipse files
|
||||
.classpath
|
||||
.project
|
||||
.settings/**
|
||||
|
||||
# Emacs save files
|
||||
*~
|
||||
|
||||
# Vim-related files
|
||||
[._]*.s[a-w][a-z]
|
||||
[._]s[a-w][a-z]
|
||||
*.un~
|
||||
Session.vim
|
||||
.netrwhist
|
||||
|
||||
# Go test binaries
|
||||
*.test
|
||||
7
vendor/github.com/ghodss/yaml/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
7
vendor/github.com/ghodss/yaml/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
language: go
|
||||
go:
|
||||
- 1.3
|
||||
- 1.4
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- go test
|
||||
- go build
|
||||
50
vendor/github.com/ghodss/yaml/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
50
vendor/github.com/ghodss/yaml/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
The MIT License (MIT)
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2014 Sam Ghods
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2012 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
|
||||
met:
|
||||
|
||||
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
|
||||
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
|
||||
copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer
|
||||
in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
|
||||
distribution.
|
||||
* Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its
|
||||
contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
|
||||
this software without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
|
||||
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
"AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
|
||||
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
|
||||
OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
|
||||
SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
|
||||
LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
|
||||
DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
|
||||
THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
|
||||
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
|
||||
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
121
vendor/github.com/ghodss/yaml/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
121
vendor/github.com/ghodss/yaml/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
|
||||
# YAML marshaling and unmarshaling support for Go
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://travis-ci.org/ghodss/yaml)
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
A wrapper around [go-yaml](https://github.com/go-yaml/yaml) designed to enable a better way of handling YAML when marshaling to and from structs.
|
||||
|
||||
In short, this library first converts YAML to JSON using go-yaml and then uses `json.Marshal` and `json.Unmarshal` to convert to or from the struct. This means that it effectively reuses the JSON struct tags as well as the custom JSON methods `MarshalJSON` and `UnmarshalJSON` unlike go-yaml. For a detailed overview of the rationale behind this method, [see this blog post](http://ghodss.com/2014/the-right-way-to-handle-yaml-in-golang/).
|
||||
|
||||
## Compatibility
|
||||
|
||||
This package uses [go-yaml](https://github.com/go-yaml/yaml) and therefore supports [everything go-yaml supports](https://github.com/go-yaml/yaml#compatibility).
|
||||
|
||||
## Caveats
|
||||
|
||||
**Caveat #1:** When using `yaml.Marshal` and `yaml.Unmarshal`, binary data should NOT be preceded with the `!!binary` YAML tag. If you do, go-yaml will convert the binary data from base64 to native binary data, which is not compatible with JSON. You can still use binary in your YAML files though - just store them without the `!!binary` tag and decode the base64 in your code (e.g. in the custom JSON methods `MarshalJSON` and `UnmarshalJSON`). This also has the benefit that your YAML and your JSON binary data will be decoded exactly the same way. As an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
BAD:
|
||||
exampleKey: !!binary gIGC
|
||||
|
||||
GOOD:
|
||||
exampleKey: gIGC
|
||||
... and decode the base64 data in your code.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Caveat #2:** When using `YAMLToJSON` directly, maps with keys that are maps will result in an error since this is not supported by JSON. This error will occur in `Unmarshal` as well since you can't unmarshal map keys anyways since struct fields can't be keys.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation and usage
|
||||
|
||||
To install, run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ go get github.com/ghodss/yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And import using:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import "github.com/ghodss/yaml"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Usage is very similar to the JSON library:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/ghodss/yaml"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type Person struct {
|
||||
Name string `json:"name"` // Affects YAML field names too.
|
||||
Age int `json:"age"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
// Marshal a Person struct to YAML.
|
||||
p := Person{"John", 30}
|
||||
y, err := yaml.Marshal(p)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Printf("err: %v\n", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
fmt.Println(string(y))
|
||||
/* Output:
|
||||
age: 30
|
||||
name: John
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
// Unmarshal the YAML back into a Person struct.
|
||||
var p2 Person
|
||||
err = yaml.Unmarshal(y, &p2)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Printf("err: %v\n", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
fmt.Println(p2)
|
||||
/* Output:
|
||||
{John 30}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`yaml.YAMLToJSON` and `yaml.JSONToYAML` methods are also available:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/ghodss/yaml"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
j := []byte(`{"name": "John", "age": 30}`)
|
||||
y, err := yaml.JSONToYAML(j)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Printf("err: %v\n", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
fmt.Println(string(y))
|
||||
/* Output:
|
||||
name: John
|
||||
age: 30
|
||||
*/
|
||||
j2, err := yaml.YAMLToJSON(y)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Printf("err: %v\n", err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
fmt.Println(string(j2))
|
||||
/* Output:
|
||||
{"age":30,"name":"John"}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
501
vendor/github.com/ghodss/yaml/fields.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
501
vendor/github.com/ghodss/yaml/fields.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,501 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2013 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
package yaml
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"encoding"
|
||||
"encoding/json"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// indirect walks down v allocating pointers as needed,
|
||||
// until it gets to a non-pointer.
|
||||
// if it encounters an Unmarshaler, indirect stops and returns that.
|
||||
// if decodingNull is true, indirect stops at the last pointer so it can be set to nil.
|
||||
func indirect(v reflect.Value, decodingNull bool) (json.Unmarshaler, encoding.TextUnmarshaler, reflect.Value) {
|
||||
// If v is a named type and is addressable,
|
||||
// start with its address, so that if the type has pointer methods,
|
||||
// we find them.
|
||||
if v.Kind() != reflect.Ptr && v.Type().Name() != "" && v.CanAddr() {
|
||||
v = v.Addr()
|
||||
}
|
||||
for {
|
||||
// Load value from interface, but only if the result will be
|
||||
// usefully addressable.
|
||||
if v.Kind() == reflect.Interface && !v.IsNil() {
|
||||
e := v.Elem()
|
||||
if e.Kind() == reflect.Ptr && !e.IsNil() && (!decodingNull || e.Elem().Kind() == reflect.Ptr) {
|
||||
v = e
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if v.Kind() != reflect.Ptr {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if v.Elem().Kind() != reflect.Ptr && decodingNull && v.CanSet() {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if v.IsNil() {
|
||||
if v.CanSet() {
|
||||
v.Set(reflect.New(v.Type().Elem()))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
v = reflect.New(v.Type().Elem())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if v.Type().NumMethod() > 0 {
|
||||
if u, ok := v.Interface().(json.Unmarshaler); ok {
|
||||
return u, nil, reflect.Value{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if u, ok := v.Interface().(encoding.TextUnmarshaler); ok {
|
||||
return nil, u, reflect.Value{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
v = v.Elem()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, nil, v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A field represents a single field found in a struct.
|
||||
type field struct {
|
||||
name string
|
||||
nameBytes []byte // []byte(name)
|
||||
equalFold func(s, t []byte) bool // bytes.EqualFold or equivalent
|
||||
|
||||
tag bool
|
||||
index []int
|
||||
typ reflect.Type
|
||||
omitEmpty bool
|
||||
quoted bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func fillField(f field) field {
|
||||
f.nameBytes = []byte(f.name)
|
||||
f.equalFold = foldFunc(f.nameBytes)
|
||||
return f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// byName sorts field by name, breaking ties with depth,
|
||||
// then breaking ties with "name came from json tag", then
|
||||
// breaking ties with index sequence.
|
||||
type byName []field
|
||||
|
||||
func (x byName) Len() int { return len(x) }
|
||||
|
||||
func (x byName) Swap(i, j int) { x[i], x[j] = x[j], x[i] }
|
||||
|
||||
func (x byName) Less(i, j int) bool {
|
||||
if x[i].name != x[j].name {
|
||||
return x[i].name < x[j].name
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(x[i].index) != len(x[j].index) {
|
||||
return len(x[i].index) < len(x[j].index)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if x[i].tag != x[j].tag {
|
||||
return x[i].tag
|
||||
}
|
||||
return byIndex(x).Less(i, j)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// byIndex sorts field by index sequence.
|
||||
type byIndex []field
|
||||
|
||||
func (x byIndex) Len() int { return len(x) }
|
||||
|
||||
func (x byIndex) Swap(i, j int) { x[i], x[j] = x[j], x[i] }
|
||||
|
||||
func (x byIndex) Less(i, j int) bool {
|
||||
for k, xik := range x[i].index {
|
||||
if k >= len(x[j].index) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if xik != x[j].index[k] {
|
||||
return xik < x[j].index[k]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return len(x[i].index) < len(x[j].index)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// typeFields returns a list of fields that JSON should recognize for the given type.
|
||||
// The algorithm is breadth-first search over the set of structs to include - the top struct
|
||||
// and then any reachable anonymous structs.
|
||||
func typeFields(t reflect.Type) []field {
|
||||
// Anonymous fields to explore at the current level and the next.
|
||||
current := []field{}
|
||||
next := []field{{typ: t}}
|
||||
|
||||
// Count of queued names for current level and the next.
|
||||
count := map[reflect.Type]int{}
|
||||
nextCount := map[reflect.Type]int{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Types already visited at an earlier level.
|
||||
visited := map[reflect.Type]bool{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fields found.
|
||||
var fields []field
|
||||
|
||||
for len(next) > 0 {
|
||||
current, next = next, current[:0]
|
||||
count, nextCount = nextCount, map[reflect.Type]int{}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, f := range current {
|
||||
if visited[f.typ] {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
visited[f.typ] = true
|
||||
|
||||
// Scan f.typ for fields to include.
|
||||
for i := 0; i < f.typ.NumField(); i++ {
|
||||
sf := f.typ.Field(i)
|
||||
if sf.PkgPath != "" { // unexported
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
tag := sf.Tag.Get("json")
|
||||
if tag == "-" {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
name, opts := parseTag(tag)
|
||||
if !isValidTag(name) {
|
||||
name = ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
index := make([]int, len(f.index)+1)
|
||||
copy(index, f.index)
|
||||
index[len(f.index)] = i
|
||||
|
||||
ft := sf.Type
|
||||
if ft.Name() == "" && ft.Kind() == reflect.Ptr {
|
||||
// Follow pointer.
|
||||
ft = ft.Elem()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Record found field and index sequence.
|
||||
if name != "" || !sf.Anonymous || ft.Kind() != reflect.Struct {
|
||||
tagged := name != ""
|
||||
if name == "" {
|
||||
name = sf.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
fields = append(fields, fillField(field{
|
||||
name: name,
|
||||
tag: tagged,
|
||||
index: index,
|
||||
typ: ft,
|
||||
omitEmpty: opts.Contains("omitempty"),
|
||||
quoted: opts.Contains("string"),
|
||||
}))
|
||||
if count[f.typ] > 1 {
|
||||
// If there were multiple instances, add a second,
|
||||
// so that the annihilation code will see a duplicate.
|
||||
// It only cares about the distinction between 1 or 2,
|
||||
// so don't bother generating any more copies.
|
||||
fields = append(fields, fields[len(fields)-1])
|
||||
}
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Record new anonymous struct to explore in next round.
|
||||
nextCount[ft]++
|
||||
if nextCount[ft] == 1 {
|
||||
next = append(next, fillField(field{name: ft.Name(), index: index, typ: ft}))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sort.Sort(byName(fields))
|
||||
|
||||
// Delete all fields that are hidden by the Go rules for embedded fields,
|
||||
// except that fields with JSON tags are promoted.
|
||||
|
||||
// The fields are sorted in primary order of name, secondary order
|
||||
// of field index length. Loop over names; for each name, delete
|
||||
// hidden fields by choosing the one dominant field that survives.
|
||||
out := fields[:0]
|
||||
for advance, i := 0, 0; i < len(fields); i += advance {
|
||||
// One iteration per name.
|
||||
// Find the sequence of fields with the name of this first field.
|
||||
fi := fields[i]
|
||||
name := fi.name
|
||||
for advance = 1; i+advance < len(fields); advance++ {
|
||||
fj := fields[i+advance]
|
||||
if fj.name != name {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if advance == 1 { // Only one field with this name
|
||||
out = append(out, fi)
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
dominant, ok := dominantField(fields[i : i+advance])
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
out = append(out, dominant)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fields = out
|
||||
sort.Sort(byIndex(fields))
|
||||
|
||||
return fields
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// dominantField looks through the fields, all of which are known to
|
||||
// have the same name, to find the single field that dominates the
|
||||
// others using Go's embedding rules, modified by the presence of
|
||||
// JSON tags. If there are multiple top-level fields, the boolean
|
||||
// will be false: This condition is an error in Go and we skip all
|
||||
// the fields.
|
||||
func dominantField(fields []field) (field, bool) {
|
||||
// The fields are sorted in increasing index-length order. The winner
|
||||
// must therefore be one with the shortest index length. Drop all
|
||||
// longer entries, which is easy: just truncate the slice.
|
||||
length := len(fields[0].index)
|
||||
tagged := -1 // Index of first tagged field.
|
||||
for i, f := range fields {
|
||||
if len(f.index) > length {
|
||||
fields = fields[:i]
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if f.tag {
|
||||
if tagged >= 0 {
|
||||
// Multiple tagged fields at the same level: conflict.
|
||||
// Return no field.
|
||||
return field{}, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
tagged = i
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if tagged >= 0 {
|
||||
return fields[tagged], true
|
||||
}
|
||||
// All remaining fields have the same length. If there's more than one,
|
||||
// we have a conflict (two fields named "X" at the same level) and we
|
||||
// return no field.
|
||||
if len(fields) > 1 {
|
||||
return field{}, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fields[0], true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var fieldCache struct {
|
||||
sync.RWMutex
|
||||
m map[reflect.Type][]field
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// cachedTypeFields is like typeFields but uses a cache to avoid repeated work.
|
||||
func cachedTypeFields(t reflect.Type) []field {
|
||||
fieldCache.RLock()
|
||||
f := fieldCache.m[t]
|
||||
fieldCache.RUnlock()
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
return f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Compute fields without lock.
|
||||
// Might duplicate effort but won't hold other computations back.
|
||||
f = typeFields(t)
|
||||
if f == nil {
|
||||
f = []field{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fieldCache.Lock()
|
||||
if fieldCache.m == nil {
|
||||
fieldCache.m = map[reflect.Type][]field{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
fieldCache.m[t] = f
|
||||
fieldCache.Unlock()
|
||||
return f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func isValidTag(s string) bool {
|
||||
if s == "" {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, c := range s {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case strings.ContainsRune("!#$%&()*+-./:<=>?@[]^_{|}~ ", c):
|
||||
// Backslash and quote chars are reserved, but
|
||||
// otherwise any punctuation chars are allowed
|
||||
// in a tag name.
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if !unicode.IsLetter(c) && !unicode.IsDigit(c) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
caseMask = ^byte(0x20) // Mask to ignore case in ASCII.
|
||||
kelvin = '\u212a'
|
||||
smallLongEss = '\u017f'
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// foldFunc returns one of four different case folding equivalence
|
||||
// functions, from most general (and slow) to fastest:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 1) bytes.EqualFold, if the key s contains any non-ASCII UTF-8
|
||||
// 2) equalFoldRight, if s contains special folding ASCII ('k', 'K', 's', 'S')
|
||||
// 3) asciiEqualFold, no special, but includes non-letters (including _)
|
||||
// 4) simpleLetterEqualFold, no specials, no non-letters.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The letters S and K are special because they map to 3 runes, not just 2:
|
||||
// * S maps to s and to U+017F 'ſ' Latin small letter long s
|
||||
// * k maps to K and to U+212A 'K' Kelvin sign
|
||||
// See http://play.golang.org/p/tTxjOc0OGo
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The returned function is specialized for matching against s and
|
||||
// should only be given s. It's not curried for performance reasons.
|
||||
func foldFunc(s []byte) func(s, t []byte) bool {
|
||||
nonLetter := false
|
||||
special := false // special letter
|
||||
for _, b := range s {
|
||||
if b >= utf8.RuneSelf {
|
||||
return bytes.EqualFold
|
||||
}
|
||||
upper := b & caseMask
|
||||
if upper < 'A' || upper > 'Z' {
|
||||
nonLetter = true
|
||||
} else if upper == 'K' || upper == 'S' {
|
||||
// See above for why these letters are special.
|
||||
special = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if special {
|
||||
return equalFoldRight
|
||||
}
|
||||
if nonLetter {
|
||||
return asciiEqualFold
|
||||
}
|
||||
return simpleLetterEqualFold
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// equalFoldRight is a specialization of bytes.EqualFold when s is
|
||||
// known to be all ASCII (including punctuation), but contains an 's',
|
||||
// 'S', 'k', or 'K', requiring a Unicode fold on the bytes in t.
|
||||
// See comments on foldFunc.
|
||||
func equalFoldRight(s, t []byte) bool {
|
||||
for _, sb := range s {
|
||||
if len(t) == 0 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
tb := t[0]
|
||||
if tb < utf8.RuneSelf {
|
||||
if sb != tb {
|
||||
sbUpper := sb & caseMask
|
||||
if 'A' <= sbUpper && sbUpper <= 'Z' {
|
||||
if sbUpper != tb&caseMask {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
t = t[1:]
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
// sb is ASCII and t is not. t must be either kelvin
|
||||
// sign or long s; sb must be s, S, k, or K.
|
||||
tr, size := utf8.DecodeRune(t)
|
||||
switch sb {
|
||||
case 's', 'S':
|
||||
if tr != smallLongEss {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
case 'k', 'K':
|
||||
if tr != kelvin {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
t = t[size:]
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(t) > 0 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// asciiEqualFold is a specialization of bytes.EqualFold for use when
|
||||
// s is all ASCII (but may contain non-letters) and contains no
|
||||
// special-folding letters.
|
||||
// See comments on foldFunc.
|
||||
func asciiEqualFold(s, t []byte) bool {
|
||||
if len(s) != len(t) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i, sb := range s {
|
||||
tb := t[i]
|
||||
if sb == tb {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ('a' <= sb && sb <= 'z') || ('A' <= sb && sb <= 'Z') {
|
||||
if sb&caseMask != tb&caseMask {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// simpleLetterEqualFold is a specialization of bytes.EqualFold for
|
||||
// use when s is all ASCII letters (no underscores, etc) and also
|
||||
// doesn't contain 'k', 'K', 's', or 'S'.
|
||||
// See comments on foldFunc.
|
||||
func simpleLetterEqualFold(s, t []byte) bool {
|
||||
if len(s) != len(t) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i, b := range s {
|
||||
if b&caseMask != t[i]&caseMask {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// tagOptions is the string following a comma in a struct field's "json"
|
||||
// tag, or the empty string. It does not include the leading comma.
|
||||
type tagOptions string
|
||||
|
||||
// parseTag splits a struct field's json tag into its name and
|
||||
// comma-separated options.
|
||||
func parseTag(tag string) (string, tagOptions) {
|
||||
if idx := strings.Index(tag, ","); idx != -1 {
|
||||
return tag[:idx], tagOptions(tag[idx+1:])
|
||||
}
|
||||
return tag, tagOptions("")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Contains reports whether a comma-separated list of options
|
||||
// contains a particular substr flag. substr must be surrounded by a
|
||||
// string boundary or commas.
|
||||
func (o tagOptions) Contains(optionName string) bool {
|
||||
if len(o) == 0 {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
s := string(o)
|
||||
for s != "" {
|
||||
var next string
|
||||
i := strings.Index(s, ",")
|
||||
if i >= 0 {
|
||||
s, next = s[:i], s[i+1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s == optionName {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
s = next
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
277
vendor/github.com/ghodss/yaml/yaml.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
277
vendor/github.com/ghodss/yaml/yaml.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,277 @@
|
||||
package yaml
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"encoding/json"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
"gopkg.in/yaml.v2"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Marshals the object into JSON then converts JSON to YAML and returns the
|
||||
// YAML.
|
||||
func Marshal(o interface{}) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
j, err := json.Marshal(o)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error marshaling into JSON: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
y, err := JSONToYAML(j)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error converting JSON to YAML: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return y, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Converts YAML to JSON then uses JSON to unmarshal into an object.
|
||||
func Unmarshal(y []byte, o interface{}) error {
|
||||
vo := reflect.ValueOf(o)
|
||||
j, err := yamlToJSON(y, &vo)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error converting YAML to JSON: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
err = json.Unmarshal(j, o)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("error unmarshaling JSON: %v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Convert JSON to YAML.
|
||||
func JSONToYAML(j []byte) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
// Convert the JSON to an object.
|
||||
var jsonObj interface{}
|
||||
// We are using yaml.Unmarshal here (instead of json.Unmarshal) because the
|
||||
// Go JSON library doesn't try to pick the right number type (int, float,
|
||||
// etc.) when unmarshalling to interface{}, it just picks float64
|
||||
// universally. go-yaml does go through the effort of picking the right
|
||||
// number type, so we can preserve number type throughout this process.
|
||||
err := yaml.Unmarshal(j, &jsonObj)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Marshal this object into YAML.
|
||||
return yaml.Marshal(jsonObj)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Convert YAML to JSON. Since JSON is a subset of YAML, passing JSON through
|
||||
// this method should be a no-op.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Things YAML can do that are not supported by JSON:
|
||||
// * In YAML you can have binary and null keys in your maps. These are invalid
|
||||
// in JSON. (int and float keys are converted to strings.)
|
||||
// * Binary data in YAML with the !!binary tag is not supported. If you want to
|
||||
// use binary data with this library, encode the data as base64 as usual but do
|
||||
// not use the !!binary tag in your YAML. This will ensure the original base64
|
||||
// encoded data makes it all the way through to the JSON.
|
||||
func YAMLToJSON(y []byte) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
return yamlToJSON(y, nil)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func yamlToJSON(y []byte, jsonTarget *reflect.Value) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
// Convert the YAML to an object.
|
||||
var yamlObj interface{}
|
||||
err := yaml.Unmarshal(y, &yamlObj)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// YAML objects are not completely compatible with JSON objects (e.g. you
|
||||
// can have non-string keys in YAML). So, convert the YAML-compatible object
|
||||
// to a JSON-compatible object, failing with an error if irrecoverable
|
||||
// incompatibilties happen along the way.
|
||||
jsonObj, err := convertToJSONableObject(yamlObj, jsonTarget)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Convert this object to JSON and return the data.
|
||||
return json.Marshal(jsonObj)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func convertToJSONableObject(yamlObj interface{}, jsonTarget *reflect.Value) (interface{}, error) {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
|
||||
// Resolve jsonTarget to a concrete value (i.e. not a pointer or an
|
||||
// interface). We pass decodingNull as false because we're not actually
|
||||
// decoding into the value, we're just checking if the ultimate target is a
|
||||
// string.
|
||||
if jsonTarget != nil {
|
||||
ju, tu, pv := indirect(*jsonTarget, false)
|
||||
// We have a JSON or Text Umarshaler at this level, so we can't be trying
|
||||
// to decode into a string.
|
||||
if ju != nil || tu != nil {
|
||||
jsonTarget = nil
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
jsonTarget = &pv
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If yamlObj is a number or a boolean, check if jsonTarget is a string -
|
||||
// if so, coerce. Else return normal.
|
||||
// If yamlObj is a map or array, find the field that each key is
|
||||
// unmarshaling to, and when you recurse pass the reflect.Value for that
|
||||
// field back into this function.
|
||||
switch typedYAMLObj := yamlObj.(type) {
|
||||
case map[interface{}]interface{}:
|
||||
// JSON does not support arbitrary keys in a map, so we must convert
|
||||
// these keys to strings.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// From my reading of go-yaml v2 (specifically the resolve function),
|
||||
// keys can only have the types string, int, int64, float64, binary
|
||||
// (unsupported), or null (unsupported).
|
||||
strMap := make(map[string]interface{})
|
||||
for k, v := range typedYAMLObj {
|
||||
// Resolve the key to a string first.
|
||||
var keyString string
|
||||
switch typedKey := k.(type) {
|
||||
case string:
|
||||
keyString = typedKey
|
||||
case int:
|
||||
keyString = strconv.Itoa(typedKey)
|
||||
case int64:
|
||||
// go-yaml will only return an int64 as a key if the system
|
||||
// architecture is 32-bit and the key's value is between 32-bit
|
||||
// and 64-bit. Otherwise the key type will simply be int.
|
||||
keyString = strconv.FormatInt(typedKey, 10)
|
||||
case float64:
|
||||
// Stolen from go-yaml to use the same conversion to string as
|
||||
// the go-yaml library uses to convert float to string when
|
||||
// Marshaling.
|
||||
s := strconv.FormatFloat(typedKey, 'g', -1, 32)
|
||||
switch s {
|
||||
case "+Inf":
|
||||
s = ".inf"
|
||||
case "-Inf":
|
||||
s = "-.inf"
|
||||
case "NaN":
|
||||
s = ".nan"
|
||||
}
|
||||
keyString = s
|
||||
case bool:
|
||||
if typedKey {
|
||||
keyString = "true"
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
keyString = "false"
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Unsupported map key of type: %s, key: %+#v, value: %+#v",
|
||||
reflect.TypeOf(k), k, v)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// jsonTarget should be a struct or a map. If it's a struct, find
|
||||
// the field it's going to map to and pass its reflect.Value. If
|
||||
// it's a map, find the element type of the map and pass the
|
||||
// reflect.Value created from that type. If it's neither, just pass
|
||||
// nil - JSON conversion will error for us if it's a real issue.
|
||||
if jsonTarget != nil {
|
||||
t := *jsonTarget
|
||||
if t.Kind() == reflect.Struct {
|
||||
keyBytes := []byte(keyString)
|
||||
// Find the field that the JSON library would use.
|
||||
var f *field
|
||||
fields := cachedTypeFields(t.Type())
|
||||
for i := range fields {
|
||||
ff := &fields[i]
|
||||
if bytes.Equal(ff.nameBytes, keyBytes) {
|
||||
f = ff
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Do case-insensitive comparison.
|
||||
if f == nil && ff.equalFold(ff.nameBytes, keyBytes) {
|
||||
f = ff
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
// Find the reflect.Value of the most preferential
|
||||
// struct field.
|
||||
jtf := t.Field(f.index[0])
|
||||
strMap[keyString], err = convertToJSONableObject(v, &jtf)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if t.Kind() == reflect.Map {
|
||||
// Create a zero value of the map's element type to use as
|
||||
// the JSON target.
|
||||
jtv := reflect.Zero(t.Type().Elem())
|
||||
strMap[keyString], err = convertToJSONableObject(v, &jtv)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
strMap[keyString], err = convertToJSONableObject(v, nil)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return strMap, nil
|
||||
case []interface{}:
|
||||
// We need to recurse into arrays in case there are any
|
||||
// map[interface{}]interface{}'s inside and to convert any
|
||||
// numbers to strings.
|
||||
|
||||
// If jsonTarget is a slice (which it really should be), find the
|
||||
// thing it's going to map to. If it's not a slice, just pass nil
|
||||
// - JSON conversion will error for us if it's a real issue.
|
||||
var jsonSliceElemValue *reflect.Value
|
||||
if jsonTarget != nil {
|
||||
t := *jsonTarget
|
||||
if t.Kind() == reflect.Slice {
|
||||
// By default slices point to nil, but we need a reflect.Value
|
||||
// pointing to a value of the slice type, so we create one here.
|
||||
ev := reflect.Indirect(reflect.New(t.Type().Elem()))
|
||||
jsonSliceElemValue = &ev
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Make and use a new array.
|
||||
arr := make([]interface{}, len(typedYAMLObj))
|
||||
for i, v := range typedYAMLObj {
|
||||
arr[i], err = convertToJSONableObject(v, jsonSliceElemValue)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return arr, nil
|
||||
default:
|
||||
// If the target type is a string and the YAML type is a number,
|
||||
// convert the YAML type to a string.
|
||||
if jsonTarget != nil && (*jsonTarget).Kind() == reflect.String {
|
||||
// Based on my reading of go-yaml, it may return int, int64,
|
||||
// float64, or uint64.
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
switch typedVal := typedYAMLObj.(type) {
|
||||
case int:
|
||||
s = strconv.FormatInt(int64(typedVal), 10)
|
||||
case int64:
|
||||
s = strconv.FormatInt(typedVal, 10)
|
||||
case float64:
|
||||
s = strconv.FormatFloat(typedVal, 'g', -1, 32)
|
||||
case uint64:
|
||||
s = strconv.FormatUint(typedVal, 10)
|
||||
case bool:
|
||||
if typedVal {
|
||||
s = "true"
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
s = "false"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(s) > 0 {
|
||||
yamlObj = interface{}(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return yamlObj, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
24
vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
24
vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
||||
# Compiled Object files, Static and Dynamic libs (Shared Objects)
|
||||
*.o
|
||||
*.a
|
||||
*.so
|
||||
|
||||
# Folders
|
||||
_obj
|
||||
_test
|
||||
|
||||
# Architecture specific extensions/prefixes
|
||||
*.[568vq]
|
||||
[568vq].out
|
||||
|
||||
*.cgo1.go
|
||||
*.cgo2.c
|
||||
_cgo_defun.c
|
||||
_cgo_gotypes.go
|
||||
_cgo_export.*
|
||||
|
||||
_testmain.go
|
||||
|
||||
*.exe
|
||||
*.test
|
||||
*.prof
|
||||
11
vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
11
vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
language: go
|
||||
go_import_path: github.com/pkg/errors
|
||||
go:
|
||||
- 1.4.3
|
||||
- 1.5.4
|
||||
- 1.6.2
|
||||
- 1.7.1
|
||||
- tip
|
||||
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- go test -v ./...
|
||||
23
vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
23
vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2015, Dave Cheney <dave@cheney.net>
|
||||
All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
|
||||
|
||||
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this
|
||||
list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
|
||||
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
|
||||
this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
|
||||
and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
|
||||
AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
|
||||
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
|
||||
DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
|
||||
FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
|
||||
DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
|
||||
SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
|
||||
CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY,
|
||||
OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
|
||||
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
52
vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
52
vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
# errors [](https://travis-ci.org/pkg/errors) [](https://ci.appveyor.com/project/davecheney/errors/branch/master) [](http://godoc.org/github.com/pkg/errors) [](https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/pkg/errors)
|
||||
|
||||
Package errors provides simple error handling primitives.
|
||||
|
||||
`go get github.com/pkg/errors`
|
||||
|
||||
The traditional error handling idiom in Go is roughly akin to
|
||||
```go
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
which applied recursively up the call stack results in error reports without context or debugging information. The errors package allows programmers to add context to the failure path in their code in a way that does not destroy the original value of the error.
|
||||
|
||||
## Adding context to an error
|
||||
|
||||
The errors.Wrap function returns a new error that adds context to the original error. For example
|
||||
```go
|
||||
_, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return errors.Wrap(err, "read failed")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Retrieving the cause of an error
|
||||
|
||||
Using `errors.Wrap` constructs a stack of errors, adding context to the preceding error. Depending on the nature of the error it may be necessary to reverse the operation of errors.Wrap to retrieve the original error for inspection. Any error value which implements this interface can be inspected by `errors.Cause`.
|
||||
```go
|
||||
type causer interface {
|
||||
Cause() error
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
`errors.Cause` will recursively retrieve the topmost error which does not implement `causer`, which is assumed to be the original cause. For example:
|
||||
```go
|
||||
switch err := errors.Cause(err).(type) {
|
||||
case *MyError:
|
||||
// handle specifically
|
||||
default:
|
||||
// unknown error
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[Read the package documentation for more information](https://godoc.org/github.com/pkg/errors).
|
||||
|
||||
## Contributing
|
||||
|
||||
We welcome pull requests, bug fixes and issue reports. With that said, the bar for adding new symbols to this package is intentionally set high.
|
||||
|
||||
Before proposing a change, please discuss your change by raising an issue.
|
||||
|
||||
## Licence
|
||||
|
||||
BSD-2-Clause
|
||||
32
vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/appveyor.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
32
vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/appveyor.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
version: build-{build}.{branch}
|
||||
|
||||
clone_folder: C:\gopath\src\github.com\pkg\errors
|
||||
shallow_clone: true # for startup speed
|
||||
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
GOPATH: C:\gopath
|
||||
|
||||
platform:
|
||||
- x64
|
||||
|
||||
# http://www.appveyor.com/docs/installed-software
|
||||
install:
|
||||
# some helpful output for debugging builds
|
||||
- go version
|
||||
- go env
|
||||
# pre-installed MinGW at C:\MinGW is 32bit only
|
||||
# but MSYS2 at C:\msys64 has mingw64
|
||||
- set PATH=C:\msys64\mingw64\bin;%PATH%
|
||||
- gcc --version
|
||||
- g++ --version
|
||||
|
||||
build_script:
|
||||
- go install -v ./...
|
||||
|
||||
test_script:
|
||||
- set PATH=C:\gopath\bin;%PATH%
|
||||
- go test -v ./...
|
||||
|
||||
#artifacts:
|
||||
# - path: '%GOPATH%\bin\*.exe'
|
||||
deploy: off
|
||||
269
vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/errors.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
269
vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/errors.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,269 @@
|
||||
// Package errors provides simple error handling primitives.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The traditional error handling idiom in Go is roughly akin to
|
||||
//
|
||||
// if err != nil {
|
||||
// return err
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// which applied recursively up the call stack results in error reports
|
||||
// without context or debugging information. The errors package allows
|
||||
// programmers to add context to the failure path in their code in a way
|
||||
// that does not destroy the original value of the error.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Adding context to an error
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The errors.Wrap function returns a new error that adds context to the
|
||||
// original error by recording a stack trace at the point Wrap is called,
|
||||
// and the supplied message. For example
|
||||
//
|
||||
// _, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r)
|
||||
// if err != nil {
|
||||
// return errors.Wrap(err, "read failed")
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If additional control is required the errors.WithStack and errors.WithMessage
|
||||
// functions destructure errors.Wrap into its component operations of annotating
|
||||
// an error with a stack trace and an a message, respectively.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Retrieving the cause of an error
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Using errors.Wrap constructs a stack of errors, adding context to the
|
||||
// preceding error. Depending on the nature of the error it may be necessary
|
||||
// to reverse the operation of errors.Wrap to retrieve the original error
|
||||
// for inspection. Any error value which implements this interface
|
||||
//
|
||||
// type causer interface {
|
||||
// Cause() error
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// can be inspected by errors.Cause. errors.Cause will recursively retrieve
|
||||
// the topmost error which does not implement causer, which is assumed to be
|
||||
// the original cause. For example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// switch err := errors.Cause(err).(type) {
|
||||
// case *MyError:
|
||||
// // handle specifically
|
||||
// default:
|
||||
// // unknown error
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// causer interface is not exported by this package, but is considered a part
|
||||
// of stable public API.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Formatted printing of errors
|
||||
//
|
||||
// All error values returned from this package implement fmt.Formatter and can
|
||||
// be formatted by the fmt package. The following verbs are supported
|
||||
//
|
||||
// %s print the error. If the error has a Cause it will be
|
||||
// printed recursively
|
||||
// %v see %s
|
||||
// %+v extended format. Each Frame of the error's StackTrace will
|
||||
// be printed in detail.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Retrieving the stack trace of an error or wrapper
|
||||
//
|
||||
// New, Errorf, Wrap, and Wrapf record a stack trace at the point they are
|
||||
// invoked. This information can be retrieved with the following interface.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// type stackTracer interface {
|
||||
// StackTrace() errors.StackTrace
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where errors.StackTrace is defined as
|
||||
//
|
||||
// type StackTrace []Frame
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The Frame type represents a call site in the stack trace. Frame supports
|
||||
// the fmt.Formatter interface that can be used for printing information about
|
||||
// the stack trace of this error. For example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// if err, ok := err.(stackTracer); ok {
|
||||
// for _, f := range err.StackTrace() {
|
||||
// fmt.Printf("%+s:%d", f)
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// stackTracer interface is not exported by this package, but is considered a part
|
||||
// of stable public API.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See the documentation for Frame.Format for more details.
|
||||
package errors
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// New returns an error with the supplied message.
|
||||
// New also records the stack trace at the point it was called.
|
||||
func New(message string) error {
|
||||
return &fundamental{
|
||||
msg: message,
|
||||
stack: callers(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Errorf formats according to a format specifier and returns the string
|
||||
// as a value that satisfies error.
|
||||
// Errorf also records the stack trace at the point it was called.
|
||||
func Errorf(format string, args ...interface{}) error {
|
||||
return &fundamental{
|
||||
msg: fmt.Sprintf(format, args...),
|
||||
stack: callers(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// fundamental is an error that has a message and a stack, but no caller.
|
||||
type fundamental struct {
|
||||
msg string
|
||||
*stack
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *fundamental) Error() string { return f.msg }
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *fundamental) Format(s fmt.State, verb rune) {
|
||||
switch verb {
|
||||
case 'v':
|
||||
if s.Flag('+') {
|
||||
io.WriteString(s, f.msg)
|
||||
f.stack.Format(s, verb)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case 's':
|
||||
io.WriteString(s, f.msg)
|
||||
case 'q':
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(s, "%q", f.msg)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithStack annotates err with a stack trace at the point WithStack was called.
|
||||
// If err is nil, WithStack returns nil.
|
||||
func WithStack(err error) error {
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return &withStack{
|
||||
err,
|
||||
callers(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type withStack struct {
|
||||
error
|
||||
*stack
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *withStack) Cause() error { return w.error }
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *withStack) Format(s fmt.State, verb rune) {
|
||||
switch verb {
|
||||
case 'v':
|
||||
if s.Flag('+') {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(s, "%+v", w.Cause())
|
||||
w.stack.Format(s, verb)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case 's':
|
||||
io.WriteString(s, w.Error())
|
||||
case 'q':
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(s, "%q", w.Error())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Wrap returns an error annotating err with a stack trace
|
||||
// at the point Wrap is called, and the supplied message.
|
||||
// If err is nil, Wrap returns nil.
|
||||
func Wrap(err error, message string) error {
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
err = &withMessage{
|
||||
cause: err,
|
||||
msg: message,
|
||||
}
|
||||
return &withStack{
|
||||
err,
|
||||
callers(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Wrapf returns an error annotating err with a stack trace
|
||||
// at the point Wrapf is call, and the format specifier.
|
||||
// If err is nil, Wrapf returns nil.
|
||||
func Wrapf(err error, format string, args ...interface{}) error {
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
err = &withMessage{
|
||||
cause: err,
|
||||
msg: fmt.Sprintf(format, args...),
|
||||
}
|
||||
return &withStack{
|
||||
err,
|
||||
callers(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithMessage annotates err with a new message.
|
||||
// If err is nil, WithMessage returns nil.
|
||||
func WithMessage(err error, message string) error {
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return &withMessage{
|
||||
cause: err,
|
||||
msg: message,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type withMessage struct {
|
||||
cause error
|
||||
msg string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *withMessage) Error() string { return w.msg + ": " + w.cause.Error() }
|
||||
func (w *withMessage) Cause() error { return w.cause }
|
||||
|
||||
func (w *withMessage) Format(s fmt.State, verb rune) {
|
||||
switch verb {
|
||||
case 'v':
|
||||
if s.Flag('+') {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(s, "%+v\n", w.Cause())
|
||||
io.WriteString(s, w.msg)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case 's', 'q':
|
||||
io.WriteString(s, w.Error())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Cause returns the underlying cause of the error, if possible.
|
||||
// An error value has a cause if it implements the following
|
||||
// interface:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// type causer interface {
|
||||
// Cause() error
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the error does not implement Cause, the original error will
|
||||
// be returned. If the error is nil, nil will be returned without further
|
||||
// investigation.
|
||||
func Cause(err error) error {
|
||||
type causer interface {
|
||||
Cause() error
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for err != nil {
|
||||
cause, ok := err.(causer)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
err = cause.Cause()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
178
vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/stack.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
178
vendor/github.com/pkg/errors/stack.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,178 @@
|
||||
package errors
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"path"
|
||||
"runtime"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Frame represents a program counter inside a stack frame.
|
||||
type Frame uintptr
|
||||
|
||||
// pc returns the program counter for this frame;
|
||||
// multiple frames may have the same PC value.
|
||||
func (f Frame) pc() uintptr { return uintptr(f) - 1 }
|
||||
|
||||
// file returns the full path to the file that contains the
|
||||
// function for this Frame's pc.
|
||||
func (f Frame) file() string {
|
||||
fn := runtime.FuncForPC(f.pc())
|
||||
if fn == nil {
|
||||
return "unknown"
|
||||
}
|
||||
file, _ := fn.FileLine(f.pc())
|
||||
return file
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// line returns the line number of source code of the
|
||||
// function for this Frame's pc.
|
||||
func (f Frame) line() int {
|
||||
fn := runtime.FuncForPC(f.pc())
|
||||
if fn == nil {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
_, line := fn.FileLine(f.pc())
|
||||
return line
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Format formats the frame according to the fmt.Formatter interface.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// %s source file
|
||||
// %d source line
|
||||
// %n function name
|
||||
// %v equivalent to %s:%d
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Format accepts flags that alter the printing of some verbs, as follows:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// %+s path of source file relative to the compile time GOPATH
|
||||
// %+v equivalent to %+s:%d
|
||||
func (f Frame) Format(s fmt.State, verb rune) {
|
||||
switch verb {
|
||||
case 's':
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case s.Flag('+'):
|
||||
pc := f.pc()
|
||||
fn := runtime.FuncForPC(pc)
|
||||
if fn == nil {
|
||||
io.WriteString(s, "unknown")
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
file, _ := fn.FileLine(pc)
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(s, "%s\n\t%s", fn.Name(), file)
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
io.WriteString(s, path.Base(f.file()))
|
||||
}
|
||||
case 'd':
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(s, "%d", f.line())
|
||||
case 'n':
|
||||
name := runtime.FuncForPC(f.pc()).Name()
|
||||
io.WriteString(s, funcname(name))
|
||||
case 'v':
|
||||
f.Format(s, 's')
|
||||
io.WriteString(s, ":")
|
||||
f.Format(s, 'd')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StackTrace is stack of Frames from innermost (newest) to outermost (oldest).
|
||||
type StackTrace []Frame
|
||||
|
||||
func (st StackTrace) Format(s fmt.State, verb rune) {
|
||||
switch verb {
|
||||
case 'v':
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case s.Flag('+'):
|
||||
for _, f := range st {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(s, "\n%+v", f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case s.Flag('#'):
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(s, "%#v", []Frame(st))
|
||||
default:
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(s, "%v", []Frame(st))
|
||||
}
|
||||
case 's':
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(s, "%s", []Frame(st))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// stack represents a stack of program counters.
|
||||
type stack []uintptr
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *stack) Format(st fmt.State, verb rune) {
|
||||
switch verb {
|
||||
case 'v':
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case st.Flag('+'):
|
||||
for _, pc := range *s {
|
||||
f := Frame(pc)
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(st, "\n%+v", f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *stack) StackTrace() StackTrace {
|
||||
f := make([]Frame, len(*s))
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(f); i++ {
|
||||
f[i] = Frame((*s)[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
return f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func callers() *stack {
|
||||
const depth = 32
|
||||
var pcs [depth]uintptr
|
||||
n := runtime.Callers(3, pcs[:])
|
||||
var st stack = pcs[0:n]
|
||||
return &st
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// funcname removes the path prefix component of a function's name reported by func.Name().
|
||||
func funcname(name string) string {
|
||||
i := strings.LastIndex(name, "/")
|
||||
name = name[i+1:]
|
||||
i = strings.Index(name, ".")
|
||||
return name[i+1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func trimGOPATH(name, file string) string {
|
||||
// Here we want to get the source file path relative to the compile time
|
||||
// GOPATH. As of Go 1.6.x there is no direct way to know the compiled
|
||||
// GOPATH at runtime, but we can infer the number of path segments in the
|
||||
// GOPATH. We note that fn.Name() returns the function name qualified by
|
||||
// the import path, which does not include the GOPATH. Thus we can trim
|
||||
// segments from the beginning of the file path until the number of path
|
||||
// separators remaining is one more than the number of path separators in
|
||||
// the function name. For example, given:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// GOPATH /home/user
|
||||
// file /home/user/src/pkg/sub/file.go
|
||||
// fn.Name() pkg/sub.Type.Method
|
||||
//
|
||||
// We want to produce:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// pkg/sub/file.go
|
||||
//
|
||||
// From this we can easily see that fn.Name() has one less path separator
|
||||
// than our desired output. We count separators from the end of the file
|
||||
// path until it finds two more than in the function name and then move
|
||||
// one character forward to preserve the initial path segment without a
|
||||
// leading separator.
|
||||
const sep = "/"
|
||||
goal := strings.Count(name, sep) + 2
|
||||
i := len(file)
|
||||
for n := 0; n < goal; n++ {
|
||||
i = strings.LastIndex(file[:i], sep)
|
||||
if i == -1 {
|
||||
// not enough separators found, set i so that the slice expression
|
||||
// below leaves file unmodified
|
||||
i = -len(sep)
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// get back to 0 or trim the leading separator
|
||||
file = file[i+len(sep):]
|
||||
return file
|
||||
}
|
||||
15
vendor/github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
15
vendor/github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
language: go
|
||||
|
||||
go:
|
||||
- 1.8.x
|
||||
- 1.9.x
|
||||
- 1.10.x
|
||||
|
||||
before_install:
|
||||
- go get -t -v ./...
|
||||
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- go test -coverprofile=coverage.txt -covermode=atomic
|
||||
|
||||
after_success:
|
||||
- bash <(curl -s https://codecov.io/bash)
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
21
vendor/github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2018 Swaggo
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
72
vendor/github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
72
vendor/github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
# echo-swagger
|
||||
|
||||
echo middleware to automatically generate RESTful API documentation with Swagger 2.0.
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://travis-ci.org/swaggo/echo-swagger)
|
||||
[](https://codecov.io/gh/swaggo/echo-swagger)
|
||||
[](https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
### Start using it
|
||||
1. Add comments to your API source code, [See Declarative Comments Format](https://github.com/swaggo/swag#declarative-comments-format).
|
||||
2. Download [Swag](https://github.com/swaggo/swag) for Go by using:
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
$ go get github.com/swaggo/swag/cmd/swag
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Run the [Swag](https://github.com/swaggo/swag) in your Go project root folder which contains `main.go` file, [Swag](https://github.com/swaggo/swag) will parse comments and generate required files(`docs` folder and `docs/doc.go`).
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
$ swag init
|
||||
```
|
||||
4.Download [echo-swagger](https://github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger) by using:
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
$ go get -u github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger
|
||||
```
|
||||
And import following in your code:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import "github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger" // echo-swagger middleware
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Canonical example:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"github.com/labstack/echo"
|
||||
"github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger"
|
||||
|
||||
_ "github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger/example/docs" // docs is generated by Swag CLI, you have to import it.
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// @title Swagger Example API
|
||||
// @version 1.0
|
||||
// @description This is a sample server Petstore server.
|
||||
// @termsOfService http://swagger.io/terms/
|
||||
|
||||
// @contact.name API Support
|
||||
// @contact.url http://www.swagger.io/support
|
||||
// @contact.email support@swagger.io
|
||||
|
||||
// @license.name Apache 2.0
|
||||
// @license.url http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html
|
||||
|
||||
// @host petstore.swagger.io
|
||||
// @BasePath /v2
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
e := echo.New()
|
||||
|
||||
e.GET("/swagger/*", echoSwagger.WrapHandler)
|
||||
|
||||
e.Logger.Fatal(e.Start(":1323"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Run it, and browser to http://localhost:1323/swagger/index.html, you can see Swagger 2.0 Api documents.
|
||||
|
||||
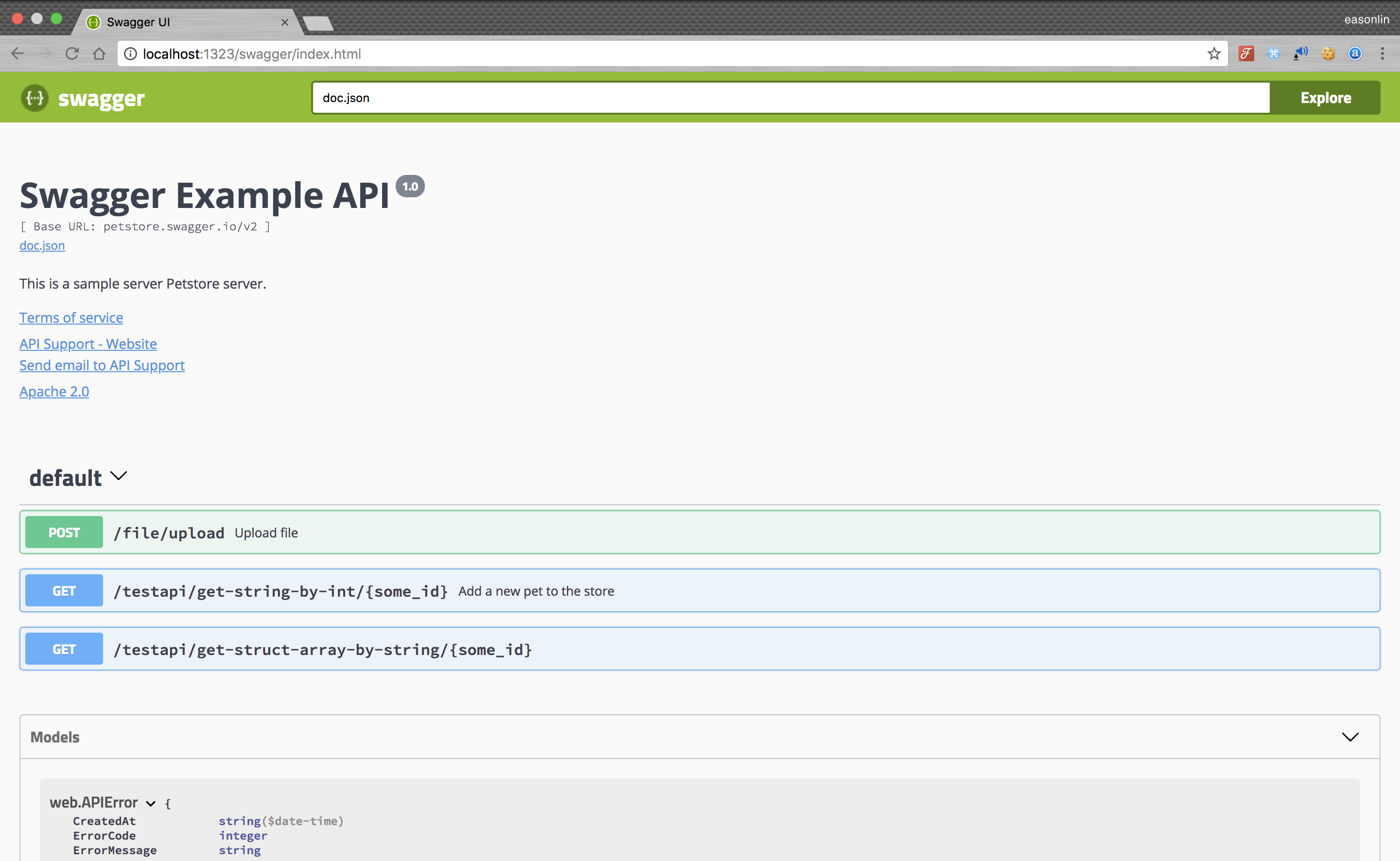
|
||||
|
||||
151
vendor/github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger/swagger.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
151
vendor/github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger/swagger.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,151 @@
|
||||
package echoSwagger
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"golang.org/x/net/webdav"
|
||||
"html/template"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"regexp"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/labstack/echo"
|
||||
"github.com/swaggo/files"
|
||||
"github.com/swaggo/swag"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// WrapHandler wraps swaggerFiles.Handler and returns echo.HandlerFunc
|
||||
var WrapHandler = wrapHandler(swaggerFiles.Handler)
|
||||
|
||||
// wapHandler wraps `http.Handler` into `gin.HandlerFunc`.
|
||||
func wrapHandler(h *webdav.Handler) echo.HandlerFunc {
|
||||
//create a template with name
|
||||
t := template.New("swagger_index.html")
|
||||
index, _ := t.Parse(indexTempl)
|
||||
|
||||
type pro struct {
|
||||
Host string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var re = regexp.MustCompile(`(.*)(index\.html|doc\.json|favicon-16x16\.png|favicon-32x32\.png|/oauth2-redirect\.html|swagger-ui\.css|swagger-ui\.css\.map|swagger-ui\.js|swagger-ui\.js\.map|swagger-ui-bundle\.js|swagger-ui-bundle\.js\.map|swagger-ui-standalone-preset\.js|swagger-ui-standalone-preset\.js\.map)[\?|.]*`)
|
||||
|
||||
return func(c echo.Context) error {
|
||||
var matches []string
|
||||
if matches = re.FindStringSubmatch(c.Request().RequestURI); len(matches) != 3 {
|
||||
|
||||
return c.String(http.StatusNotFound, "404 page not found")
|
||||
}
|
||||
path := matches[2]
|
||||
prefix := matches[1]
|
||||
h.Prefix = prefix
|
||||
|
||||
switch path {
|
||||
case "index.html":
|
||||
s := &pro{
|
||||
Host: "doc.json", //TODO: provide to customs?
|
||||
}
|
||||
index.Execute(c.Response().Writer, s)
|
||||
case "doc.json":
|
||||
doc, _ := swag.ReadDoc()
|
||||
c.Response().Write([]byte(doc))
|
||||
default:
|
||||
h.ServeHTTP(c.Response().Writer, c.Request())
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const indexTempl = `<!-- HTML for static distribution bundle build -->
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
||||
<html lang="en">
|
||||
<head>
|
||||
<meta charset="UTF-8">
|
||||
<title>Swagger UI</title>
|
||||
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Open+Sans:400,700|Source+Code+Pro:300,600|Titillium+Web:400,600,700" rel="stylesheet">
|
||||
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./swagger-ui.css" >
|
||||
<link rel="icon" type="image/png" href="./favicon-32x32.png" sizes="32x32" />
|
||||
<link rel="icon" type="image/png" href="./favicon-16x16.png" sizes="16x16" />
|
||||
<style>
|
||||
html
|
||||
{
|
||||
box-sizing: border-box;
|
||||
overflow: -moz-scrollbars-vertical;
|
||||
overflow-y: scroll;
|
||||
}
|
||||
*,
|
||||
*:before,
|
||||
*:after
|
||||
{
|
||||
box-sizing: inherit;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
body {
|
||||
margin:0;
|
||||
background: #fafafa;
|
||||
}
|
||||
</style>
|
||||
</head>
|
||||
|
||||
<body>
|
||||
|
||||
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" style="position:absolute;width:0;height:0">
|
||||
<defs>
|
||||
<symbol viewBox="0 0 20 20" id="unlocked">
|
||||
<path d="M15.8 8H14V5.6C14 2.703 12.665 1 10 1 7.334 1 6 2.703 6 5.6V6h2v-.801C8 3.754 8.797 3 10 3c1.203 0 2 .754 2 2.199V8H4c-.553 0-1 .646-1 1.199V17c0 .549.428 1.139.951 1.307l1.197.387C5.672 18.861 6.55 19 7.1 19h5.8c.549 0 1.428-.139 1.951-.307l1.196-.387c.524-.167.953-.757.953-1.306V9.199C17 8.646 16.352 8 15.8 8z"></path>
|
||||
</symbol>
|
||||
|
||||
<symbol viewBox="0 0 20 20" id="locked">
|
||||
<path d="M15.8 8H14V5.6C14 2.703 12.665 1 10 1 7.334 1 6 2.703 6 5.6V8H4c-.553 0-1 .646-1 1.199V17c0 .549.428 1.139.951 1.307l1.197.387C5.672 18.861 6.55 19 7.1 19h5.8c.549 0 1.428-.139 1.951-.307l1.196-.387c.524-.167.953-.757.953-1.306V9.199C17 8.646 16.352 8 15.8 8zM12 8H8V5.199C8 3.754 8.797 3 10 3c1.203 0 2 .754 2 2.199V8z"/>
|
||||
</symbol>
|
||||
|
||||
<symbol viewBox="0 0 20 20" id="close">
|
||||
<path d="M14.348 14.849c-.469.469-1.229.469-1.697 0L10 11.819l-2.651 3.029c-.469.469-1.229.469-1.697 0-.469-.469-.469-1.229 0-1.697l2.758-3.15-2.759-3.152c-.469-.469-.469-1.228 0-1.697.469-.469 1.228-.469 1.697 0L10 8.183l2.651-3.031c.469-.469 1.228-.469 1.697 0 .469.469.469 1.229 0 1.697l-2.758 3.152 2.758 3.15c.469.469.469 1.229 0 1.698z"/>
|
||||
</symbol>
|
||||
|
||||
<symbol viewBox="0 0 20 20" id="large-arrow">
|
||||
<path d="M13.25 10L6.109 2.58c-.268-.27-.268-.707 0-.979.268-.27.701-.27.969 0l7.83 7.908c.268.271.268.709 0 .979l-7.83 7.908c-.268.271-.701.27-.969 0-.268-.269-.268-.707 0-.979L13.25 10z"/>
|
||||
</symbol>
|
||||
|
||||
<symbol viewBox="0 0 20 20" id="large-arrow-down">
|
||||
<path d="M17.418 6.109c.272-.268.709-.268.979 0s.271.701 0 .969l-7.908 7.83c-.27.268-.707.268-.979 0l-7.908-7.83c-.27-.268-.27-.701 0-.969.271-.268.709-.268.979 0L10 13.25l7.418-7.141z"/>
|
||||
</symbol>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<symbol viewBox="0 0 24 24" id="jump-to">
|
||||
<path d="M19 7v4H5.83l3.58-3.59L8 6l-6 6 6 6 1.41-1.41L5.83 13H21V7z"/>
|
||||
</symbol>
|
||||
|
||||
<symbol viewBox="0 0 24 24" id="expand">
|
||||
<path d="M10 18h4v-2h-4v2zM3 6v2h18V6H3zm3 7h12v-2H6v2z"/>
|
||||
</symbol>
|
||||
|
||||
</defs>
|
||||
</svg>
|
||||
|
||||
<div id="swagger-ui"></div>
|
||||
|
||||
<script src="./swagger-ui-bundle.js"> </script>
|
||||
<script src="./swagger-ui-standalone-preset.js"> </script>
|
||||
<script>
|
||||
window.onload = function() {
|
||||
// Build a system
|
||||
const ui = SwaggerUIBundle({
|
||||
url: "{{.Host}}",
|
||||
dom_id: '#swagger-ui',
|
||||
validatorUrl: null,
|
||||
presets: [
|
||||
SwaggerUIBundle.presets.apis,
|
||||
SwaggerUIStandalonePreset
|
||||
],
|
||||
plugins: [
|
||||
SwaggerUIBundle.plugins.DownloadUrl
|
||||
],
|
||||
layout: "StandaloneLayout"
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
window.ui = ui
|
||||
}
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
</body>
|
||||
|
||||
</html>
|
||||
`
|
||||
1
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
1
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
# swaggerFiles
|
||||
131
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/ab0x.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
131
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/ab0x.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
|
||||
// Code generated by fileb0x at "2017-11-26 17:57:18.000591466 +0600 +06 m=+3.756909921" from config file "b0x.yml" DO NOT EDIT.
|
||||
|
||||
package swaggerFiles
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/net/context"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/net/webdav"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
// CTX is a context for webdav vfs
|
||||
CTX = context.Background()
|
||||
|
||||
// FS is a virtual memory file system
|
||||
FS = webdav.NewMemFS()
|
||||
|
||||
// Handler is used to server files through a http handler
|
||||
Handler *webdav.Handler
|
||||
|
||||
// HTTP is the http file system
|
||||
HTTP http.FileSystem = new(HTTPFS)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// HTTPFS implements http.FileSystem
|
||||
type HTTPFS struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
if CTX.Err() != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatal(CTX.Err())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//var err error
|
||||
|
||||
Handler = &webdav.Handler{
|
||||
FileSystem: FS,
|
||||
LockSystem: webdav.NewMemLS(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Open a file
|
||||
func (hfs *HTTPFS) Open(path string) (http.File, error) {
|
||||
f, err := FS.OpenFile(CTX, path, os.O_RDONLY, 0644)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return f, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReadFile is adapTed from ioutil
|
||||
func ReadFile(path string) ([]byte, error) {
|
||||
f, err := FS.OpenFile(CTX, path, os.O_RDONLY, 0644)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
buf := bytes.NewBuffer(make([]byte, 0, bytes.MinRead))
|
||||
|
||||
// If the buffer overflows, we will get bytes.ErrTooLarge.
|
||||
// Return that as an error. Any other panic remains.
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
e := recover()
|
||||
if e == nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
if panicErr, ok := e.(error); ok && panicErr == bytes.ErrTooLarge {
|
||||
err = panicErr
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
panic(e)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
_, err = buf.ReadFrom(f)
|
||||
return buf.Bytes(), err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WriteFile is adapTed from ioutil
|
||||
func WriteFile(filename string, data []byte, perm os.FileMode) error {
|
||||
f, err := FS.OpenFile(CTX, filename, os.O_WRONLY|os.O_CREATE|os.O_TRUNC, perm)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
n, err := f.Write(data)
|
||||
if err == nil && n < len(data) {
|
||||
err = io.ErrShortWrite
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err1 := f.Close(); err == nil {
|
||||
err = err1
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WalkDirs looks for files in the given dir and returns a list of files in it
|
||||
// usage for all files in the b0x: WalkDirs("", false)
|
||||
func WalkDirs(name string, includeDirsInList bool, files ...string) ([]string, error) {
|
||||
f, err := FS.OpenFile(CTX, name, os.O_RDONLY, 0)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fileInfos, err := f.Readdir(0)
|
||||
f.Close()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, info := range fileInfos {
|
||||
filename := path.Join(name, info.Name())
|
||||
|
||||
if includeDirsInList || !info.IsDir() {
|
||||
files = append(files, filename)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if info.IsDir() {
|
||||
files, err = WalkDirs(filename, includeDirsInList, files...)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return files, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__favicon-16x16.png.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__favicon-16x16.png.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
// Code generaTed by fileb0x at "2017-11-26 17:57:23.142282087 +0600 +06 m=+8.898600553" from config file "b0x.yml" DO NOT EDIT.
|
||||
|
||||
package swaggerFiles
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// FileFavicon16x16Png is "/favicon-16x16.png"
|
||||
var FileFavicon16x16Png = []byte("\x89\x50\x4e\x47\x0d\x0a\x1a\x0a\x00\x00\x00\x0d\x49\x48\x44\x52\x00\x00\x00\x10\x00\x00\x00\x10\x08\x06\x00\x00\x00\x1f\xf3\xff\x61\x00\x00\x01\x84\x49\x44\x41\x54\x78\x01\x95\x53\x03\x4c\x75\x71\x1c\xfd\x8c\xf1\xc3\xec\x30\xa7\x29\xcd\x61\xb6\x6b\x36\xb2\x9b\xf9\xb2\x6b\xc8\x35\x2f\xdb\x8d\x71\x78\xc6\x94\x6d\xcc\x7b\xef\x7f\x4f\xff\xf3\x6c\xdc\xed\xf2\xe0\xfe\xf8\xc9\xff\x50\x14\x11\x2f\x14\x5b\xa3\x50\xc4\xa1\xbc\x3f\xf1\x74\x3e\x37\x12\x73\x13\x03\x85\xca\x37\x49\x52\x09\x61\xb5\x6a\x8f\xa7\x31\xbe\x5d\x88\xf6\xb9\x4c\xf0\x1c\x93\xcf\xda\xe3\x29\x10\x93\x66\x8d\xe4\x06\x13\xcf\xde\x3c\x9b\xd1\x34\x95\x8a\x92\x81\x4f\x41\xcf\x46\x89\xdd\x3c\x9b\x20\x4d\xe6\x7d\x4c\xe4\x07\x15\xc5\xf5\xe3\xff\x49\x0c\x7b\xd6\x8d\xff\x73\x99\x34\xba\x73\x66\x68\xae\x3f\xaf\x6b\x1a\x70\x72\x77\x10\x20\x3c\xb9\xdb\xc7\x86\xa6\xd1\x19\x49\x0a\xa8\xb1\xd7\x84\x79\x33\x67\x17\x31\x54\x24\xb5\x63\x7f\x71\xfb\x62\x71\xbf\x6b\x8e\x27\x1d\x51\xb0\xc2\x2c\x92\x0b\x78\x7c\x3b\x46\xe5\xf0\xef\x00\x83\xf2\xa1\x1f\x78\x7c\x3f\x71\xbd\xcb\xc2\x16\x80\x5a\x46\xf0\xc4\x4a\xf3\xe3\xe4\x6e\x31\xcc\x17\x6b\x60\x3a\x7d\xcb\x79\xe8\x98\xcb\x42\xc7\x7c\x36\x7a\x97\x72\xd1\x34\x9d\x06\xd3\xf9\x8a\xe4\x94\x90\x8b\xb6\xd9\x0c\x50\xeb\x63\x40\xd0\x7c\xbe\x2a\xc9\x34\xc8\xa7\x98\x27\xcd\x68\x00\xe3\xd9\x32\xa6\x76\x4b\x7d\x0c\x42\xa4\xf0\x2b\x44\x0a\xc7\x81\x29\xb0\x10\x9a\xe3\xa9\xd8\x8b\x78\xe4\x28\xa2\xbb\x8d\x6c\x0d\x01\xb6\x8a\x2d\xf3\x37\x38\xbe\xdd\xc7\xa6\xb6\xc9\xd9\xc6\x64\xd8\x5c\x6d\xf4\x0c\x92\x09\x75\x51\x0e\xd2\xf5\xb3\xd1\xf1\x77\xdf\x51\x16\xb3\x34\x61\x24\xa1\xc4\xc4\x28\x56\xbc\x46\xd9\xdf\xa4\x91\xe9\xb0\x26\x2c\x12\x2b\xcd\x93\xcf\x1c\x1c\x62\xdc\xca\x00\x71\x74\xeb\xcc\x2d\x14\x89\xfe\xfc\x0f\x6d\x32\x6a\x88\xec\xcc\x73\x18\x00\x00\x00\x00\x49\x45\x4e\x44\xae\x42\x60\x82")
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
|
||||
f, err := FS.OpenFile(CTX, "/favicon-16x16.png", os.O_RDWR|os.O_CREATE|os.O_TRUNC, 0777)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatal(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
_, err = f.Write(FileFavicon16x16Png)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatal(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
err = f.Close()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatal(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__favicon-32x32.png.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__favicon-32x32.png.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
// Code generaTed by fileb0x at "2017-11-26 17:57:18.759175324 +0600 +06 m=+4.515493805" from config file "b0x.yml" DO NOT EDIT.
|
||||
|
||||
package swaggerFiles
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// FileFavicon32x32Png is "/favicon-32x32.png"
|
||||
var FileFavicon32x32Png = []byte("\x89\x50\x4e\x47\x0d\x0a\x1a\x0a\x00\x00\x00\x0d\x49\x48\x44\x52\x00\x00\x00\x20\x00\x00\x00\x20\x08\x06\x00\x00\x00\x73\x7a\x7a\xf4\x00\x00\x04\x3c\x49\x44\x41\x54\x78\x01\xbd\x57\x03\xcc\x65\x59\x0c\x7e\x6b\xdb\xb6\x6d\xc4\x5e\xc7\x5e\xdb\xb6\x3d\x46\xf0\xdb\xb6\x6d\xdb\xb6\x6d\xf3\xa2\xd3\x6f\xf2\xce\x33\x7f\x35\x69\xee\x61\xdb\x5b\x1f\x8d\xa3\xa0\xaa\xea\xa9\xb2\xb2\xf9\xa4\xac\x48\x3f\xf2\x37\x42\x92\xd7\xab\x78\x3c\x02\x94\xe4\x8d\x1a\xfe\x46\x61\x0f\x67\x70\x56\xb3\x53\xa0\xa8\xf2\x85\x4c\xf8\x7b\x45\x91\xfa\x88\x54\x72\x04\x70\x96\x05\xf9\x91\xef\x5e\x6c\x8f\xbe\x9d\x3f\x96\xde\x66\x22\x53\x82\x30\xaf\xd1\xf0\x74\x03\x95\xb4\x7a\x52\x62\xe5\xcf\x14\x5e\xf4\x21\x90\xc7\x3f\x51\x71\xab\x07\xef\xd5\x13\xce\x08\xc0\x5d\xa6\xf1\x2e\x68\x39\xc9\x5c\xb9\x98\xff\x20\x4e\x10\x5b\xdf\x5c\xa6\xbc\xa6\xe3\xf4\x6f\xc4\xdd\xf4\x99\xa7\xc6\x26\xfe\x13\x71\x17\xe5\x36\x1e\xe3\x3b\x4b\x3a\xa1\x59\x88\x04\xd0\x74\x94\xf9\xd5\x7c\xa1\x41\x5c\xae\xea\x0a\xa1\x5f\x82\xaf\x01\x71\xa7\xf0\x97\xa0\xab\xa9\xb2\x33\x08\x34\x84\x59\x9a\x98\xf6\xb5\x76\xff\x5c\x30\x67\xc7\xa2\x90\xfc\xb7\x41\x6c\x5b\x18\x9c\xff\x26\xb1\xc3\x1a\x08\xa1\x5e\x6c\xcb\xe6\x71\x82\xb9\x47\xc6\x2b\x20\xb0\x23\xe8\x9e\xf6\xa2\xa1\x10\x09\x16\x7d\x02\x0e\x07\x75\x01\x43\xf2\xdf\xc2\xc5\x1d\xc5\xa0\xbc\x37\x48\xd0\x87\x63\x9a\xaa\xfe\x42\xf6\xd8\x09\x62\xa8\xea\x0a\x36\xba\xf8\xb5\xcf\x39\x54\xd1\x11\x40\xab\xeb\x73\x34\x34\x55\x6b\x97\xd1\xe0\x54\x0d\xad\x6e\xcc\xc3\xfe\xf4\xb5\xef\xb9\x46\x7b\x15\x9d\x01\xba\xe8\x30\x0a\x51\xc4\xb9\xf0\x76\x53\x87\x8b\x2e\xfd\x82\x00\xe3\x73\x6d\x94\xdd\x70\xc8\xae\x00\xd9\xf5\x07\x69\x6c\xb6\x85\x00\xb1\x65\x5f\x1b\xed\xfd\x1c\x74\x95\x2e\x3a\x90\xb4\x74\xb6\x67\xbb\xf4\x60\x31\x8f\xc3\xc7\x94\x20\xa2\x00\xb0\x3f\xfa\x21\x87\xd5\xfd\x5f\xd4\x7d\x04\xa8\xed\x89\x30\xdb\xcb\x69\x38\xa2\xf5\x05\xb9\xef\xa4\x2f\x20\x75\x8a\x90\x43\x0c\x9b\x5e\x68\x19\x4c\x21\xc0\xef\xa1\x37\x39\x2c\x00\xb4\x08\x68\x1d\x4c\x33\xdb\xfb\x3b\xfc\x0e\x5d\x68\x32\xef\xa7\x35\x50\x05\x26\xc8\x62\x38\x60\x2e\x40\x1a\x01\x7e\x0b\xb9\xde\x61\x01\x7e\x0c\xbc\x1c\x4c\xa8\x75\x28\xdd\xd2\x3e\x7c\x49\x44\xc4\xcf\xd0\x40\x04\x26\x25\xad\x1e\x16\x0f\xf7\x8d\x97\x41\x52\xfa\xca\xe7\x6c\x87\x05\xf8\xd2\xfb\x0c\x84\x1d\x0d\x4c\x56\x59\xdc\x2f\x6a\x75\x13\x1a\x88\xd2\xa0\xaa\x61\x82\x7c\x6e\x7a\x70\x5f\xf4\x03\xc8\x09\xd4\x3b\x5e\x8a\x39\x7d\xee\x75\x9a\x91\x20\x60\x04\x14\x73\xec\xe1\x0c\xc6\x5d\xa3\x05\x60\x60\xd1\x77\x12\x2a\x7e\x20\x00\xf3\xae\xd3\xa0\x9c\x62\x82\xa2\x62\x78\x28\xb3\x6e\x1f\x71\x78\xd2\xf2\xda\x34\x1d\x8a\x7d\x1c\x6b\xd4\x3e\x9c\x49\x2b\xeb\xb3\xf4\x6b\xc8\x75\x60\x4c\x93\xf3\x5d\x34\xb5\xd0\xc3\xe3\x33\xd9\xee\xd7\xf2\xd9\x19\xea\x18\xc9\xc1\x59\x3a\x18\xfb\x28\x2d\xad\x4e\x82\x06\x65\xd5\x1f\x30\xa2\x1d\x56\xf8\xbe\x30\xc1\x98\x35\x01\xf8\xd2\x7e\x5c\xa6\xa5\xb5\x29\x26\xf6\x98\x56\x80\x6c\xe4\x03\xf8\x03\x04\x00\x73\x9a\x5e\xec\x85\x00\xf4\x2b\x0b\x00\xe1\x3a\x47\xf2\x70\x96\x0e\xc4\x3c\x42\x8b\xab\x13\xa0\x81\xd0\xb4\x2e\x00\xab\xd8\xaa\x09\xf6\xc7\x3c\xac\x35\x41\x09\xe6\xf4\x05\xab\xf7\x6b\x23\x13\x9c\x09\x34\x32\xc1\x17\x3a\x13\xe4\xc3\x04\x10\xde\xae\x09\x22\x30\x29\xb6\xe6\x84\x13\xc2\x09\xcf\x72\xda\x09\xfb\x27\x2b\x2d\x3b\x61\x8b\x70\x42\x29\x66\x77\xc2\x30\xc0\x66\x18\x22\x5d\x0b\x01\x10\x86\x92\x41\x22\xba\x73\x0f\x12\xd1\xed\x06\x89\x48\x7a\x5a\x9b\x8a\xe5\x3e\x2c\xe4\x36\x1e\x35\xbb\x50\xdd\x15\x4a\x80\x7d\xce\xa4\xe2\xc8\x7b\x6d\xa4\xe2\xc3\xc2\x01\x07\xc0\xdb\xa4\x18\x2d\xa1\x93\x31\xba\x10\x53\xfa\x25\xb6\x50\x60\x10\x19\x76\x99\x23\x7c\x47\x67\x9b\x09\x10\x57\xf6\x8d\x49\x31\xba\x92\xd6\x36\x17\x45\x12\xfa\xd9\xa8\xf3\x55\x54\x65\x0a\x1b\x95\x9d\x81\x66\xe5\x18\xa5\x75\x6d\x63\x81\x86\xa6\xeb\xec\x09\x80\x34\xcb\x67\x17\xa1\x39\xfa\xc6\xf7\x3c\xa3\xbd\xf2\x0e\x7f\x02\x80\x97\x59\xc7\xac\x18\x34\x24\x68\xa3\x76\xba\x21\x09\xcc\x7b\xcd\xb4\x21\xb1\xd8\x92\x25\x68\xe3\x93\xdc\xd3\x5f\xda\x31\xe6\xae\x69\xcf\x83\xa6\x70\xbc\x24\xf0\xb2\xda\x94\xa2\x71\x14\x42\x40\x13\xdb\xff\xf3\xd7\x0d\xfa\x41\xb9\xc5\x6e\x7b\x8e\xd6\x59\x08\x01\x75\xc1\x27\x7e\x16\x8e\xe9\x04\xa2\xfb\x41\x2b\xc7\x34\x0c\x98\xab\xd7\x3a\xfc\x30\xd1\x76\xaf\x24\xa2\x23\xb7\xf1\x08\xfd\x6d\x21\x4f\x58\x68\x38\x10\x6a\x7c\x67\xd1\xe0\x61\xb2\x99\x04\x9a\x5b\x79\x9a\xbd\x6b\xf2\x34\x43\x24\xa0\x9e\x23\x9f\xa3\xa8\x00\x31\xc6\x1a\x22\xc0\xe4\x69\xa6\xcc\x30\xf3\xf7\xb7\xf5\x58\x45\xb8\xe0\xa1\xc9\xc2\x0c\x90\x83\x80\x24\x83\x38\xdf\xd6\xe3\xd4\x82\x46\x4e\x47\x0f\x87\x36\x8a\xbf\x31\xa8\x64\x28\xa7\x40\x8c\x51\x58\x90\xdb\x19\x9f\xc5\x59\x47\xe9\x9e\x00\xa5\x79\x33\x5d\x9a\x4a\xe1\x22\x00\x00\x00\x00\x49\x45\x4e\x44\xae\x42\x60\x82")
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
|
||||
f, err := FS.OpenFile(CTX, "/favicon-32x32.png", os.O_RDWR|os.O_CREATE|os.O_TRUNC, 0777)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatal(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
_, err = f.Write(FileFavicon32x32Png)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatal(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
err = f.Close()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatal(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__index.html.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__index.html.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__oauth2-redirect.html.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__oauth2-redirect.html.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui-bundle.js.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui-bundle.js.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui-bundle.js.map.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui-bundle.js.map.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui-standalone-preset.js.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui-standalone-preset.js.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui-standalone-preset.js.map.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui-standalone-preset.js.map.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui.css.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui.css.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui.css.map.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui.css.map.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
// Code generaTed by fileb0x at "2017-11-26 17:57:18.489607614 +0600 +06 m=+4.245926076" from config file "b0x.yml" DO NOT EDIT.
|
||||
|
||||
package swaggerFiles
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// FileSwaggerUICSSMap is "/swagger-ui.css.map"
|
||||
var FileSwaggerUICSSMap = []byte("\x7b\x22\x76\x65\x72\x73\x69\x6f\x6e\x22\x3a\x33\x2c\x22\x73\x6f\x75\x72\x63\x65\x73\x22\x3a\x5b\x5d\x2c\x22\x6e\x61\x6d\x65\x73\x22\x3a\x5b\x5d\x2c\x22\x6d\x61\x70\x70\x69\x6e\x67\x73\x22\x3a\x22\x22\x2c\x22\x66\x69\x6c\x65\x22\x3a\x22\x73\x77\x61\x67\x67\x65\x72\x2d\x75\x69\x2e\x63\x73\x73\x22\x2c\x22\x73\x6f\x75\x72\x63\x65\x52\x6f\x6f\x74\x22\x3a\x22\x22\x7d")
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
|
||||
f, err := FS.OpenFile(CTX, "/swagger-ui.css.map", os.O_RDWR|os.O_CREATE|os.O_TRUNC, 0777)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatal(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
_, err = f.Write(FileSwaggerUICSSMap)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatal(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
err = f.Close()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Fatal(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui.js.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui.js.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui.js.map.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/swaggo/files/b0xfile__swagger-ui.js.map.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
14
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
14
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
swag
|
||||
testdata/simple/docs
|
||||
cover.out
|
||||
|
||||
# Test binary, build with `go test -c`
|
||||
*.test
|
||||
|
||||
# Output of the go coverage tool, specifically when used with LiteIDE
|
||||
*.out
|
||||
.idea
|
||||
.vscode
|
||||
|
||||
# Etc
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
1
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/.golint_exclude
generated
vendored
Normal file
1
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/.golint_exclude
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
^example
|
||||
17
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
17
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
language: go
|
||||
|
||||
go:
|
||||
- 1.9.x
|
||||
- 1.10.x
|
||||
- 1.11.x
|
||||
|
||||
before_install:
|
||||
- make deps
|
||||
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- make lint
|
||||
- make build
|
||||
- make test
|
||||
|
||||
after_success:
|
||||
- bash <(curl -s https://codecov.io/bash)
|
||||
46
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
46
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
# Contributor Covenant Code of Conduct
|
||||
|
||||
## Our Pledge
|
||||
|
||||
In the interest of fostering an open and welcoming environment, we as contributors and maintainers pledge to making participation in our project and our community a harassment-free experience for everyone, regardless of age, body size, disability, ethnicity, gender identity and expression, level of experience, nationality, personal appearance, race, religion, or sexual identity and orientation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Our Standards
|
||||
|
||||
Examples of behavior that contributes to creating a positive environment include:
|
||||
|
||||
* Using welcoming and inclusive language
|
||||
* Being respectful of differing viewpoints and experiences
|
||||
* Gracefully accepting constructive criticism
|
||||
* Focusing on what is best for the community
|
||||
* Showing empathy towards other community members
|
||||
|
||||
Examples of unacceptable behavior by participants include:
|
||||
|
||||
* The use of sexualized language or imagery and unwelcome sexual attention or advances
|
||||
* Trolling, insulting/derogatory comments, and personal or political attacks
|
||||
* Public or private harassment
|
||||
* Publishing others' private information, such as a physical or electronic address, without explicit permission
|
||||
* Other conduct which could reasonably be considered inappropriate in a professional setting
|
||||
|
||||
## Our Responsibilities
|
||||
|
||||
Project maintainers are responsible for clarifying the standards of acceptable behavior and are expected to take appropriate and fair corrective action in response to any instances of unacceptable behavior.
|
||||
|
||||
Project maintainers have the right and responsibility to remove, edit, or reject comments, commits, code, wiki edits, issues, and other contributions that are not aligned to this Code of Conduct, or to ban temporarily or permanently any contributor for other behaviors that they deem inappropriate, threatening, offensive, or harmful.
|
||||
|
||||
## Scope
|
||||
|
||||
This Code of Conduct applies both within project spaces and in public spaces when an individual is representing the project or its community. Examples of representing a project or community include using an official project e-mail address, posting via an official social media account, or acting as an appointed representative at an online or offline event. Representation of a project may be further defined and clarified by project maintainers.
|
||||
|
||||
## Enforcement
|
||||
|
||||
Instances of abusive, harassing, or otherwise unacceptable behavior may be reported by contacting the project team at [gitter.im/swaggo/swag](https://gitter.im/swaggo/swag).The project team will review and investigate all complaints, and will respond in a way that it deems appropriate to the circumstances. The project team is obligated to maintain confidentiality with regard to the reporter of an incident. Further details of specific enforcement policies may be posted separately.
|
||||
|
||||
Project maintainers who do not follow or enforce the Code of Conduct in good faith may face temporary or permanent repercussions as determined by other members of the project's leadership.
|
||||
|
||||
## Attribution
|
||||
|
||||
This Code of Conduct is adapted from the [Contributor Covenant][homepage], version 1.4, available at [http://contributor-covenant.org/version/1/4][version]
|
||||
|
||||
[homepage]: http://contributor-covenant.org
|
||||
[version]: http://contributor-covenant.org/version/1/4/
|
||||
16
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/CONTRIBUTING.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
16
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/CONTRIBUTING.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
# Contributing
|
||||
|
||||
When contributing to this repository, please first discuss the change you wish to make via issue,
|
||||
email, or any other method with the owners of this repository before making a change.
|
||||
|
||||
Please note we have a code of conduct, please follow it in all your interactions with the project.
|
||||
|
||||
## Pull Request Process
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork it
|
||||
2. Create your feature branch (`git checkout -b my-new-feature`)
|
||||
3. Commit your changes (`git commit -am 'Add some feature'`)
|
||||
4. Push to the branch (`git push origin my-new-feature`)
|
||||
5. Create new Pull Request
|
||||
|
||||
Please make an issue first if the change is likely to increase.
|
||||
43
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/Makefile
generated
vendored
Normal file
43
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/Makefile
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/make
|
||||
GOCMD=$(shell which go)
|
||||
GOLINT=$(shell which golint)
|
||||
GOIMPORT=$(shell which goimports)
|
||||
GOBUILD=$(GOCMD) build
|
||||
GOCLEAN=$(GOCMD) clean
|
||||
GOTEST=$(GOCMD) test
|
||||
GOGET=$(GOCMD) get
|
||||
GOLIST=$(GOCMD) list
|
||||
BINARY_NAME=swag
|
||||
|
||||
all: test build
|
||||
|
||||
build:
|
||||
$(GOBUILD) -o $(BINARY_NAME) -v ./cmd/...
|
||||
|
||||
test:
|
||||
$(GOTEST) -v ./...
|
||||
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
$(GOCLEAN)
|
||||
rm -f $(BINARY_NAME)
|
||||
|
||||
DIRS=$(shell $(GOLIST) -f {{.Dir}} ./...)
|
||||
lint:
|
||||
@for d in $(DIRS) ; do \
|
||||
if [ "`$(GOIMPORT) -l $$d/*.go | tee /dev/stderr`" ]; then \
|
||||
echo "^ - Repo contains improperly formatted go files" && echo && exit 1; \
|
||||
fi \
|
||||
done
|
||||
@if [ "`$(GOLINT) ./... | grep -vf .golint_exclude | tee /dev/stderr`" ]; then \
|
||||
echo "^ - Lint errors!" && echo && exit 1; \
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
deps:
|
||||
$(GOGET) -v ./...
|
||||
$(GOGET) github.com/stretchr/testify/assert
|
||||
$(GOGET) golang.org/x/lint/golint
|
||||
$(GOGET) golang.org/x/tools/cmd/goimports
|
||||
|
||||
view-covered:
|
||||
$(GOTEST) -coverprofile=cover.out $(TARGET)
|
||||
$(GOCMD) tool cover -html=cover.out
|
||||
8
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
8
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
**Describe the PR**
|
||||
e.g. add cool parser.
|
||||
|
||||
**Relation issue**
|
||||
e.g. https://github.com/swaggo/swag/pull/118/files
|
||||
|
||||
**Additional context**
|
||||
Add any other context about the problem here.
|
||||
527
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
527
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,527 @@
|
||||
# swag
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img alt="swaggo" src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/swaggo/swag/master/assets/swaggo.png" width="200">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
Automatically generate RESTful API documentation with Swagger 2.0 for Go.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://travis-ci.org/swaggo/swag"><img alt="Travis Status" src="https://img.shields.io/travis/swaggo/swag/master.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://codecov.io/gh/swaggo/swag"><img alt="Coverage Status" src="https://img.shields.io/codecov/c/github/swaggo/swag/master.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://goreportcard.com/badge/github.com/swaggo/swag"><img alt="Go Report Card" src="https://goreportcard.com/badge/github.com/swaggo/swag"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://codebeat.co/projects/github-com-swaggo-swag-master"><img alt="codebeat badge" src="https://codebeat.co/badges/71e2f5e5-9e6b-405d-baf9-7cc8b5037330" /></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://godoc.org/github.com/swaggo/swag"><img alt="Go Doc" src="https://godoc.org/github.com/swaggo/swagg?status.svg"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">gopher image source is <a href="https://github.com/tenntenn/gopher-stickers">tenntenn/gopher-stickers.</a> It has licenses <a href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en">creative commons licensing.</a></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## Content
|
||||
- [Getting started](#getting-started)
|
||||
- [Go web frameworks](#supported-web-frameworks)
|
||||
- [Supported Web Frameworks](#supported-web-frameworks)
|
||||
- [How to use it with `gin`?](#how-to-use-it-with-`gin`?)
|
||||
- [Implementation Status](#implementation-status)
|
||||
- [swag cli](#swag-cli)
|
||||
- [General API Info](#general-api-info)
|
||||
- [Security](#security)
|
||||
- [API Operation](#api-operation)
|
||||
- [TIPS](#tips)
|
||||
- [User defined structure with an array type](#user-defined-structure-with-an-array-type)
|
||||
- [Use multiple path params](#use-multiple-path-params)
|
||||
- [Example value of struct](#example-value-of-struct)
|
||||
- [Description of struct](#description-of-struct)
|
||||
- [About the Project](#about-the-project)
|
||||
|
||||
## Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Swag converts Go annotations to Swagger Documentation 2.0. We've created a variety of plugins for popular [Go web frameworks](#supported-web-frameworks). This allows you to quickly integrate with an existing Go project (using Swagger UI).
|
||||
|
||||
## Examples
|
||||
|
||||
[swaggo + gin](https://github.com/swaggo/swag/tree/master/example)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting started
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add comments to your API source code, [See Declarative Comments Format](#general-api-info).
|
||||
|
||||
2. Download swag by using:
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
$ go get -u github.com/swaggo/swag/cmd/swag
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Run `swag init` in the project's root folder which contains the `main.go` file. This will parse your comments and generate the required files (`docs` folder and `docs/docs.go`).
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
$ swag init
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. In order to serve these files, you can utilize one of our supported plugins. For go's core library, check out [net/http](https://github.com/swaggo/http-swagger).
|
||||
|
||||
* Make sure to import the generated `docs/docs.go` so that your specific configuration gets `init`'ed.
|
||||
* If your General API annotation do not live in `main.go`, you can let swag know with `-g`.
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
swag init -g http/api.go
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported Web Frameworks
|
||||
|
||||
- [gin](http://github.com/swaggo/gin-swagger)
|
||||
- [echo](http://github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger)
|
||||
- [net/http](https://github.com/swaggo/http-swagger)
|
||||
|
||||
## How to use it with `gin`?
|
||||
|
||||
Find the example source code [here](https://github.com/swaggo/swag/tree/master/example/celler).
|
||||
|
||||
1. After using `swag init` to generate Swagger 2.0 docs, import the following packages:
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import "github.com/swaggo/gin-swagger" // gin-swagger middleware
|
||||
import "github.com/swaggo/gin-swagger/swaggerFiles" // swagger embed files
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Add [General API](#general-api-info) annotations in `main.go` code:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// @title Swagger Example API
|
||||
// @version 1.0
|
||||
// @description This is a sample server celler server.
|
||||
// @termsOfService http://swagger.io/terms/
|
||||
|
||||
// @contact.name API Support
|
||||
// @contact.url http://www.swagger.io/support
|
||||
// @contact.email support@swagger.io
|
||||
|
||||
// @license.name Apache 2.0
|
||||
// @license.url http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html
|
||||
|
||||
// @host localhost:8080
|
||||
// @BasePath /api/v1
|
||||
|
||||
// @securityDefinitions.basic BasicAuth
|
||||
|
||||
// @securityDefinitions.apikey ApiKeyAuth
|
||||
// @in header
|
||||
// @name Authorization
|
||||
|
||||
// @securitydefinitions.oauth2.application OAuth2Application
|
||||
// @tokenUrl https://example.com/oauth/token
|
||||
// @scope.write Grants write access
|
||||
// @scope.admin Grants read and write access to administrative information
|
||||
|
||||
// @securitydefinitions.oauth2.implicit OAuth2Implicit
|
||||
// @authorizationurl https://example.com/oauth/authorize
|
||||
// @scope.write Grants write access
|
||||
// @scope.admin Grants read and write access to administrative information
|
||||
|
||||
// @securitydefinitions.oauth2.password OAuth2Password
|
||||
// @tokenUrl https://example.com/oauth/token
|
||||
// @scope.read Grants read access
|
||||
// @scope.write Grants write access
|
||||
// @scope.admin Grants read and write access to administrative information
|
||||
|
||||
// @securitydefinitions.oauth2.accessCode OAuth2AccessCode
|
||||
// @tokenUrl https://example.com/oauth/token
|
||||
// @authorizationurl https://example.com/oauth/authorize
|
||||
// @scope.admin Grants read and write access to administrative information
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
r := gin.Default()
|
||||
|
||||
c := controller.NewController()
|
||||
|
||||
v1 := r.Group("/api/v1")
|
||||
{
|
||||
accounts := v1.Group("/accounts")
|
||||
{
|
||||
accounts.GET(":id", c.ShowAccount)
|
||||
accounts.GET("", c.ListAccounts)
|
||||
accounts.POST("", c.AddAccount)
|
||||
accounts.DELETE(":id", c.DeleteAccount)
|
||||
accounts.PATCH(":id", c.UpdateAccount)
|
||||
accounts.POST(":id/images", c.UploadAccountImage)
|
||||
}
|
||||
//...
|
||||
}
|
||||
r.GET("/swagger/*any", ginSwagger.WrapHandler(swaggerFiles.Handler))
|
||||
r.Run(":8080")
|
||||
}
|
||||
//...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally some general API info can be set dynamically. The generated code package `docs` exports `SwaggerInfo` variable which we can use to set the title, description, version, host and base path programatically. Example using Gin:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
|
||||
"github.com/swaggo/gin-swagger"
|
||||
"github.com/swaggo/gin-swagger/swaggerFiles"
|
||||
|
||||
"./docs" // docs is generated by Swag CLI, you have to import it.
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// @contact.name API Support
|
||||
// @contact.url http://www.swagger.io/support
|
||||
// @contact.email support@swagger.io
|
||||
|
||||
// @license.name Apache 2.0
|
||||
// @license.url http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html
|
||||
|
||||
// @termsOfService http://swagger.io/terms/
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
|
||||
// programatically set swagger info
|
||||
docs.Title = "Swagger Example API"
|
||||
docs.Description = "This is a sample server Petstore server."
|
||||
docs.SwaggerInfo.Version = "1.0"
|
||||
docs.SwaggerInfo.Host = "petstore.swagger.io"
|
||||
docs.SwaggerInfo.BasePath = "/v2"
|
||||
|
||||
r := gin.New()
|
||||
|
||||
// use ginSwagger middleware to serve the API docs
|
||||
r.GET("/swagger/*any", ginSwagger.WrapHandler(swaggerFiles.Handler))
|
||||
|
||||
r.Run()
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Add [API Operation](#api-operation) annotations in `controller` code
|
||||
|
||||
``` go
|
||||
package controller
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
|
||||
"github.com/swaggo/swag/example/celler/httputil"
|
||||
"github.com/swaggo/swag/example/celler/model"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ShowAccount godoc
|
||||
// @Summary Show a account
|
||||
// @Description get string by ID
|
||||
// @ID get-string-by-int
|
||||
// @Accept json
|
||||
// @Produce json
|
||||
// @Param id path int true "Account ID"
|
||||
// @Success 200 {object} model.Account
|
||||
// @Failure 400 {object} httputil.HTTPError
|
||||
// @Failure 404 {object} httputil.HTTPError
|
||||
// @Failure 500 {object} httputil.HTTPError
|
||||
// @Router /accounts/{id} [get]
|
||||
func (c *Controller) ShowAccount(ctx *gin.Context) {
|
||||
id := ctx.Param("id")
|
||||
aid, err := strconv.Atoi(id)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
httputil.NewError(ctx, http.StatusBadRequest, err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
account, err := model.AccountOne(aid)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
httputil.NewError(ctx, http.StatusNotFound, err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, account)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ListAccounts godoc
|
||||
// @Summary List accounts
|
||||
// @Description get accounts
|
||||
// @Accept json
|
||||
// @Produce json
|
||||
// @Param q query string false "name search by q"
|
||||
// @Success 200 {array} model.Account
|
||||
// @Failure 400 {object} httputil.HTTPError
|
||||
// @Failure 404 {object} httputil.HTTPError
|
||||
// @Failure 500 {object} httputil.HTTPError
|
||||
// @Router /accounts [get]
|
||||
func (c *Controller) ListAccounts(ctx *gin.Context) {
|
||||
q := ctx.Request.URL.Query().Get("q")
|
||||
accounts, err := model.AccountsAll(q)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
httputil.NewError(ctx, http.StatusNotFound, err)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, accounts)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ swag init
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4.Run your app, and browse to http://localhost:8080/swagger/index.html. You will see Swagger 2.0 Api documents as shown below:
|
||||
|
||||
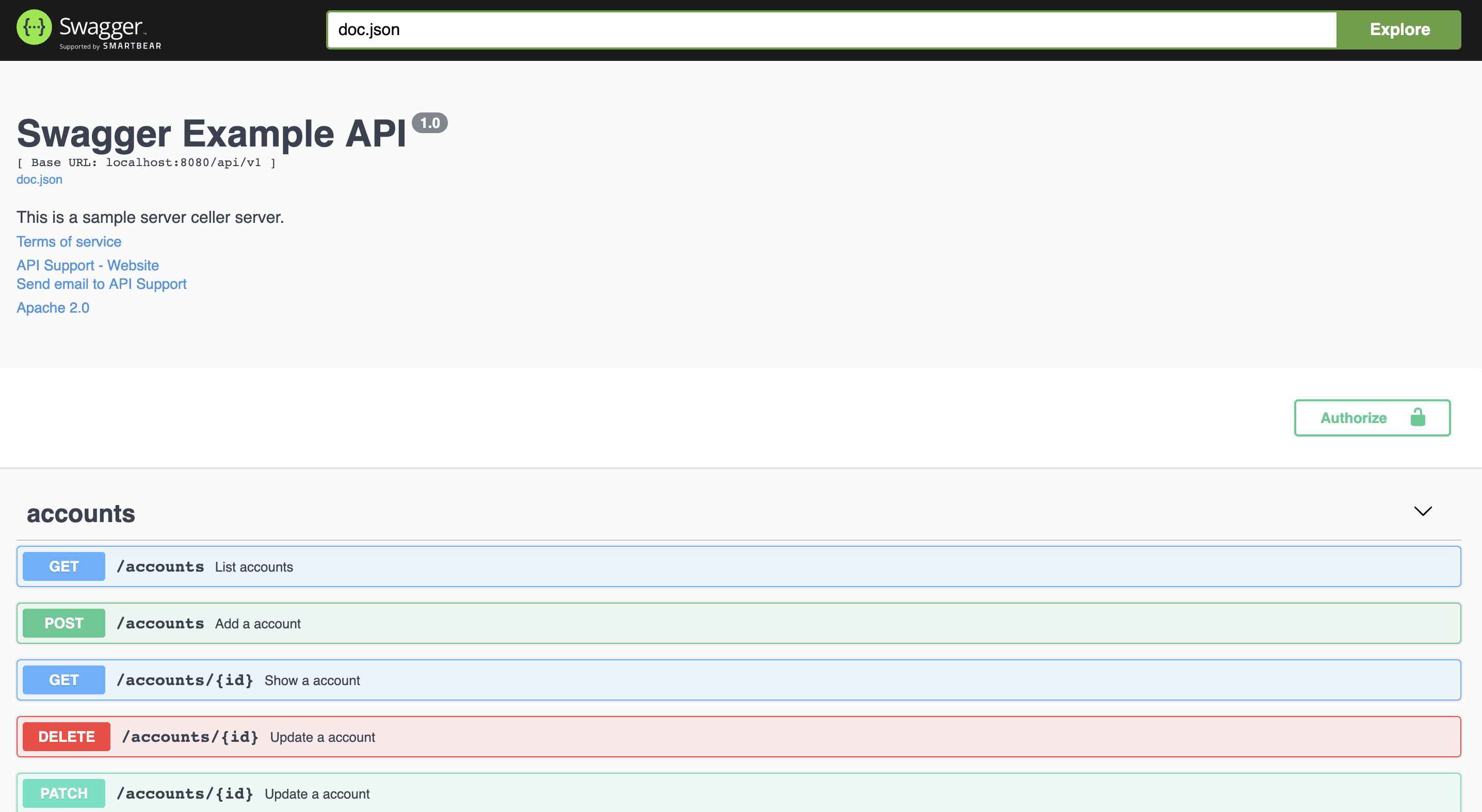
|
||||
|
||||
## Implementation Status
|
||||
|
||||
[Swagger 2.0 document](https://swagger.io/docs/specification/2-0/basic-structure/)
|
||||
|
||||
- [x] Basic Structure
|
||||
- [x] API Host and Base Path
|
||||
- [x] Paths and Operations
|
||||
- [x] Describing Parameters
|
||||
- [x] Describing Request Body
|
||||
- [x] Describing Responses
|
||||
- [x] MIME Types
|
||||
- [x] Authentication
|
||||
- [x] Basic Authentication
|
||||
- [x] API Keys
|
||||
- [x] Adding Examples
|
||||
- [x] File Upload
|
||||
- [x] Enums
|
||||
- [x] Grouping Operations With Tags
|
||||
- [ ] Swagger Extensions
|
||||
|
||||
# swag cli
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ swag init -h
|
||||
NAME:
|
||||
swag init - Create docs.go
|
||||
|
||||
USAGE:
|
||||
swag init [command options] [arguments...]
|
||||
|
||||
OPTIONS:
|
||||
--generalInfo value, -g value Go file path in which 'swagger general API Info' is written (default: "main.go")
|
||||
--dir value, -d value Directory you want to parse (default: "./")
|
||||
--swagger value, -s value Output the swagger conf for json and yaml (default: "./docs/swagger")
|
||||
--propertyStrategy value, -p value Property Naming Strategy like snakecase,camelcase,pascalcase (default: "camelcase")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# General API Info
|
||||
|
||||
**Example**
|
||||
[celler/main.go](https://github.com/swaggo/swag/blob/master/example/celler/main.go)
|
||||
|
||||
| annotation | description | example |
|
||||
|--------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| title | **Required.** The title of the application. | // @title Swagger Example API |
|
||||
| version | **Required.** Provides the version of the application API. | // @version 1.0 |
|
||||
| description | A short description of the application. | // @description This is a sample server celler server. |
|
||||
| termsOfService | The Terms of Service for the API. | // @termsOfService http://swagger.io/terms/ |
|
||||
| contact.name | The contact information for the exposed API. | // @contact.name API Support |
|
||||
| contact.url | The URL pointing to the contact information. MUST be in the format of a URL. | // @contact.url http://www.swagger.io/support |
|
||||
| contact.email | The email address of the contact person/organization. MUST be in the format of an email address.| // @contact.email support@swagger.io |
|
||||
| license.name | **Required.** The license name used for the API. | // @license.name Apache 2.0 |
|
||||
| license.url | A URL to the license used for the API. MUST be in the format of a URL. | // @license.url http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html |
|
||||
| host | The host (name or ip) serving the API. | // @host localhost:8080 |
|
||||
| BasePath | The base path on which the API is served. | // @BasePath /api/v1 |
|
||||
|
||||
## Security
|
||||
|
||||
| annotation | description | parameters | example |
|
||||
|-----------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| securitydefinitions.basic | [Basic](https://swagger.io/docs/specification/2-0/authentication/basic-authentication/) auth. | | // @securityDefinitions.basic BasicAuth |
|
||||
| securitydefinitions.apikey | [API key](https://swagger.io/docs/specification/2-0/authentication/api-keys/) auth. | in, name | // @securityDefinitions.apikey ApiKeyAuth |
|
||||
| securitydefinitions.oauth2.application | [OAuth2 application](https://swagger.io/docs/specification/authentication/oauth2/) auth. | tokenUrl, scope | // @securitydefinitions.oauth2.application OAuth2Application |
|
||||
| securitydefinitions.oauth2.implicit | [OAuth2 implicit](https://swagger.io/docs/specification/authentication/oauth2/) auth. | authorizationUrl, scope | // @securitydefinitions.oauth2.implicit OAuth2Implicit |
|
||||
| securitydefinitions.oauth2.password | [OAuth2 password](https://swagger.io/docs/specification/authentication/oauth2/) auth. | tokenUrl, scope | // @securitydefinitions.oauth2.password OAuth2Password |
|
||||
| securitydefinitions.oauth2.accessCode | [OAuth2 access code](https://swagger.io/docs/specification/authentication/oauth2/) auth. | tokenUrl, authorizationUrl, scope | // @securitydefinitions.oauth2.accessCode OAuth2AccessCode |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| parameters annotation | example |
|
||||
|-----------------------|----------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| in | // @in header |
|
||||
| name | // @name Authorization |
|
||||
| tokenUrl | // @tokenUrl https://example.com/oauth/token |
|
||||
| authorizationurl | // @authorizationurl https://example.com/oauth/authorize |
|
||||
| scope.hoge | // @scope.write Grants write access |
|
||||
|
||||
# API Operation
|
||||
|
||||
**Example**
|
||||
[celler/controller](https://github.com/swaggo/swag/tree/master/example/celler/controller)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| annotation | description |
|
||||
|--------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| description | A verbose explanation of the operation behavior. |
|
||||
| id | A unique string used to identify the operation. Must be unique among all API operations. |
|
||||
| tags | A list of tags to each API operation that separated by commas. |
|
||||
| summary | A short summary of what the operation does. |
|
||||
| accept | A list of MIME types the APIs can consume. Value MUST be as described under [Mime Types](#mime-types). |
|
||||
| produce | A list of MIME types the APIs can produce. Value MUST be as described under [Mime Types](#mime-types). |
|
||||
| param | Parameters that separated by spaces. `param name`,`param type`,`data type`,`is mandatory?`,`comment` `attribute(optional)` |
|
||||
| security | [Security](#security) to each API operation. |
|
||||
| success | Success response that separated by spaces. `return code`,`{param type}`,`data type`,`comment` |
|
||||
| failure | Failure response that separated by spaces. `return code`,`{param type}`,`data type`,`comment` |
|
||||
| router | Path definition that separated by spaces. `path`,`[httpMethod]` |
|
||||
|
||||
## Mime Types
|
||||
|
||||
| Mime Type | annotation |
|
||||
|-----------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| application/json | application/json, json |
|
||||
| text/xml | text/xml, xml |
|
||||
| text/plain | text/plain, plain |
|
||||
| html | text/html, html |
|
||||
| multipart/form-data | multipart/form-data, mpfd |
|
||||
| application/x-www-form-urlencoded | application/x-www-form-urlencoded, x-www-form-urlencoded |
|
||||
| application/vnd.api+json | application/vnd.api+json, json-api |
|
||||
| application/x-json-stream | application/x-json-stream, json-stream |
|
||||
| application/octet-stream | application/octet-stream, octet-stream |
|
||||
| image/png | image/png, png |
|
||||
| image/jpeg | image/jpeg, jpeg |
|
||||
| image/gif | image/gif, gif |
|
||||
|
||||
## Security
|
||||
|
||||
General API info.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// @securityDefinitions.basic BasicAuth
|
||||
|
||||
// @securitydefinitions.oauth2.application OAuth2Application
|
||||
// @tokenUrl https://example.com/oauth/token
|
||||
// @scope.write Grants write access
|
||||
// @scope.admin Grants read and write access to administrative information
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Each API operation.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// @Security ApiKeyAuth
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Make it AND condition
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// @Security ApiKeyAuth
|
||||
// @Security OAuth2Application[write, admin]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Param Type
|
||||
|
||||
- object (struct)
|
||||
- string (string)
|
||||
- integer (int, uint, uint32, uint64)
|
||||
- number (float32)
|
||||
- boolean (bool)
|
||||
- array
|
||||
|
||||
## Data Type
|
||||
|
||||
- string (string)
|
||||
- integer (int, uint, uint32, uint64)
|
||||
- number (float32)
|
||||
- boolean (bool)
|
||||
- user defined struct
|
||||
|
||||
## Attribute
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// @Param enumstring query string false "string enums" Enums(A, B, C)
|
||||
// @Param enumint query int false "int enums" Enums(1, 2, 3)
|
||||
// @Param enumnumber query number false "int enums" Enums(1.1, 1.2, 1.3)
|
||||
// @Param string query string false "string valid" minlength(5) maxlength(10)
|
||||
// @Param int query int false "int valid" mininum(1) maxinum(10)
|
||||
// @Param default query string false "string default" default(A)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It also works for the struct fields:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
type Foo struct {
|
||||
Bar string `minLength:"4" maxLength:"16"`
|
||||
Baz int `minimum:"10" maximum:"20" default:"15"`
|
||||
Qux []string `enums:"foo,bar,baz"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Available
|
||||
|
||||
Field Name | Type | Description
|
||||
---|:---:|---
|
||||
<a name="parameterDefault"></a>default | * | Declares the value of the parameter that the server will use if none is provided, for example a "count" to control the number of results per page might default to 100 if not supplied by the client in the request. (Note: "default" has no meaning for required parameters.) See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-6.2. Unlike JSON Schema this value MUST conform to the defined [`type`](#parameterType) for this parameter.
|
||||
<a name="parameterMaximum"></a>maximum | `number` | See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.1.2.
|
||||
<a name="parameterMinimum"></a>minimum | `number` | See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.1.3.
|
||||
<a name="parameterMaxLength"></a>maxLength | `integer` | See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.2.1.
|
||||
<a name="parameterMinLength"></a>minLength | `integer` | See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.2.2.
|
||||
<a name="parameterEnums"></a>enums | [\*] | See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.5.1.
|
||||
|
||||
### Future
|
||||
|
||||
Field Name | Type | Description
|
||||
---|:---:|---
|
||||
<a name="parameterFormat"></a>format | `string` | The extending format for the previously mentioned [`type`](#parameterType). See [Data Type Formats](#dataTypeFormat) for further details.
|
||||
<a name="parameterMultipleOf"></a>multipleOf | `number` | See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.1.1.
|
||||
<a name="parameterPattern"></a>pattern | `string` | See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.2.3.
|
||||
<a name="parameterMaxItems"></a>maxItems | `integer` | See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.3.2.
|
||||
<a name="parameterMinItems"></a>minItems | `integer` | See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.3.3.
|
||||
<a name="parameterUniqueItems"></a>uniqueItems | `boolean` | See https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-fge-json-schema-validation-00#section-5.3.4.
|
||||
<a name="parameterCollectionFormat"></a>collectionFormat | `string` | Determines the format of the array if type array is used. Possible values are: <ul><li>`csv` - comma separated values `foo,bar`. <li>`ssv` - space separated values `foo bar`. <li>`tsv` - tab separated values `foo\tbar`. <li>`pipes` - pipe separated values <code>foo|bar</code>. <li>`multi` - corresponds to multiple parameter instances instead of multiple values for a single instance `foo=bar&foo=baz`. This is valid only for parameters [`in`](#parameterIn) "query" or "formData". </ul> Default value is `csv`.
|
||||
|
||||
## TIPS
|
||||
|
||||
### User defined structure with an array type
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// @Success 200 {array} model.Account <-- This is a user defined struct.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
package model
|
||||
|
||||
type Account struct {
|
||||
ID int `json:"id" example:"1"`
|
||||
Name string `json:"name" example:"account name"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Use multiple path params
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
/// ...
|
||||
// @Param group_id path int true "Group ID"
|
||||
// @Param account_id path int true "Account ID"
|
||||
// ...
|
||||
// @Router /examples/groups/{group_id}/accounts/{account_id} [get]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Example value of struct
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
type Account struct {
|
||||
ID int `json:"id" example:"1"`
|
||||
Name string `json:"name" example:"account name"`
|
||||
PhotoUrls []string `json:"photo_urls" example:"http://test/image/1.jpg,http://test/image/2.jpg"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Description of struct
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
type Account struct {
|
||||
// ID this is userid
|
||||
ID int `json:"id"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Override swagger type of a struct field
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
type Account struct {
|
||||
// Override primitive type by simply specifying it via `swaggertype` tag
|
||||
ID sql.NullInt64 `json:"id" swaggertype:"integer"`
|
||||
|
||||
// Array types can be overridden using "array,<prim_type>" format
|
||||
Coeffs []big.Float `json:"coeffs" swaggertype:"array,number"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## About the Project
|
||||
This project was inspired by [yvasiyarov/swagger](https://github.com/yvasiyarov/swagger) but we simplified the usage and added support a variety of [web frameworks](#supported-web-frameworks).
|
||||
5
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/doc.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
5
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/doc.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Package swag converts Go annotations to Swagger Documentation 2.0.
|
||||
See https://github.com/swaggo/swag for more information about swag.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
package swag // import "github.com/swaggo/swag"
|
||||
126
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/gen/gen.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
126
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/gen/gen.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
|
||||
package gen
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"encoding/json"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path"
|
||||
"text/template"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/ghodss/yaml"
|
||||
"github.com/pkg/errors"
|
||||
"github.com/swaggo/swag"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Gen presents a generate tool for swag.
|
||||
type Gen struct {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// New creates a new Gen.
|
||||
func New() *Gen {
|
||||
return &Gen{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Build builds swagger json file for gived searchDir and mainAPIFile. Returns json
|
||||
func (g *Gen) Build(searchDir, mainAPIFile, swaggerConfDir, propNamingStrategy string) error {
|
||||
log.Println("Generate swagger docs....")
|
||||
p := swag.New()
|
||||
p.PropNamingStrategy = propNamingStrategy
|
||||
p.ParseAPI(searchDir, mainAPIFile)
|
||||
swagger := p.GetSwagger()
|
||||
|
||||
b, err := json.MarshalIndent(swagger, "", " ")
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
os.MkdirAll(path.Join(searchDir, "docs"), os.ModePerm)
|
||||
docs, err := os.Create(path.Join(searchDir, "docs", "docs.go"))
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer docs.Close()
|
||||
|
||||
os.Mkdir(swaggerConfDir, os.ModePerm)
|
||||
swaggerJSON, err := os.Create(path.Join(swaggerConfDir, "swagger.json"))
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
defer swaggerJSON.Close()
|
||||
swaggerJSON.Write(b)
|
||||
|
||||
swaggerYAML, err := os.Create(path.Join(swaggerConfDir, "swagger.yaml"))
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
defer swaggerYAML.Close()
|
||||
y, err := yaml.JSONToYAML(b)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return errors.Wrap(err, "cannot covert json to yaml")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
swaggerYAML.Write(y)
|
||||
|
||||
if err := packageTemplate.Execute(docs, struct {
|
||||
Timestamp time.Time
|
||||
Doc string
|
||||
}{
|
||||
Timestamp: time.Now(),
|
||||
Doc: "`" + string(b) + "`",
|
||||
}); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
log.Printf("create docs.go at %+v", docs.Name())
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var packageTemplate = template.Must(template.New("").Parse(`// GENERATED BY THE COMMAND ABOVE; DO NOT EDIT
|
||||
// This file was generated by swaggo/swag at
|
||||
// {{ .Timestamp }}
|
||||
|
||||
package docs
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/alecthomas/template"
|
||||
"github.com/swaggo/swag"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var doc = {{.Doc}}
|
||||
|
||||
type swaggerInfo struct {
|
||||
Version string
|
||||
Host string
|
||||
BasePath string
|
||||
Title string
|
||||
Description string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SwaggerInfo holds exported Swagger Info so clients can modify it
|
||||
var SwaggerInfo swaggerInfo
|
||||
|
||||
type s struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s *s) ReadDoc() string {
|
||||
t, err := template.New("swagger_info").Parse(doc)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return doc
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var tpl bytes.Buffer
|
||||
if err := t.Execute(&tpl, SwaggerInfo); err != nil {
|
||||
return doc
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return tpl.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
swag.Register(swag.Name, &s{})
|
||||
}
|
||||
`))
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/license
generated
vendored
Normal file
21
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/license
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2017 Eason Lin
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
674
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/operation.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
674
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/operation.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,674 @@
|
||||
package swag
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
goparser "go/parser"
|
||||
"go/token"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"regexp"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/go-openapi/jsonreference"
|
||||
"github.com/go-openapi/spec"
|
||||
"github.com/pkg/errors"
|
||||
"golang.org/x/tools/go/loader"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Operation describes a single API operation on a path.
|
||||
// For more information: https://github.com/swaggo/swag#api-operation
|
||||
type Operation struct {
|
||||
HTTPMethod string
|
||||
Path string
|
||||
spec.Operation
|
||||
|
||||
parser *Parser
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewOperation creates a new Operation with default properties.
|
||||
// map[int]Response
|
||||
func NewOperation() *Operation {
|
||||
return &Operation{
|
||||
HTTPMethod: "get",
|
||||
Operation: spec.Operation{
|
||||
OperationProps: spec.OperationProps{},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseComment parses comment for given comment string and returns error if error occurs.
|
||||
func (operation *Operation) ParseComment(comment string, astFile *ast.File) error {
|
||||
commentLine := strings.TrimSpace(strings.TrimLeft(comment, "//"))
|
||||
if len(commentLine) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
attribute := strings.Fields(commentLine)[0]
|
||||
lineRemainder := strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):])
|
||||
switch strings.ToLower(attribute) {
|
||||
case "@description":
|
||||
if operation.Description == "" {
|
||||
operation.Description = lineRemainder
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
operation.Description += "<br>" + lineRemainder
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "@summary":
|
||||
operation.Summary = lineRemainder
|
||||
case "@id":
|
||||
operation.ID = lineRemainder
|
||||
case "@tags":
|
||||
operation.ParseTagsComment(lineRemainder)
|
||||
case "@accept":
|
||||
if err := operation.ParseAcceptComment(lineRemainder); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "@produce":
|
||||
if err := operation.ParseProduceComment(lineRemainder); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "@param":
|
||||
if err := operation.ParseParamComment(lineRemainder, astFile); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "@success", "@failure":
|
||||
if err := operation.ParseResponseComment(lineRemainder, astFile); err != nil {
|
||||
if err := operation.ParseEmptyResponseComment(lineRemainder); err != nil {
|
||||
if err := operation.ParseEmptyResponseOnly(lineRemainder); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case "@router":
|
||||
if err := operation.ParseRouterComment(strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):])); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "@security":
|
||||
if err := operation.ParseSecurityComment(strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):])); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseParamComment parses params return []string of param properties
|
||||
// @Param queryText form string true "The email for login"
|
||||
// [param name] [paramType] [data type] [is mandatory?] [Comment]
|
||||
// @Param some_id path int true "Some ID"
|
||||
func (operation *Operation) ParseParamComment(commentLine string, astFile *ast.File) error {
|
||||
re := regexp.MustCompile(`([-\w]+)[\s]+([\w]+)[\s]+([\S.]+)[\s]+([\w]+)[\s]+"([^"]+)"`)
|
||||
matches := re.FindStringSubmatch(commentLine)
|
||||
if len(matches) != 6 {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("can not parse param comment \"%s\"", commentLine)
|
||||
}
|
||||
name := matches[1]
|
||||
paramType := matches[2]
|
||||
|
||||
schemaType := matches[3]
|
||||
|
||||
requiredText := strings.ToLower(matches[4])
|
||||
required := requiredText == "true" || requiredText == "required"
|
||||
description := matches[5]
|
||||
|
||||
var param spec.Parameter
|
||||
|
||||
//five possible parameter types.
|
||||
switch paramType {
|
||||
case "query", "path", "header":
|
||||
param = createParameter(paramType, description, name, TransToValidSchemeType(schemaType), required)
|
||||
case "body":
|
||||
param = createParameter(paramType, description, name, "object", required) // TODO: if Parameter types can be objects, but also primitives and arrays
|
||||
// TODO: this snippets have to extract out
|
||||
refSplit := strings.Split(schemaType, ".")
|
||||
if len(refSplit) == 2 {
|
||||
pkgName := refSplit[0]
|
||||
typeName := refSplit[1]
|
||||
if typeSpec, ok := operation.parser.TypeDefinitions[pkgName][typeName]; ok {
|
||||
operation.parser.registerTypes[schemaType] = typeSpec
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
var typeSpec *ast.TypeSpec
|
||||
if astFile != nil {
|
||||
for _, imp := range astFile.Imports {
|
||||
if imp.Name != nil && imp.Name.Name == pkgName { // the import had an alias that matched
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
impPath := strings.Replace(imp.Path.Value, `"`, ``, -1)
|
||||
if strings.HasSuffix(impPath, "/"+pkgName) {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
typeSpec, err = findTypeDef(impPath, typeName)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return errors.Wrapf(err, "can not find ref type: %q", schemaType)
|
||||
}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if typeSpec == nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("can not find ref type:\"%s\"", schemaType)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
operation.parser.TypeDefinitions[pkgName][typeName] = typeSpec
|
||||
operation.parser.registerTypes[schemaType] = typeSpec
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
param.Schema.Ref = spec.Ref{
|
||||
Ref: jsonreference.MustCreateRef("#/definitions/" + schemaType),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "formData":
|
||||
param = createParameter(paramType, description, name, TransToValidSchemeType(schemaType), required)
|
||||
}
|
||||
param = operation.parseAndExtractionParamAttribute(commentLine, schemaType, param)
|
||||
operation.Operation.Parameters = append(operation.Operation.Parameters, param)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var regexAttributes = map[string]*regexp.Regexp{
|
||||
// for Enums(A, B)
|
||||
"enums": regexp.MustCompile(`(?i)enums\(.*\)`),
|
||||
// for Minimum(0)
|
||||
"maxinum": regexp.MustCompile(`(?i)maxinum\(.*\)`),
|
||||
// for Maximum(0)
|
||||
"mininum": regexp.MustCompile(`(?i)mininum\(.*\)`),
|
||||
// for Maximum(0)
|
||||
"default": regexp.MustCompile(`(?i)default\(.*\)`),
|
||||
// for minlength(0)
|
||||
"minlength": regexp.MustCompile(`(?i)minlength\(.*\)`),
|
||||
// for maxlength(0)
|
||||
"maxlength": regexp.MustCompile(`(?i)maxlength\(.*\)`),
|
||||
// for format(email)
|
||||
"format": regexp.MustCompile(`(?i)format\(.*\)`),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (operation *Operation) parseAndExtractionParamAttribute(commentLine, schemaType string, param spec.Parameter) spec.Parameter {
|
||||
schemaType = TransToValidSchemeType(schemaType)
|
||||
for attrKey, re := range regexAttributes {
|
||||
switch attrKey {
|
||||
case "enums":
|
||||
attr := re.FindString(commentLine)
|
||||
l := strings.Index(attr, "(")
|
||||
r := strings.Index(attr, ")")
|
||||
if !(l == -1 && r == -1) {
|
||||
enums := strings.Split(attr[l+1:r], ",")
|
||||
for _, e := range enums {
|
||||
e = strings.TrimSpace(e)
|
||||
param.Enum = append(param.Enum, defineType(schemaType, e))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "maxinum":
|
||||
attr := re.FindString(commentLine)
|
||||
l := strings.Index(attr, "(")
|
||||
r := strings.Index(attr, ")")
|
||||
if !(l == -1 && r == -1) {
|
||||
if schemaType != "integer" && schemaType != "number" {
|
||||
log.Panicf("maxinum is attribute to set to a number. comment=%s got=%s", commentLine, schemaType)
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr = strings.TrimSpace(attr[l+1 : r])
|
||||
n, err := strconv.ParseFloat(attr, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Panicf("maximum is allow only a number. comment=%s got=%s", commentLine, attr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
param.Maximum = &n
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "mininum":
|
||||
attr := re.FindString(commentLine)
|
||||
l := strings.Index(attr, "(")
|
||||
r := strings.Index(attr, ")")
|
||||
if !(l == -1 && r == -1) {
|
||||
if schemaType != "integer" && schemaType != "number" {
|
||||
log.Panicf("mininum is attribute to set to a number. comment=%s got=%s", commentLine, schemaType)
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr = strings.TrimSpace(attr[l+1 : r])
|
||||
n, err := strconv.ParseFloat(attr, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Panicf("mininum is allow only a number got=%s", attr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
param.Minimum = &n
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "default":
|
||||
attr := re.FindString(commentLine)
|
||||
l := strings.Index(attr, "(")
|
||||
r := strings.Index(attr, ")")
|
||||
if !(l == -1 && r == -1) {
|
||||
attr = strings.TrimSpace(attr[l+1 : r])
|
||||
param.Default = defineType(schemaType, attr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "maxlength":
|
||||
attr := re.FindString(commentLine)
|
||||
l := strings.Index(attr, "(")
|
||||
r := strings.Index(attr, ")")
|
||||
if !(l == -1 && r == -1) {
|
||||
if schemaType != "string" {
|
||||
log.Panicf("maxlength is attribute to set to a number. comment=%s got=%s", commentLine, schemaType)
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr = strings.TrimSpace(attr[l+1 : r])
|
||||
n, err := strconv.ParseInt(attr, 10, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Panicf("maxlength is allow only a number got=%s", attr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
param.MaxLength = &n
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "minlength":
|
||||
attr := re.FindString(commentLine)
|
||||
l := strings.Index(attr, "(")
|
||||
r := strings.Index(attr, ")")
|
||||
if !(l == -1 && r == -1) {
|
||||
if schemaType != "string" {
|
||||
log.Panicf("maxlength is attribute to set to a number. comment=%s got=%s", commentLine, schemaType)
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr = strings.TrimSpace(attr[l+1 : r])
|
||||
n, err := strconv.ParseInt(attr, 10, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Panicf("minlength is allow only a number got=%s", attr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
param.MinLength = &n
|
||||
}
|
||||
case "format":
|
||||
attr := re.FindString(commentLine)
|
||||
l := strings.Index(attr, "(")
|
||||
r := strings.Index(attr, ")")
|
||||
if !(l == -1 && r == -1) {
|
||||
param.Format = strings.TrimSpace(attr[l+1 : r])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return param
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// defineType enum value define the type (object and array unsupported)
|
||||
func defineType(schemaType string, value string) interface{} {
|
||||
schemaType = TransToValidSchemeType(schemaType)
|
||||
switch schemaType {
|
||||
case "string":
|
||||
return value
|
||||
case "number":
|
||||
v, err := strconv.ParseFloat(value, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf("enum value %s can't convert to %s err: %s", value, schemaType, err))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
case "integer":
|
||||
v, err := strconv.Atoi(value)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf("enum value %s can't convert to %s err: %s", value, schemaType, err))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
case "boolean":
|
||||
v, err := strconv.ParseBool(value)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf("enum value %s can't convert to %s err: %s", value, schemaType, err))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf("%s is unsupported type in enum value", schemaType))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseTagsComment parses comment for given `tag` comment string.
|
||||
func (operation *Operation) ParseTagsComment(commentLine string) {
|
||||
tags := strings.Split(commentLine, ",")
|
||||
for _, tag := range tags {
|
||||
operation.Tags = append(operation.Tags, strings.TrimSpace(tag))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseAcceptComment parses comment for given `accept` comment string.
|
||||
func (operation *Operation) ParseAcceptComment(commentLine string) error {
|
||||
accepts := strings.Split(commentLine, ",")
|
||||
for _, a := range accepts {
|
||||
switch a {
|
||||
case "json", "application/json":
|
||||
operation.Consumes = append(operation.Consumes, "application/json")
|
||||
case "xml", "text/xml":
|
||||
operation.Consumes = append(operation.Consumes, "text/xml")
|
||||
case "plain", "text/plain":
|
||||
operation.Consumes = append(operation.Consumes, "text/plain")
|
||||
case "html", "text/html":
|
||||
operation.Consumes = append(operation.Consumes, "text/html")
|
||||
case "mpfd", "multipart/form-data":
|
||||
operation.Consumes = append(operation.Consumes, "multipart/form-data")
|
||||
case "x-www-form-urlencoded", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded":
|
||||
operation.Consumes = append(operation.Consumes, "application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
|
||||
case "json-api", "application/vnd.api+json":
|
||||
operation.Consumes = append(operation.Consumes, "application/vnd.api+json")
|
||||
case "json-stream", "application/x-json-stream":
|
||||
operation.Consumes = append(operation.Consumes, "application/x-json-stream")
|
||||
case "octet-stream", "application/octet-stream":
|
||||
operation.Consumes = append(operation.Consumes, "application/octet-stream")
|
||||
case "png", "image/png":
|
||||
operation.Consumes = append(operation.Consumes, "image/png")
|
||||
case "jpeg", "image/jpeg":
|
||||
operation.Consumes = append(operation.Consumes, "image/jpeg")
|
||||
case "gif", "image/gif":
|
||||
operation.Consumes = append(operation.Consumes, "image/gif")
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%v accept type can't accepted", a)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseProduceComment parses comment for gived `produce` comment string.
|
||||
func (operation *Operation) ParseProduceComment(commentLine string) error {
|
||||
produces := strings.Split(commentLine, ",")
|
||||
for _, a := range produces {
|
||||
switch a {
|
||||
case "json", "application/json":
|
||||
operation.Produces = append(operation.Produces, "application/json")
|
||||
case "xml", "text/xml":
|
||||
operation.Produces = append(operation.Produces, "text/xml")
|
||||
case "plain", "text/plain":
|
||||
operation.Produces = append(operation.Produces, "text/plain")
|
||||
case "html", "text/html":
|
||||
operation.Produces = append(operation.Produces, "text/html")
|
||||
case "mpfd", "multipart/form-data":
|
||||
operation.Produces = append(operation.Produces, "multipart/form-data")
|
||||
case "x-www-form-urlencoded", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded":
|
||||
operation.Produces = append(operation.Produces, "application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
|
||||
case "json-api", "application/vnd.api+json":
|
||||
operation.Produces = append(operation.Produces, "application/vnd.api+json")
|
||||
case "json-stream", "application/x-json-stream":
|
||||
operation.Produces = append(operation.Produces, "application/x-json-stream")
|
||||
case "octet-stream", "application/octet-stream":
|
||||
operation.Produces = append(operation.Produces, "application/octet-stream")
|
||||
case "png", "image/png":
|
||||
operation.Produces = append(operation.Produces, "image/png")
|
||||
case "jpeg", "image/jpeg":
|
||||
operation.Produces = append(operation.Produces, "image/jpeg")
|
||||
case "gif", "image/gif":
|
||||
operation.Produces = append(operation.Produces, "image/gif")
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%v produce type can't accepted", a)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseRouterComment parses comment for gived `router` comment string.
|
||||
func (operation *Operation) ParseRouterComment(commentLine string) error {
|
||||
re := regexp.MustCompile(`([\w\.\/\-{}\+]+)[^\[]+\[([^\]]+)`)
|
||||
var matches []string
|
||||
|
||||
if matches = re.FindStringSubmatch(commentLine); len(matches) != 3 {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("can not parse router comment \"%s\"", commentLine)
|
||||
}
|
||||
path := matches[1]
|
||||
httpMethod := matches[2]
|
||||
|
||||
operation.Path = path
|
||||
operation.HTTPMethod = strings.ToUpper(httpMethod)
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseSecurityComment parses comment for gived `security` comment string.
|
||||
func (operation *Operation) ParseSecurityComment(commentLine string) error {
|
||||
securitySource := commentLine[strings.Index(commentLine, "@Security")+1:]
|
||||
l := strings.Index(securitySource, "[")
|
||||
r := strings.Index(securitySource, "]")
|
||||
// exists scope
|
||||
if !(l == -1 && r == -1) {
|
||||
scopes := securitySource[l+1 : r]
|
||||
s := []string{}
|
||||
for _, scope := range strings.Split(scopes, ",") {
|
||||
scope = strings.TrimSpace(scope)
|
||||
s = append(s, scope)
|
||||
}
|
||||
securityKey := securitySource[0:l]
|
||||
securityMap := map[string][]string{}
|
||||
securityMap[securityKey] = append(securityMap[securityKey], s...)
|
||||
operation.Security = append(operation.Security, securityMap)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
securityKey := strings.TrimSpace(securitySource)
|
||||
securityMap := map[string][]string{}
|
||||
securityMap[securityKey] = []string{}
|
||||
operation.Security = append(operation.Security, securityMap)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// findTypeDef attempts to find the *ast.TypeSpec for a specific type given the
|
||||
// type's name and the package's import path
|
||||
func findTypeDef(importPath, typeName string) (*ast.TypeSpec, error) {
|
||||
cwd, err := os.Getwd()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
conf := loader.Config{
|
||||
ParserMode: goparser.SpuriousErrors,
|
||||
Cwd: cwd,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
conf.Import(importPath)
|
||||
|
||||
lprog, err := conf.Load()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If the pkg is vendored, the actual pkg path is going to resemble
|
||||
// something like "{importPath}/vendor/{importPath}"
|
||||
for k := range lprog.AllPackages {
|
||||
realPkgPath := k.Path()
|
||||
|
||||
if strings.Contains(realPkgPath, "vendor/"+importPath) {
|
||||
importPath = realPkgPath
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pkgInfo := lprog.Package(importPath)
|
||||
|
||||
if pkgInfo == nil {
|
||||
return nil, errors.New("package was nil")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: possibly cache pkgInfo since it's an expensive operation
|
||||
|
||||
for i := range pkgInfo.Files {
|
||||
for _, astDeclaration := range pkgInfo.Files[i].Decls {
|
||||
if generalDeclaration, ok := astDeclaration.(*ast.GenDecl); ok && generalDeclaration.Tok == token.TYPE {
|
||||
for _, astSpec := range generalDeclaration.Specs {
|
||||
if typeSpec, ok := astSpec.(*ast.TypeSpec); ok {
|
||||
if typeSpec.Name.String() == typeName {
|
||||
return typeSpec, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, errors.New("type spec not found")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseResponseComment parses comment for gived `response` comment string.
|
||||
func (operation *Operation) ParseResponseComment(commentLine string, astFile *ast.File) error {
|
||||
re := regexp.MustCompile(`([\d]+)[\s]+([\w\{\}]+)[\s]+([\w\-\.\/]+)[^"]*(.*)?`)
|
||||
var matches []string
|
||||
|
||||
if matches = re.FindStringSubmatch(commentLine); len(matches) != 5 {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("can not parse response comment \"%s\"", commentLine)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
response := spec.Response{}
|
||||
|
||||
code, _ := strconv.Atoi(matches[1])
|
||||
|
||||
responseDescription := strings.Trim(matches[4], "\"")
|
||||
if responseDescription == "" {
|
||||
responseDescription = http.StatusText(code)
|
||||
}
|
||||
response.Description = responseDescription
|
||||
|
||||
schemaType := strings.Trim(matches[2], "{}")
|
||||
refType := matches[3]
|
||||
|
||||
if operation.parser != nil { // checking refType has existing in 'TypeDefinitions'
|
||||
refSplit := strings.Split(refType, ".")
|
||||
if len(refSplit) == 2 {
|
||||
pkgName := refSplit[0]
|
||||
typeName := refSplit[1]
|
||||
|
||||
if typeSpec, ok := operation.parser.TypeDefinitions[pkgName][typeName]; ok {
|
||||
operation.parser.registerTypes[refType] = typeSpec
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
var typeSpec *ast.TypeSpec
|
||||
if astFile != nil {
|
||||
for _, imp := range astFile.Imports {
|
||||
if imp.Name != nil && imp.Name.Name == pkgName { // the import had an alias that matched
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
impPath := strings.Replace(imp.Path.Value, `"`, ``, -1)
|
||||
|
||||
if strings.HasSuffix(impPath, "/"+pkgName) {
|
||||
var err error
|
||||
|
||||
typeSpec, err = findTypeDef(impPath, typeName)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return errors.Wrapf(err, "can not find ref type: %q", refType)
|
||||
}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if typeSpec == nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("can not find ref type: %q", refType)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if _, ok := operation.parser.TypeDefinitions[pkgName]; !ok {
|
||||
operation.parser.TypeDefinitions[pkgName] = make(map[string]*ast.TypeSpec)
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
operation.parser.TypeDefinitions[pkgName][typeName] = typeSpec
|
||||
operation.parser.registerTypes[refType] = typeSpec
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// so we have to know all type in app
|
||||
//TODO: we might omitted schema.type if schemaType equals 'object'
|
||||
response.Schema = &spec.Schema{SchemaProps: spec.SchemaProps{Type: []string{schemaType}}}
|
||||
|
||||
if schemaType == "object" {
|
||||
response.Schema.Ref = spec.Ref{
|
||||
Ref: jsonreference.MustCreateRef("#/definitions/" + refType),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if schemaType == "array" {
|
||||
refType = TransToValidSchemeType(refType)
|
||||
if IsPrimitiveType(refType) {
|
||||
response.Schema.Items = &spec.SchemaOrArray{
|
||||
Schema: &spec.Schema{
|
||||
SchemaProps: spec.SchemaProps{
|
||||
Type: spec.StringOrArray{refType},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
response.Schema.Items = &spec.SchemaOrArray{
|
||||
Schema: &spec.Schema{
|
||||
SchemaProps: spec.SchemaProps{
|
||||
Ref: spec.Ref{Ref: jsonreference.MustCreateRef("#/definitions/" + refType)},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if operation.Responses == nil {
|
||||
operation.Responses = &spec.Responses{
|
||||
ResponsesProps: spec.ResponsesProps{
|
||||
StatusCodeResponses: make(map[int]spec.Response),
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
operation.Responses.StatusCodeResponses[code] = response
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseEmptyResponseComment parse only comment out status code and description,eg: @Success 200 "it's ok"
|
||||
func (operation *Operation) ParseEmptyResponseComment(commentLine string) error {
|
||||
re := regexp.MustCompile(`([\d]+)[\s]+"(.*)"`)
|
||||
var matches []string
|
||||
|
||||
if matches = re.FindStringSubmatch(commentLine); len(matches) != 3 {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("can not parse response comment \"%s\"", commentLine)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
response := spec.Response{}
|
||||
|
||||
code, _ := strconv.Atoi(matches[1])
|
||||
|
||||
response.Description = strings.Trim(matches[2], "")
|
||||
|
||||
if operation.Responses == nil {
|
||||
operation.Responses = &spec.Responses{
|
||||
ResponsesProps: spec.ResponsesProps{
|
||||
StatusCodeResponses: make(map[int]spec.Response),
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
operation.Responses.StatusCodeResponses[code] = response
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//ParseEmptyResponseOnly parse only comment out status code ,eg: @Success 200
|
||||
func (operation *Operation) ParseEmptyResponseOnly(commentLine string) error {
|
||||
response := spec.Response{}
|
||||
|
||||
code, err := strconv.Atoi(commentLine)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("can not parse response comment \"%s\"", commentLine)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if operation.Responses == nil {
|
||||
operation.Responses = &spec.Responses{
|
||||
ResponsesProps: spec.ResponsesProps{
|
||||
StatusCodeResponses: make(map[int]spec.Response),
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
operation.Responses.StatusCodeResponses[code] = response
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// createParameter returns swagger spec.Parameter for gived paramType, description, paramName, schemaType, required
|
||||
func createParameter(paramType, description, paramName, schemaType string, required bool) spec.Parameter {
|
||||
// //five possible parameter types. query, path, body, header, form
|
||||
paramProps := spec.ParamProps{
|
||||
Name: paramName,
|
||||
Description: description,
|
||||
Required: required,
|
||||
In: paramType,
|
||||
}
|
||||
if paramType == "body" {
|
||||
paramProps.Schema = &spec.Schema{
|
||||
SchemaProps: spec.SchemaProps{
|
||||
Type: []string{schemaType},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
parameter := spec.Parameter{
|
||||
ParamProps: paramProps,
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parameter
|
||||
}
|
||||
parameter := spec.Parameter{
|
||||
ParamProps: paramProps,
|
||||
SimpleSchema: spec.SimpleSchema{
|
||||
Type: schemaType,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parameter
|
||||
}
|
||||
892
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/parser.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
892
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/parser.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,892 @@
|
||||
package swag
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
goparser "go/parser"
|
||||
"go/token"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/go-openapi/jsonreference"
|
||||
"github.com/go-openapi/spec"
|
||||
"github.com/pkg/errors"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// CamelCase indicates using CamelCase strategy for struct field.
|
||||
CamelCase = "camelcase"
|
||||
|
||||
// PascalCase indicates using PascalCase strategy for struct field.
|
||||
PascalCase = "pascalcase"
|
||||
|
||||
// SnakeCase indicates using SnakeCase strategy for struct field.
|
||||
SnakeCase = "snakecase"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Parser implements a parser for Go source files.
|
||||
type Parser struct {
|
||||
// swagger represents the root document object for the API specification
|
||||
swagger *spec.Swagger
|
||||
|
||||
//files is a map that stores map[real_go_file_path][astFile]
|
||||
files map[string]*ast.File
|
||||
|
||||
// TypeDefinitions is a map that stores [package name][type name][*ast.TypeSpec]
|
||||
TypeDefinitions map[string]map[string]*ast.TypeSpec
|
||||
|
||||
// CustomPrimitiveTypes is a map that stores custom primitive types to actual golang types [type name][string]
|
||||
CustomPrimitiveTypes map[string]string
|
||||
|
||||
//registerTypes is a map that stores [refTypeName][*ast.TypeSpec]
|
||||
registerTypes map[string]*ast.TypeSpec
|
||||
|
||||
PropNamingStrategy string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// New creates a new Parser with default properties.
|
||||
func New() *Parser {
|
||||
parser := &Parser{
|
||||
swagger: &spec.Swagger{
|
||||
SwaggerProps: spec.SwaggerProps{
|
||||
Info: &spec.Info{
|
||||
InfoProps: spec.InfoProps{
|
||||
Contact: &spec.ContactInfo{},
|
||||
License: &spec.License{},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
Paths: &spec.Paths{
|
||||
Paths: make(map[string]spec.PathItem),
|
||||
},
|
||||
Definitions: make(map[string]spec.Schema),
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
files: make(map[string]*ast.File),
|
||||
TypeDefinitions: make(map[string]map[string]*ast.TypeSpec),
|
||||
CustomPrimitiveTypes: make(map[string]string),
|
||||
registerTypes: make(map[string]*ast.TypeSpec),
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parser
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseAPI parses general api info for gived searchDir and mainAPIFile
|
||||
func (parser *Parser) ParseAPI(searchDir string, mainAPIFile string) error {
|
||||
log.Println("Generate general API Info")
|
||||
if err := parser.getAllGoFileInfo(searchDir); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
parser.ParseGeneralAPIInfo(path.Join(searchDir, mainAPIFile))
|
||||
|
||||
for _, astFile := range parser.files {
|
||||
parser.ParseType(astFile)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, astFile := range parser.files {
|
||||
parser.ParseRouterAPIInfo(astFile)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
parser.ParseDefinitions()
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseGeneralAPIInfo parses general api info for gived mainAPIFile path
|
||||
func (parser *Parser) ParseGeneralAPIInfo(mainAPIFile string) error {
|
||||
fileSet := token.NewFileSet()
|
||||
fileTree, err := goparser.ParseFile(fileSet, mainAPIFile, nil, goparser.ParseComments)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return errors.Wrap(err, "cannot parse soure files")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
parser.swagger.Swagger = "2.0"
|
||||
securityMap := map[string]*spec.SecurityScheme{}
|
||||
|
||||
// templated defaults
|
||||
parser.swagger.Info.Version = "{{.Version}}"
|
||||
parser.swagger.Info.Title = "{{.Title}}"
|
||||
parser.swagger.Info.Description = "{{.Description}}"
|
||||
parser.swagger.Host = "{{.Host}}"
|
||||
parser.swagger.BasePath = "{{.BasePath}}"
|
||||
|
||||
if fileTree.Comments != nil {
|
||||
for _, comment := range fileTree.Comments {
|
||||
comments := strings.Split(comment.Text(), "\n")
|
||||
for _, commentLine := range comments {
|
||||
attribute := strings.ToLower(strings.Split(commentLine, " ")[0])
|
||||
switch attribute {
|
||||
case "@version":
|
||||
parser.swagger.Info.Version = strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):])
|
||||
case "@title":
|
||||
parser.swagger.Info.Title = strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):])
|
||||
case "@description":
|
||||
parser.swagger.Info.Description = strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):])
|
||||
case "@termsofservice":
|
||||
parser.swagger.Info.TermsOfService = strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):])
|
||||
case "@contact.name":
|
||||
parser.swagger.Info.Contact.Name = strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):])
|
||||
case "@contact.email":
|
||||
parser.swagger.Info.Contact.Email = strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):])
|
||||
case "@contact.url":
|
||||
parser.swagger.Info.Contact.URL = strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):])
|
||||
case "@license.name":
|
||||
parser.swagger.Info.License.Name = strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):])
|
||||
case "@license.url":
|
||||
parser.swagger.Info.License.URL = strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):])
|
||||
case "@host":
|
||||
parser.swagger.Host = strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):])
|
||||
case "@basepath":
|
||||
parser.swagger.BasePath = strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):])
|
||||
case "@schemes":
|
||||
parser.swagger.Schemes = GetSchemes(commentLine)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(comments); i++ {
|
||||
attribute := strings.ToLower(strings.Split(comments[i], " ")[0])
|
||||
switch attribute {
|
||||
case "@securitydefinitions.basic":
|
||||
securityMap[strings.TrimSpace(comments[i][len(attribute):])] = spec.BasicAuth()
|
||||
case "@securitydefinitions.apikey":
|
||||
attrMap := map[string]string{}
|
||||
for _, v := range comments[i+1:] {
|
||||
securityAttr := strings.ToLower(strings.Split(v, " ")[0])
|
||||
if securityAttr == "@in" || securityAttr == "@name" {
|
||||
attrMap[securityAttr] = strings.TrimSpace(v[len(securityAttr):])
|
||||
}
|
||||
// next securityDefinitions
|
||||
if strings.Index(securityAttr, "@securitydefinitions.") == 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(attrMap) != 2 {
|
||||
log.Panic("@securitydefinitions.apikey is @name and @in required")
|
||||
}
|
||||
securityMap[strings.TrimSpace(comments[i][len(attribute):])] = spec.APIKeyAuth(attrMap["@name"], attrMap["@in"])
|
||||
case "@securitydefinitions.oauth2.application":
|
||||
attrMap := map[string]string{}
|
||||
scopes := map[string]string{}
|
||||
for _, v := range comments[i+1:] {
|
||||
securityAttr := strings.ToLower(strings.Split(v, " ")[0])
|
||||
if securityAttr == "@tokenurl" {
|
||||
attrMap[securityAttr] = strings.TrimSpace(v[len(securityAttr):])
|
||||
} else if isExistsScope(securityAttr) {
|
||||
scopes[getScopeScheme(securityAttr)] = v[len(securityAttr):]
|
||||
}
|
||||
// next securityDefinitions
|
||||
if strings.Index(securityAttr, "@securitydefinitions.") == 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(attrMap) != 1 {
|
||||
log.Panic("@securitydefinitions.oauth2.application is @tokenUrl required")
|
||||
}
|
||||
securityScheme := spec.OAuth2Application(attrMap["@tokenurl"])
|
||||
for scope, description := range scopes {
|
||||
securityScheme.AddScope(scope, description)
|
||||
}
|
||||
securityMap[strings.TrimSpace(comments[i][len(attribute):])] = securityScheme
|
||||
case "@securitydefinitions.oauth2.implicit":
|
||||
attrMap := map[string]string{}
|
||||
scopes := map[string]string{}
|
||||
for _, v := range comments[i+1:] {
|
||||
securityAttr := strings.ToLower(strings.Split(v, " ")[0])
|
||||
if securityAttr == "@authorizationurl" {
|
||||
attrMap[securityAttr] = strings.TrimSpace(v[len(securityAttr):])
|
||||
} else if isExistsScope(securityAttr) {
|
||||
scopes[getScopeScheme(securityAttr)] = v[len(securityAttr):]
|
||||
}
|
||||
// next securityDefinitions
|
||||
if strings.Index(securityAttr, "@securitydefinitions.") == 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(attrMap) != 1 {
|
||||
log.Panic("@securitydefinitions.oauth2.implicit is @authorizationUrl required")
|
||||
}
|
||||
securityScheme := spec.OAuth2Implicit(attrMap["@authorizationurl"])
|
||||
for scope, description := range scopes {
|
||||
securityScheme.AddScope(scope, description)
|
||||
}
|
||||
securityMap[strings.TrimSpace(comments[i][len(attribute):])] = securityScheme
|
||||
case "@securitydefinitions.oauth2.password":
|
||||
attrMap := map[string]string{}
|
||||
scopes := map[string]string{}
|
||||
for _, v := range comments[i+1:] {
|
||||
securityAttr := strings.ToLower(strings.Split(v, " ")[0])
|
||||
if securityAttr == "@tokenurl" {
|
||||
attrMap[securityAttr] = strings.TrimSpace(v[len(securityAttr):])
|
||||
} else if isExistsScope(securityAttr) {
|
||||
scopes[getScopeScheme(securityAttr)] = v[len(securityAttr):]
|
||||
}
|
||||
// next securityDefinitions
|
||||
if strings.Index(securityAttr, "@securitydefinitions.") == 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(attrMap) != 1 {
|
||||
log.Panic("@securitydefinitions.oauth2.password is @tokenUrl required")
|
||||
}
|
||||
securityScheme := spec.OAuth2Password(attrMap["@tokenurl"])
|
||||
for scope, description := range scopes {
|
||||
securityScheme.AddScope(scope, description)
|
||||
}
|
||||
securityMap[strings.TrimSpace(comments[i][len(attribute):])] = securityScheme
|
||||
case "@securitydefinitions.oauth2.accesscode":
|
||||
attrMap := map[string]string{}
|
||||
scopes := map[string]string{}
|
||||
for _, v := range comments[i+1:] {
|
||||
securityAttr := strings.ToLower(strings.Split(v, " ")[0])
|
||||
if securityAttr == "@tokenurl" || securityAttr == "@authorizationurl" {
|
||||
attrMap[securityAttr] = strings.TrimSpace(v[len(securityAttr):])
|
||||
} else if isExistsScope(securityAttr) {
|
||||
scopes[getScopeScheme(securityAttr)] = v[len(securityAttr):]
|
||||
}
|
||||
// next securityDefinitions
|
||||
if strings.Index(securityAttr, "@securitydefinitions.") == 0 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(attrMap) != 2 {
|
||||
log.Panic("@securitydefinitions.oauth2.accessCode is @tokenUrl and @authorizationUrl required")
|
||||
}
|
||||
securityScheme := spec.OAuth2AccessToken(attrMap["@authorizationurl"], attrMap["@tokenurl"])
|
||||
for scope, description := range scopes {
|
||||
securityScheme.AddScope(scope, description)
|
||||
}
|
||||
securityMap[strings.TrimSpace(comments[i][len(attribute):])] = securityScheme
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(securityMap) > 0 {
|
||||
parser.swagger.SecurityDefinitions = securityMap
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getScopeScheme(scope string) string {
|
||||
scopeValue := scope[strings.Index(scope, "@scope."):]
|
||||
if scopeValue == "" {
|
||||
panic("@scope is empty")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return scope[len("@scope."):]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func isExistsScope(scope string) bool {
|
||||
s := strings.Fields(scope)
|
||||
for _, v := range s {
|
||||
if strings.Index(v, "@scope.") != -1 {
|
||||
if strings.Index(v, ",") != -1 {
|
||||
panic("@scope can't use comma(,) get=" + v)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return strings.Index(scope, "@scope.") != -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetSchemes parses swagger schemes for given commentLine
|
||||
func GetSchemes(commentLine string) []string {
|
||||
attribute := strings.ToLower(strings.Split(commentLine, " ")[0])
|
||||
return strings.Split(strings.TrimSpace(commentLine[len(attribute):]), " ")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseRouterAPIInfo parses router api info for given astFile
|
||||
func (parser *Parser) ParseRouterAPIInfo(astFile *ast.File) {
|
||||
for _, astDescription := range astFile.Decls {
|
||||
switch astDeclaration := astDescription.(type) {
|
||||
case *ast.FuncDecl:
|
||||
if astDeclaration.Doc != nil && astDeclaration.Doc.List != nil {
|
||||
operation := NewOperation() //for per 'function' comment, create a new 'Operation' object
|
||||
operation.parser = parser
|
||||
for _, comment := range astDeclaration.Doc.List {
|
||||
if err := operation.ParseComment(comment.Text, astFile); err != nil {
|
||||
log.Panicf("ParseComment panic:%+v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
var pathItem spec.PathItem
|
||||
var ok bool
|
||||
|
||||
if pathItem, ok = parser.swagger.Paths.Paths[operation.Path]; !ok {
|
||||
pathItem = spec.PathItem{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch strings.ToUpper(operation.HTTPMethod) {
|
||||
case http.MethodGet:
|
||||
pathItem.Get = &operation.Operation
|
||||
case http.MethodPost:
|
||||
pathItem.Post = &operation.Operation
|
||||
case http.MethodDelete:
|
||||
pathItem.Delete = &operation.Operation
|
||||
case http.MethodPut:
|
||||
pathItem.Put = &operation.Operation
|
||||
case http.MethodPatch:
|
||||
pathItem.Patch = &operation.Operation
|
||||
case http.MethodHead:
|
||||
pathItem.Head = &operation.Operation
|
||||
case http.MethodOptions:
|
||||
pathItem.Options = &operation.Operation
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
parser.swagger.Paths.Paths[operation.Path] = pathItem
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseType parses type info for given astFile.
|
||||
func (parser *Parser) ParseType(astFile *ast.File) {
|
||||
if _, ok := parser.TypeDefinitions[astFile.Name.String()]; !ok {
|
||||
parser.TypeDefinitions[astFile.Name.String()] = make(map[string]*ast.TypeSpec)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, astDeclaration := range astFile.Decls {
|
||||
if generalDeclaration, ok := astDeclaration.(*ast.GenDecl); ok && generalDeclaration.Tok == token.TYPE {
|
||||
for _, astSpec := range generalDeclaration.Specs {
|
||||
if typeSpec, ok := astSpec.(*ast.TypeSpec); ok {
|
||||
typeName := fmt.Sprintf("%v", typeSpec.Type)
|
||||
// check if its a custom primitive type
|
||||
if IsGolangPrimitiveType(typeName) {
|
||||
parser.CustomPrimitiveTypes[typeSpec.Name.String()] = TransToValidSchemeType(typeName)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
parser.TypeDefinitions[astFile.Name.String()][typeSpec.Name.String()] = typeSpec
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseDefinitions parses Swagger Api definitions.
|
||||
func (parser *Parser) ParseDefinitions() {
|
||||
for refTypeName, typeSpec := range parser.registerTypes {
|
||||
ss := strings.Split(refTypeName, ".")
|
||||
pkgName := ss[0]
|
||||
parser.ParseDefinition(pkgName, typeSpec, typeSpec.Name.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var structStacks []string
|
||||
|
||||
// isNotRecurringNestStruct check if a structure that is not a not repeating
|
||||
func isNotRecurringNestStruct(refTypeName string, structStacks []string) bool {
|
||||
for _, v := range structStacks {
|
||||
if refTypeName == v {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseDefinition TODO: NEEDS COMMENT INFO
|
||||
func (parser *Parser) ParseDefinition(pkgName string, typeSpec *ast.TypeSpec, typeName string) {
|
||||
var refTypeName string
|
||||
if len(pkgName) > 0 {
|
||||
refTypeName = pkgName + "." + typeName
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
refTypeName = typeName
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, already := parser.swagger.Definitions[refTypeName]; already {
|
||||
log.Println("Skipping '" + refTypeName + "', already present.")
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
properties := make(map[string]spec.Schema)
|
||||
// stop repetitive structural parsing
|
||||
if isNotRecurringNestStruct(refTypeName, structStacks) {
|
||||
structStacks = append(structStacks, refTypeName)
|
||||
parser.parseTypeSpec(pkgName, typeSpec, properties)
|
||||
}
|
||||
structStacks = []string{}
|
||||
|
||||
// created sorted list of properties keys so when we iterate over them it's deterministic
|
||||
ks := make([]string, 0, len(properties))
|
||||
for k := range properties {
|
||||
ks = append(ks, k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
sort.Strings(ks)
|
||||
|
||||
requiredFields := make([]string, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
// iterate over keys list instead of map to avoid the random shuffle of the order that go does for maps
|
||||
for _, k := range ks {
|
||||
prop := properties[k]
|
||||
|
||||
// todo find the pkgName of the property type
|
||||
tname := prop.SchemaProps.Type[0]
|
||||
if _, ok := parser.TypeDefinitions[pkgName][tname]; ok {
|
||||
tspec := parser.TypeDefinitions[pkgName][tname]
|
||||
parser.ParseDefinition(pkgName, tspec, tname)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if tname != "object" {
|
||||
requiredFields = append(requiredFields, prop.SchemaProps.Required...)
|
||||
prop.SchemaProps.Required = make([]string, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
properties[k] = prop
|
||||
}
|
||||
log.Println("Generating " + refTypeName)
|
||||
parser.swagger.Definitions[refTypeName] = spec.Schema{
|
||||
SchemaProps: spec.SchemaProps{
|
||||
Type: []string{"object"},
|
||||
Properties: properties,
|
||||
Required: requiredFields,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (parser *Parser) parseTypeSpec(pkgName string, typeSpec *ast.TypeSpec, properties map[string]spec.Schema) {
|
||||
switch typeSpec.Type.(type) {
|
||||
case *ast.StructType:
|
||||
structDecl := typeSpec.Type.(*ast.StructType)
|
||||
fields := structDecl.Fields.List
|
||||
|
||||
for _, field := range fields {
|
||||
if field.Names == nil { //anonymous field
|
||||
parser.parseAnonymousField(pkgName, field, properties)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
props := parser.parseStruct(pkgName, field)
|
||||
for k, v := range props {
|
||||
properties[k] = v
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case *ast.ArrayType:
|
||||
log.Println("ParseDefinitions not supported 'Array' yet.")
|
||||
case *ast.InterfaceType:
|
||||
log.Println("ParseDefinitions not supported 'Interface' yet.")
|
||||
case *ast.MapType:
|
||||
log.Println("ParseDefinitions not supported 'Map' yet.")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type structField struct {
|
||||
name string
|
||||
schemaType string
|
||||
arrayType string
|
||||
formatType string
|
||||
isRequired bool
|
||||
crossPkg string
|
||||
exampleValue interface{}
|
||||
maximum *float64
|
||||
minimum *float64
|
||||
maxLength *int64
|
||||
minLength *int64
|
||||
enums []interface{}
|
||||
defaultValue interface{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (parser *Parser) parseStruct(pkgName string, field *ast.Field) (properties map[string]spec.Schema) {
|
||||
properties = map[string]spec.Schema{}
|
||||
structField := parser.parseField(field)
|
||||
if structField.name == "" {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
var desc string
|
||||
if field.Doc != nil {
|
||||
desc = strings.TrimSpace(field.Doc.Text())
|
||||
}
|
||||
// TODO: find package of schemaType and/or arrayType
|
||||
|
||||
if structField.crossPkg != "" {
|
||||
pkgName = structField.crossPkg
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, ok := parser.TypeDefinitions[pkgName][structField.schemaType]; ok { // user type field
|
||||
// write definition if not yet present
|
||||
parser.ParseDefinition(pkgName, parser.TypeDefinitions[pkgName][structField.schemaType], structField.schemaType)
|
||||
properties[structField.name] = spec.Schema{
|
||||
SchemaProps: spec.SchemaProps{
|
||||
Type: []string{"object"}, // to avoid swagger validation error
|
||||
Description: desc,
|
||||
Ref: spec.Ref{
|
||||
Ref: jsonreference.MustCreateRef("#/definitions/" + pkgName + "." + structField.schemaType),
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if structField.schemaType == "array" { // array field type
|
||||
// if defined -- ref it
|
||||
if _, ok := parser.TypeDefinitions[pkgName][structField.arrayType]; ok { // user type in array
|
||||
parser.ParseDefinition(pkgName, parser.TypeDefinitions[pkgName][structField.arrayType], structField.arrayType)
|
||||
properties[structField.name] = spec.Schema{
|
||||
SchemaProps: spec.SchemaProps{
|
||||
Type: []string{structField.schemaType},
|
||||
Description: desc,
|
||||
Items: &spec.SchemaOrArray{
|
||||
Schema: &spec.Schema{
|
||||
SchemaProps: spec.SchemaProps{
|
||||
Ref: spec.Ref{
|
||||
Ref: jsonreference.MustCreateRef("#/definitions/" + pkgName + "." + structField.arrayType),
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else { // standard type in array
|
||||
required := make([]string, 0)
|
||||
if structField.isRequired {
|
||||
required = append(required, structField.name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
properties[structField.name] = spec.Schema{
|
||||
SchemaProps: spec.SchemaProps{
|
||||
Type: []string{structField.schemaType},
|
||||
Description: desc,
|
||||
Format: structField.formatType,
|
||||
Required: required,
|
||||
Items: &spec.SchemaOrArray{
|
||||
Schema: &spec.Schema{
|
||||
SchemaProps: spec.SchemaProps{
|
||||
Type: []string{structField.arrayType},
|
||||
Maximum: structField.maximum,
|
||||
Minimum: structField.minimum,
|
||||
MaxLength: structField.maxLength,
|
||||
MinLength: structField.minLength,
|
||||
Enum: structField.enums,
|
||||
Default: structField.defaultValue,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
SwaggerSchemaProps: spec.SwaggerSchemaProps{
|
||||
Example: structField.exampleValue,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
required := make([]string, 0)
|
||||
if structField.isRequired {
|
||||
required = append(required, structField.name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
properties[structField.name] = spec.Schema{
|
||||
SchemaProps: spec.SchemaProps{
|
||||
Type: []string{structField.schemaType},
|
||||
Description: desc,
|
||||
Format: structField.formatType,
|
||||
Required: required,
|
||||
Maximum: structField.maximum,
|
||||
Minimum: structField.minimum,
|
||||
MaxLength: structField.maxLength,
|
||||
MinLength: structField.minLength,
|
||||
Enum: structField.enums,
|
||||
Default: structField.defaultValue,
|
||||
},
|
||||
SwaggerSchemaProps: spec.SwaggerSchemaProps{
|
||||
Example: structField.exampleValue,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
nestStruct, ok := field.Type.(*ast.StructType)
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
props := map[string]spec.Schema{}
|
||||
nestRequired := make([]string, 0)
|
||||
for _, v := range nestStruct.Fields.List {
|
||||
p := parser.parseStruct(pkgName, v)
|
||||
for k, v := range p {
|
||||
if v.SchemaProps.Type[0] != "object" {
|
||||
nestRequired = append(nestRequired, v.SchemaProps.Required...)
|
||||
v.SchemaProps.Required = make([]string, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
props[k] = v
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
properties[structField.name] = spec.Schema{
|
||||
SchemaProps: spec.SchemaProps{
|
||||
Type: []string{structField.schemaType},
|
||||
Description: desc,
|
||||
Format: structField.formatType,
|
||||
Properties: props,
|
||||
Required: nestRequired,
|
||||
Maximum: structField.maximum,
|
||||
Minimum: structField.minimum,
|
||||
MaxLength: structField.maxLength,
|
||||
MinLength: structField.minLength,
|
||||
Enum: structField.enums,
|
||||
Default: structField.defaultValue,
|
||||
},
|
||||
SwaggerSchemaProps: spec.SwaggerSchemaProps{
|
||||
Example: structField.exampleValue,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (parser *Parser) parseAnonymousField(pkgName string, field *ast.Field, properties map[string]spec.Schema) {
|
||||
// check if ast Field is Ident type
|
||||
astTypeIdent, okTypeIdent := field.Type.(*ast.Ident)
|
||||
|
||||
// if ast Field is not Ident type we check if it's StarExpr
|
||||
// because it might be a pointer to an Ident
|
||||
if !okTypeIdent {
|
||||
if astTypeStar, okTypeStar := field.Type.(*ast.StarExpr); okTypeStar {
|
||||
astTypeIdent, okTypeIdent = astTypeStar.X.(*ast.Ident)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if okTypeIdent {
|
||||
findPgkName := pkgName
|
||||
findBaseTypeName := astTypeIdent.Name
|
||||
ss := strings.Split(astTypeIdent.Name, ".")
|
||||
if len(ss) > 1 {
|
||||
findPgkName = ss[0]
|
||||
findBaseTypeName = ss[1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
baseTypeSpec := parser.TypeDefinitions[findPgkName][findBaseTypeName]
|
||||
parser.parseTypeSpec(findPgkName, baseTypeSpec, properties)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (parser *Parser) parseField(field *ast.Field) *structField {
|
||||
prop := getPropertyName(field, parser)
|
||||
if len(prop.ArrayType) == 0 {
|
||||
CheckSchemaType(prop.SchemaType)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
CheckSchemaType("array")
|
||||
}
|
||||
structField := &structField{
|
||||
name: field.Names[0].Name,
|
||||
schemaType: prop.SchemaType,
|
||||
arrayType: prop.ArrayType,
|
||||
crossPkg: prop.CrossPkg,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch parser.PropNamingStrategy {
|
||||
case SnakeCase:
|
||||
structField.name = toSnakeCase(structField.name)
|
||||
case PascalCase:
|
||||
//use struct field name
|
||||
case CamelCase:
|
||||
structField.name = toLowerCamelCase(structField.name)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
structField.name = toLowerCamelCase(structField.name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if field.Tag == nil {
|
||||
return structField
|
||||
}
|
||||
// `json:"tag"` -> json:"tag"
|
||||
structTag := reflect.StructTag(strings.Replace(field.Tag.Value, "`", "", -1))
|
||||
jsonTag := structTag.Get("json")
|
||||
// json:"tag,hoge"
|
||||
if strings.Contains(jsonTag, ",") {
|
||||
// json:",hoge"
|
||||
if strings.HasPrefix(jsonTag, ",") {
|
||||
jsonTag = ""
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
jsonTag = strings.SplitN(jsonTag, ",", 2)[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if jsonTag == "-" {
|
||||
structField.name = ""
|
||||
} else if jsonTag != "" {
|
||||
structField.name = jsonTag
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if typeTag := structTag.Get("swaggertype"); typeTag != "" {
|
||||
parts := strings.Split(typeTag, ",")
|
||||
if 0 < len(parts) && len(parts) <= 2 {
|
||||
newSchemaType := parts[0]
|
||||
newArrayType := structField.arrayType
|
||||
if len(parts) >= 2 && newSchemaType == "array" {
|
||||
newArrayType = parts[1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
CheckSchemaType(newSchemaType)
|
||||
CheckSchemaType(newArrayType)
|
||||
structField.schemaType = newSchemaType
|
||||
structField.arrayType = newArrayType
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if exampleTag := structTag.Get("example"); exampleTag != "" {
|
||||
structField.exampleValue = defineTypeOfExample(structField.schemaType, structField.arrayType, exampleTag)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if formatTag := structTag.Get("format"); formatTag != "" {
|
||||
structField.formatType = formatTag
|
||||
}
|
||||
if bindingTag := structTag.Get("binding"); bindingTag != "" {
|
||||
for _, val := range strings.Split(bindingTag, ",") {
|
||||
if val == "required" {
|
||||
structField.isRequired = true
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if validateTag := structTag.Get("validate"); validateTag != "" {
|
||||
for _, val := range strings.Split(validateTag, ",") {
|
||||
if val == "required" {
|
||||
structField.isRequired = true
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if enumsTag := structTag.Get("enums"); enumsTag != "" {
|
||||
enumType := structField.schemaType
|
||||
if structField.schemaType == "array" {
|
||||
enumType = structField.arrayType
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, e := range strings.Split(enumsTag, ",") {
|
||||
structField.enums = append(structField.enums, defineType(enumType, e))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if defaultTag := structTag.Get("default"); defaultTag != "" {
|
||||
structField.defaultValue = defineType(structField.schemaType, defaultTag)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if IsNumericType(structField.schemaType) || IsNumericType(structField.arrayType) {
|
||||
structField.maximum = getFloatTag(structTag, "maximum")
|
||||
structField.minimum = getFloatTag(structTag, "minimum")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if structField.schemaType == "string" || structField.arrayType == "string" {
|
||||
structField.maxLength = getIntTag(structTag, "maxLength")
|
||||
structField.minLength = getIntTag(structTag, "minLength")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return structField
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getFloatTag(structTag reflect.StructTag, tagName string) *float64 {
|
||||
strValue := structTag.Get(tagName)
|
||||
if strValue == "" {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
value, err := strconv.ParseFloat(strValue, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf("can't parse numeric value of %q tag: %v", tagName, err))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return &value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getIntTag(structTag reflect.StructTag, tagName string) *int64 {
|
||||
strValue := structTag.Get(tagName)
|
||||
if strValue == "" {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
value, err := strconv.ParseInt(strValue, 10, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf("can't parse numeric value of %q tag: %v", tagName, err))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return &value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func toSnakeCase(in string) string {
|
||||
runes := []rune(in)
|
||||
length := len(runes)
|
||||
|
||||
var out []rune
|
||||
for i := 0; i < length; i++ {
|
||||
if i > 0 && unicode.IsUpper(runes[i]) && ((i+1 < length && unicode.IsLower(runes[i+1])) || unicode.IsLower(runes[i-1])) {
|
||||
out = append(out, '_')
|
||||
}
|
||||
out = append(out, unicode.ToLower(runes[i]))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return string(out)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func toLowerCamelCase(in string) string {
|
||||
runes := []rune(in)
|
||||
|
||||
var out []rune
|
||||
flag := false
|
||||
for i, curr := range runes {
|
||||
if (i == 0 && unicode.IsUpper(curr)) || (flag && unicode.IsUpper(curr)) {
|
||||
out = append(out, unicode.ToLower(curr))
|
||||
flag = true
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
out = append(out, curr)
|
||||
flag = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return string(out)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// defineTypeOfExample example value define the type (object and array unsupported)
|
||||
func defineTypeOfExample(schemaType, arrayType, exampleValue string) interface{} {
|
||||
switch schemaType {
|
||||
case "string":
|
||||
return exampleValue
|
||||
case "number":
|
||||
v, err := strconv.ParseFloat(exampleValue, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf("example value %s can't convert to %s err: %s", exampleValue, schemaType, err))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
case "integer":
|
||||
v, err := strconv.Atoi(exampleValue)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf("example value %s can't convert to %s err: %s", exampleValue, schemaType, err))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
case "boolean":
|
||||
v, err := strconv.ParseBool(exampleValue)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf("example value %s can't convert to %s err: %s", exampleValue, schemaType, err))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
case "array":
|
||||
values := strings.Split(exampleValue, ",")
|
||||
result := make([]interface{}, 0)
|
||||
for _, value := range values {
|
||||
result = append(result, defineTypeOfExample(arrayType, "", value))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result
|
||||
default:
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf("%s is unsupported type in example value", schemaType))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetAllGoFileInfo gets all Go source files information for given searchDir.
|
||||
func (parser *Parser) getAllGoFileInfo(searchDir string) error {
|
||||
return filepath.Walk(searchDir, parser.visit)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (parser *Parser) visit(path string, f os.FileInfo, err error) error {
|
||||
if err := Skip(f); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if ext := filepath.Ext(path); ext == ".go" {
|
||||
fset := token.NewFileSet() // positions are relative to fset
|
||||
astFile, err := goparser.ParseFile(fset, path, nil, goparser.ParseComments)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
log.Panicf("ParseFile panic:%+v", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
parser.files[path] = astFile
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Skip returns filepath.SkipDir error if match vendor and hidden folder
|
||||
func Skip(f os.FileInfo) error {
|
||||
// exclude vendor folder
|
||||
if f.IsDir() && f.Name() == "vendor" {
|
||||
return filepath.SkipDir
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// exclude all hidden folder
|
||||
if f.IsDir() && len(f.Name()) > 1 && f.Name()[0] == '.' {
|
||||
return filepath.SkipDir
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetSwagger returns *spec.Swagger which is the root document object for the API specification.
|
||||
func (parser *Parser) GetSwagger() *spec.Swagger {
|
||||
return parser.swagger
|
||||
}
|
||||
131
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/property.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
131
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/property.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
|
||||
package swag
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"go/ast"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ErrFailedConvertPrimitiveType Failed to convert for swag to interpretable type
|
||||
var ErrFailedConvertPrimitiveType = errors.New("swag property: failed convert primitive type")
|
||||
|
||||
type propertyName struct {
|
||||
SchemaType string
|
||||
ArrayType string
|
||||
CrossPkg string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type propertyNewFunc func(schemeType string, crossPkg string) propertyName
|
||||
|
||||
func newArrayProperty(schemeType string, crossPkg string) propertyName {
|
||||
return propertyName{
|
||||
SchemaType: "array",
|
||||
ArrayType: schemeType,
|
||||
CrossPkg: crossPkg,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func newProperty(schemeType string, crossPkg string) propertyName {
|
||||
return propertyName{
|
||||
SchemaType: schemeType,
|
||||
ArrayType: "string",
|
||||
CrossPkg: crossPkg,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func convertFromSpecificToPrimitive(typeName string) (string, error) {
|
||||
typeName = strings.ToUpper(typeName)
|
||||
switch typeName {
|
||||
case "TIME", "OBJECTID", "UUID":
|
||||
return "string", nil
|
||||
case "DECIMAL":
|
||||
return "number", nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "", ErrFailedConvertPrimitiveType
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func parseFieldSelectorExpr(astTypeSelectorExpr *ast.SelectorExpr, parser *Parser, propertyNewFunc propertyNewFunc) propertyName {
|
||||
if primitiveType, err := convertFromSpecificToPrimitive(astTypeSelectorExpr.Sel.Name); err == nil {
|
||||
return propertyNewFunc(primitiveType, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if pkgName, ok := astTypeSelectorExpr.X.(*ast.Ident); ok {
|
||||
if typeDefinitions, ok := parser.TypeDefinitions[pkgName.Name][astTypeSelectorExpr.Sel.Name]; ok {
|
||||
parser.ParseDefinition(pkgName.Name, typeDefinitions, astTypeSelectorExpr.Sel.Name)
|
||||
return propertyNewFunc(astTypeSelectorExpr.Sel.Name, pkgName.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if actualPrimitiveType, isCustomType := parser.CustomPrimitiveTypes[astTypeSelectorExpr.Sel.Name]; isCustomType {
|
||||
return propertyName{SchemaType: actualPrimitiveType, ArrayType: actualPrimitiveType}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fmt.Printf("%s is not supported. but it will be set with string temporary. Please report any problems.", astTypeSelectorExpr.Sel.Name)
|
||||
return propertyName{SchemaType: "string", ArrayType: "string"}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// getPropertyName returns the string value for the given field if it exists, otherwise it panics.
|
||||
// allowedValues: array, boolean, integer, null, number, object, string
|
||||
func getPropertyName(field *ast.Field, parser *Parser) propertyName {
|
||||
if astTypeSelectorExpr, ok := field.Type.(*ast.SelectorExpr); ok {
|
||||
return parseFieldSelectorExpr(astTypeSelectorExpr, parser, newProperty)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// check if it is a custom type
|
||||
typeName := fmt.Sprintf("%v", field.Type)
|
||||
if actualPrimitiveType, isCustomType := parser.CustomPrimitiveTypes[typeName]; isCustomType {
|
||||
return propertyName{SchemaType: actualPrimitiveType, ArrayType: actualPrimitiveType}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if astTypeIdent, ok := field.Type.(*ast.Ident); ok {
|
||||
name := astTypeIdent.Name
|
||||
schemeType := TransToValidSchemeType(name)
|
||||
return propertyName{SchemaType: schemeType, ArrayType: schemeType}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ptr, ok := field.Type.(*ast.StarExpr); ok {
|
||||
if astTypeSelectorExpr, ok := ptr.X.(*ast.SelectorExpr); ok {
|
||||
return parseFieldSelectorExpr(astTypeSelectorExpr, parser, newProperty)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if astTypeIdent, ok := ptr.X.(*ast.Ident); ok {
|
||||
name := astTypeIdent.Name
|
||||
schemeType := TransToValidSchemeType(name)
|
||||
return propertyName{SchemaType: schemeType, ArrayType: schemeType}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if astTypeArray, ok := ptr.X.(*ast.ArrayType); ok { // if array
|
||||
if astTypeArrayExpr, ok := astTypeArray.Elt.(*ast.SelectorExpr); ok {
|
||||
return parseFieldSelectorExpr(astTypeArrayExpr, parser, newArrayProperty)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if astTypeArrayIdent, ok := astTypeArray.Elt.(*ast.Ident); ok {
|
||||
name := TransToValidSchemeType(astTypeArrayIdent.Name)
|
||||
return propertyName{SchemaType: "array", ArrayType: name}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if astTypeArray, ok := field.Type.(*ast.ArrayType); ok { // if array
|
||||
if astTypeArrayExpr, ok := astTypeArray.Elt.(*ast.SelectorExpr); ok {
|
||||
return parseFieldSelectorExpr(astTypeArrayExpr, parser, newArrayProperty)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if astTypeArrayExpr, ok := astTypeArray.Elt.(*ast.StarExpr); ok {
|
||||
if astTypeArrayIdent, ok := astTypeArrayExpr.X.(*ast.Ident); ok {
|
||||
name := TransToValidSchemeType(astTypeArrayIdent.Name)
|
||||
return propertyName{SchemaType: "array", ArrayType: name}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
itemTypeName := TransToValidSchemeType(fmt.Sprintf("%s", astTypeArray.Elt))
|
||||
if actualPrimitiveType, isCustomType := parser.CustomPrimitiveTypes[itemTypeName]; isCustomType {
|
||||
itemTypeName = actualPrimitiveType
|
||||
}
|
||||
return propertyName{SchemaType: "array", ArrayType: itemTypeName}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, ok := field.Type.(*ast.MapType); ok { // if map
|
||||
//TODO: support map
|
||||
return propertyName{SchemaType: "object", ArrayType: "object"}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, ok := field.Type.(*ast.StructType); ok { // if struct
|
||||
return propertyName{SchemaType: "object", ArrayType: "object"}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, ok := field.Type.(*ast.InterfaceType); ok { // if interface{}
|
||||
return propertyName{SchemaType: "object", ArrayType: "object"}
|
||||
}
|
||||
panic("not supported" + fmt.Sprint(field.Type))
|
||||
}
|
||||
70
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/schema.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
70
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/schema.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
package swag
|
||||
|
||||
import "fmt"
|
||||
|
||||
// CheckSchemaType TODO: NEEDS COMMENT INFO
|
||||
func CheckSchemaType(typeName string) {
|
||||
if !IsPrimitiveType(typeName) {
|
||||
panic(fmt.Errorf("%s is not basic types", typeName))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsPrimitiveType determine whether the type name is a primitive type
|
||||
func IsPrimitiveType(typeName string) bool {
|
||||
switch typeName {
|
||||
case "string", "number", "integer", "boolean", "array", "object":
|
||||
return true
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsNumericType determines whether the swagger type name is a numeric type
|
||||
func IsNumericType(typeName string) bool {
|
||||
return typeName == "integer" || typeName == "number"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TransToValidSchemeType indicates type will transfer golang basic type to swagger supported type.
|
||||
func TransToValidSchemeType(typeName string) string {
|
||||
switch typeName {
|
||||
case "uint", "int", "uint8", "int8", "uint16", "int16", "byte":
|
||||
return "integer"
|
||||
case "uint32", "int32", "rune":
|
||||
return "integer"
|
||||
case "uint64", "int64":
|
||||
return "integer"
|
||||
case "float32", "float64":
|
||||
return "number"
|
||||
case "bool":
|
||||
return "boolean"
|
||||
case "string":
|
||||
return "string"
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return typeName // to support user defined types
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsGolangPrimitiveType determine whether the type name is a golang primitive type
|
||||
func IsGolangPrimitiveType(typeName string) bool {
|
||||
switch typeName {
|
||||
case "uint",
|
||||
"int",
|
||||
"uint8",
|
||||
"int8",
|
||||
"uint16",
|
||||
"int16",
|
||||
"byte",
|
||||
"uint32",
|
||||
"int32",
|
||||
"rune",
|
||||
"uint64",
|
||||
"int64",
|
||||
"float32",
|
||||
"float64",
|
||||
"bool",
|
||||
"string":
|
||||
return true
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
41
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/swagger.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
41
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/swagger.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
package swag
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Name is a unique name be used to register swag instance.
|
||||
const Name = "swagger"
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
swaggerMu sync.RWMutex
|
||||
swag Swagger
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Swagger is a interface to read swagger document.
|
||||
type Swagger interface {
|
||||
ReadDoc() string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Register registers swagger for given name.
|
||||
func Register(name string, swagger Swagger) {
|
||||
swaggerMu.Lock()
|
||||
defer swaggerMu.Unlock()
|
||||
if swagger == nil {
|
||||
panic("swagger is nil")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if swag != nil {
|
||||
panic("Register called twice for swag: " + name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
swag = swagger
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReadDoc reads swagger document.
|
||||
func ReadDoc() (string, error) {
|
||||
if swag != nil {
|
||||
return swag.ReadDoc(), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "", errors.New("not yet registered swag")
|
||||
}
|
||||
4
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/version.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
4
vendor/github.com/swaggo/swag/version.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
package swag
|
||||
|
||||
// Version of swag
|
||||
const Version = "v1.4.0"
|
||||
2
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/.flake8
generated
vendored
Normal file
2
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/.flake8
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
[flake8]
|
||||
max-line-length = 120
|
||||
2
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
2
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
*.coverprofile
|
||||
node_modules/
|
||||
27
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
27
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/.travis.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
language: go
|
||||
sudo: false
|
||||
dist: trusty
|
||||
osx_image: xcode8.3
|
||||
go: 1.8.x
|
||||
|
||||
os:
|
||||
- linux
|
||||
- osx
|
||||
|
||||
cache:
|
||||
directories:
|
||||
- node_modules
|
||||
|
||||
before_script:
|
||||
- go get github.com/urfave/gfmrun/... || true
|
||||
- go get golang.org/x/tools/cmd/goimports
|
||||
- if [ ! -f node_modules/.bin/markdown-toc ] ; then
|
||||
npm install markdown-toc ;
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- ./runtests gen
|
||||
- ./runtests vet
|
||||
- ./runtests test
|
||||
- ./runtests gfmrun
|
||||
- ./runtests toc
|
||||
435
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/CHANGELOG.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
435
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/CHANGELOG.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,435 @@
|
||||
# Change Log
|
||||
|
||||
**ATTN**: This project uses [semantic versioning](http://semver.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
## [Unreleased]
|
||||
|
||||
## 1.20.0 - 2017-08-10
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
|
||||
* `HandleExitCoder` is now correctly iterates over all errors in
|
||||
a `MultiError`. The exit code is the exit code of the last error or `1` if
|
||||
there are no `ExitCoder`s in the `MultiError`.
|
||||
* Fixed YAML file loading on Windows (previously would fail validate the file path)
|
||||
* Subcommand `Usage`, `Description`, `ArgsUsage`, `OnUsageError` correctly
|
||||
propogated
|
||||
* `ErrWriter` is now passed downwards through command structure to avoid the
|
||||
need to redefine it
|
||||
* Pass `Command` context into `OnUsageError` rather than parent context so that
|
||||
all fields are avaiable
|
||||
* Errors occuring in `Before` funcs are no longer double printed
|
||||
* Use `UsageText` in the help templates for commands and subcommands if
|
||||
defined; otherwise build the usage as before (was previously ignoring this
|
||||
field)
|
||||
* `IsSet` and `GlobalIsSet` now correctly return whether a flag is set if
|
||||
a program calls `Set` or `GlobalSet` directly after flag parsing (would
|
||||
previously only return `true` if the flag was set during parsing)
|
||||
|
||||
### Changed
|
||||
|
||||
* No longer exit the program on command/subcommand error if the error raised is
|
||||
not an `OsExiter`. This exiting behavior was introduced in 1.19.0, but was
|
||||
determined to be a regression in functionality. See [the
|
||||
PR](https://github.com/urfave/cli/pull/595) for discussion.
|
||||
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
|
||||
* `CommandsByName` type was added to make it easy to sort `Command`s by name,
|
||||
alphabetically
|
||||
* `altsrc` now handles loading of string and int arrays from TOML
|
||||
* Support for definition of custom help templates for `App` via
|
||||
`CustomAppHelpTemplate`
|
||||
* Support for arbitrary key/value fields on `App` to be used with
|
||||
`CustomAppHelpTemplate` via `ExtraInfo`
|
||||
* `HelpFlag`, `VersionFlag`, and `BashCompletionFlag` changed to explictly be
|
||||
`cli.Flag`s allowing for the use of custom flags satisfying the `cli.Flag`
|
||||
interface to be used.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.19.1] - 2016-11-21
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
|
||||
- Fixes regression introduced in 1.19.0 where using an `ActionFunc` as
|
||||
the `Action` for a command would cause it to error rather than calling the
|
||||
function. Should not have a affected declarative cases using `func(c
|
||||
*cli.Context) err)`.
|
||||
- Shell completion now handles the case where the user specifies
|
||||
`--generate-bash-completion` immediately after a flag that takes an argument.
|
||||
Previously it call the application with `--generate-bash-completion` as the
|
||||
flag value.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.19.0] - 2016-11-19
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- `FlagsByName` was added to make it easy to sort flags (e.g. `sort.Sort(cli.FlagsByName(app.Flags))`)
|
||||
- A `Description` field was added to `App` for a more detailed description of
|
||||
the application (similar to the existing `Description` field on `Command`)
|
||||
- Flag type code generation via `go generate`
|
||||
- Write to stderr and exit 1 if action returns non-nil error
|
||||
- Added support for TOML to the `altsrc` loader
|
||||
- `SkipArgReorder` was added to allow users to skip the argument reordering.
|
||||
This is useful if you want to consider all "flags" after an argument as
|
||||
arguments rather than flags (the default behavior of the stdlib `flag`
|
||||
library). This is backported functionality from the [removal of the flag
|
||||
reordering](https://github.com/urfave/cli/pull/398) in the unreleased version
|
||||
2
|
||||
- For formatted errors (those implementing `ErrorFormatter`), the errors will
|
||||
be formatted during output. Compatible with `pkg/errors`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Changed
|
||||
- Raise minimum tested/supported Go version to 1.2+
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Consider empty environment variables as set (previously environment variables
|
||||
with the equivalent of `""` would be skipped rather than their value used).
|
||||
- Return an error if the value in a given environment variable cannot be parsed
|
||||
as the flag type. Previously these errors were silently swallowed.
|
||||
- Print full error when an invalid flag is specified (which includes the invalid flag)
|
||||
- `App.Writer` defaults to `stdout` when `nil`
|
||||
- If no action is specified on a command or app, the help is now printed instead of `panic`ing
|
||||
- `App.Metadata` is initialized automatically now (previously was `nil` unless initialized)
|
||||
- Correctly show help message if `-h` is provided to a subcommand
|
||||
- `context.(Global)IsSet` now respects environment variables. Previously it
|
||||
would return `false` if a flag was specified in the environment rather than
|
||||
as an argument
|
||||
- Removed deprecation warnings to STDERR to avoid them leaking to the end-user
|
||||
- `altsrc`s import paths were updated to use `gopkg.in/urfave/cli.v1`. This
|
||||
fixes issues that occurred when `gopkg.in/urfave/cli.v1` was imported as well
|
||||
as `altsrc` where Go would complain that the types didn't match
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.18.1] - 2016-08-28
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Removed deprecation warnings to STDERR to avoid them leaking to the end-user (backported)
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.18.0] - 2016-06-27
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- `./runtests` test runner with coverage tracking by default
|
||||
- testing on OS X
|
||||
- testing on Windows
|
||||
- `UintFlag`, `Uint64Flag`, and `Int64Flag` types and supporting code
|
||||
|
||||
### Changed
|
||||
- Use spaces for alignment in help/usage output instead of tabs, making the
|
||||
output alignment consistent regardless of tab width
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Printing of command aliases in help text
|
||||
- Printing of visible flags for both struct and struct pointer flags
|
||||
- Display the `help` subcommand when using `CommandCategories`
|
||||
- No longer swallows `panic`s that occur within the `Action`s themselves when
|
||||
detecting the signature of the `Action` field
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.17.1] - 2016-08-28
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Removed deprecation warnings to STDERR to avoid them leaking to the end-user
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.17.0] - 2016-05-09
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- Pluggable flag-level help text rendering via `cli.DefaultFlagStringFunc`
|
||||
- `context.GlobalBoolT` was added as an analogue to `context.GlobalBool`
|
||||
- Support for hiding commands by setting `Hidden: true` -- this will hide the
|
||||
commands in help output
|
||||
|
||||
### Changed
|
||||
- `Float64Flag`, `IntFlag`, and `DurationFlag` default values are no longer
|
||||
quoted in help text output.
|
||||
- All flag types now include `(default: {value})` strings following usage when a
|
||||
default value can be (reasonably) detected.
|
||||
- `IntSliceFlag` and `StringSliceFlag` usage strings are now more consistent
|
||||
with non-slice flag types
|
||||
- Apps now exit with a code of 3 if an unknown subcommand is specified
|
||||
(previously they printed "No help topic for...", but still exited 0. This
|
||||
makes it easier to script around apps built using `cli` since they can trust
|
||||
that a 0 exit code indicated a successful execution.
|
||||
- cleanups based on [Go Report Card
|
||||
feedback](https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/urfave/cli)
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.16.1] - 2016-08-28
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Removed deprecation warnings to STDERR to avoid them leaking to the end-user
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.16.0] - 2016-05-02
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- `Hidden` field on all flag struct types to omit from generated help text
|
||||
|
||||
### Changed
|
||||
- `BashCompletionFlag` (`--enable-bash-completion`) is now omitted from
|
||||
generated help text via the `Hidden` field
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- handling of error values in `HandleAction` and `HandleExitCoder`
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.15.0] - 2016-04-30
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- This file!
|
||||
- Support for placeholders in flag usage strings
|
||||
- `App.Metadata` map for arbitrary data/state management
|
||||
- `Set` and `GlobalSet` methods on `*cli.Context` for altering values after
|
||||
parsing.
|
||||
- Support for nested lookup of dot-delimited keys in structures loaded from
|
||||
YAML.
|
||||
|
||||
### Changed
|
||||
- The `App.Action` and `Command.Action` now prefer a return signature of
|
||||
`func(*cli.Context) error`, as defined by `cli.ActionFunc`. If a non-nil
|
||||
`error` is returned, there may be two outcomes:
|
||||
- If the error fulfills `cli.ExitCoder`, then `os.Exit` will be called
|
||||
automatically
|
||||
- Else the error is bubbled up and returned from `App.Run`
|
||||
- Specifying an `Action` with the legacy return signature of
|
||||
`func(*cli.Context)` will produce a deprecation message to stderr
|
||||
- Specifying an `Action` that is not a `func` type will produce a non-zero exit
|
||||
from `App.Run`
|
||||
- Specifying an `Action` func that has an invalid (input) signature will
|
||||
produce a non-zero exit from `App.Run`
|
||||
|
||||
### Deprecated
|
||||
- <a name="deprecated-cli-app-runandexitonerror"></a>
|
||||
`cli.App.RunAndExitOnError`, which should now be done by returning an error
|
||||
that fulfills `cli.ExitCoder` to `cli.App.Run`.
|
||||
- <a name="deprecated-cli-app-action-signature"></a> the legacy signature for
|
||||
`cli.App.Action` of `func(*cli.Context)`, which should now have a return
|
||||
signature of `func(*cli.Context) error`, as defined by `cli.ActionFunc`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Added missing `*cli.Context.GlobalFloat64` method
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.14.0] - 2016-04-03 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- Codebeat badge
|
||||
- Support for categorization via `CategorizedHelp` and `Categories` on app.
|
||||
|
||||
### Changed
|
||||
- Use `filepath.Base` instead of `path.Base` in `Name` and `HelpName`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Ensure version is not shown in help text when `HideVersion` set.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.13.0] - 2016-03-06 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- YAML file input support.
|
||||
- `NArg` method on context.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.12.0] - 2016-02-17 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- Custom usage error handling.
|
||||
- Custom text support in `USAGE` section of help output.
|
||||
- Improved help messages for empty strings.
|
||||
- AppVeyor CI configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
### Changed
|
||||
- Removed `panic` from default help printer func.
|
||||
- De-duping and optimizations.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Correctly handle `Before`/`After` at command level when no subcommands.
|
||||
- Case of literal `-` argument causing flag reordering.
|
||||
- Environment variable hints on Windows.
|
||||
- Docs updates.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.11.1] - 2015-12-21 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Changed
|
||||
- Use `path.Base` in `Name` and `HelpName`
|
||||
- Export `GetName` on flag types.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Flag parsing when skipping is enabled.
|
||||
- Test output cleanup.
|
||||
- Move completion check to account for empty input case.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.11.0] - 2015-11-15 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- Destination scan support for flags.
|
||||
- Testing against `tip` in Travis CI config.
|
||||
|
||||
### Changed
|
||||
- Go version in Travis CI config.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Removed redundant tests.
|
||||
- Use correct example naming in tests.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.10.2] - 2015-10-29 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Remove unused var in bash completion.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.10.1] - 2015-10-21 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- Coverage and reference logos in README.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Use specified values in help and version parsing.
|
||||
- Only display app version and help message once.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.10.0] - 2015-10-06 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- More tests for existing functionality.
|
||||
- `ArgsUsage` at app and command level for help text flexibility.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Honor `HideHelp` and `HideVersion` in `App.Run`.
|
||||
- Remove juvenile word from README.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.9.0] - 2015-09-08 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- `FullName` on command with accompanying help output update.
|
||||
- Set default `$PROG` in bash completion.
|
||||
|
||||
### Changed
|
||||
- Docs formatting.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Removed self-referential imports in tests.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.8.0] - 2015-06-30 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- Support for `Copyright` at app level.
|
||||
- `Parent` func at context level to walk up context lineage.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Global flag processing at top level.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.7.1] - 2015-06-11 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- Aggregate errors from `Before`/`After` funcs.
|
||||
- Doc comments on flag structs.
|
||||
- Include non-global flags when checking version and help.
|
||||
- Travis CI config updates.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Ensure slice type flags have non-nil values.
|
||||
- Collect global flags from the full command hierarchy.
|
||||
- Docs prose.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.7.0] - 2015-05-03 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Changed
|
||||
- `HelpPrinter` signature includes output writer.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Specify go 1.1+ in docs.
|
||||
- Set `Writer` when running command as app.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.6.0] - 2015-03-23 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- Multiple author support.
|
||||
- `NumFlags` at context level.
|
||||
- `Aliases` at command level.
|
||||
|
||||
### Deprecated
|
||||
- `ShortName` at command level.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Subcommand help output.
|
||||
- Backward compatible support for deprecated `Author` and `Email` fields.
|
||||
- Docs regarding `Names`/`Aliases`.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.5.0] - 2015-02-20 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- `After` hook func support at app and command level.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Use parsed context when running command as subcommand.
|
||||
- Docs prose.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.4.1] - 2015-01-09 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- Support for hiding `-h / --help` flags, but not `help` subcommand.
|
||||
- Stop flag parsing after `--`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Help text for generic flags to specify single value.
|
||||
- Use double quotes in output for defaults.
|
||||
- Use `ParseInt` instead of `ParseUint` for int environment var values.
|
||||
- Use `0` as base when parsing int environment var values.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.4.0] - 2014-12-12 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- Support for environment variable lookup "cascade".
|
||||
- Support for `Stdout` on app for output redirection.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
- Print command help instead of app help in `ShowCommandHelp`.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.3.1] - 2014-11-13 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- Docs and example code updates.
|
||||
|
||||
### Changed
|
||||
- Default `-v / --version` flag made optional.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.3.0] - 2014-08-10 (backfilled 2016-04-25)
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- `FlagNames` at context level.
|
||||
- Exposed `VersionPrinter` var for more control over version output.
|
||||
- Zsh completion hook.
|
||||
- `AUTHOR` section in default app help template.
|
||||
- Contribution guidelines.
|
||||
- `DurationFlag` type.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.2.0] - 2014-08-02
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- Support for environment variable defaults on flags plus tests.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.1.0] - 2014-07-15
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- Bash completion.
|
||||
- Optional hiding of built-in help command.
|
||||
- Optional skipping of flag parsing at command level.
|
||||
- `Author`, `Email`, and `Compiled` metadata on app.
|
||||
- `Before` hook func support at app and command level.
|
||||
- `CommandNotFound` func support at app level.
|
||||
- Command reference available on context.
|
||||
- `GenericFlag` type.
|
||||
- `Float64Flag` type.
|
||||
- `BoolTFlag` type.
|
||||
- `IsSet` flag helper on context.
|
||||
- More flag lookup funcs at context level.
|
||||
- More tests & docs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Changed
|
||||
- Help template updates to account for presence/absence of flags.
|
||||
- Separated subcommand help template.
|
||||
- Exposed `HelpPrinter` var for more control over help output.
|
||||
|
||||
## [1.0.0] - 2013-11-01
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- `help` flag in default app flag set and each command flag set.
|
||||
- Custom handling of argument parsing errors.
|
||||
- Command lookup by name at app level.
|
||||
- `StringSliceFlag` type and supporting `StringSlice` type.
|
||||
- `IntSliceFlag` type and supporting `IntSlice` type.
|
||||
- Slice type flag lookups by name at context level.
|
||||
- Export of app and command help functions.
|
||||
- More tests & docs.
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.1.0 - 2013-07-22
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
- Initial implementation.
|
||||
|
||||
[Unreleased]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.18.0...HEAD
|
||||
[1.18.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.17.0...v1.18.0
|
||||
[1.17.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.16.0...v1.17.0
|
||||
[1.16.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.15.0...v1.16.0
|
||||
[1.15.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.14.0...v1.15.0
|
||||
[1.14.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.13.0...v1.14.0
|
||||
[1.13.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.12.0...v1.13.0
|
||||
[1.12.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.11.1...v1.12.0
|
||||
[1.11.1]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.11.0...v1.11.1
|
||||
[1.11.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.10.2...v1.11.0
|
||||
[1.10.2]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.10.1...v1.10.2
|
||||
[1.10.1]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.10.0...v1.10.1
|
||||
[1.10.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.9.0...v1.10.0
|
||||
[1.9.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.8.0...v1.9.0
|
||||
[1.8.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.7.1...v1.8.0
|
||||
[1.7.1]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.7.0...v1.7.1
|
||||
[1.7.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.6.0...v1.7.0
|
||||
[1.6.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.5.0...v1.6.0
|
||||
[1.5.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.4.1...v1.5.0
|
||||
[1.4.1]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.4.0...v1.4.1
|
||||
[1.4.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.3.1...v1.4.0
|
||||
[1.3.1]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.3.0...v1.3.1
|
||||
[1.3.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.2.0...v1.3.0
|
||||
[1.2.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.1.0...v1.2.0
|
||||
[1.1.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v1.0.0...v1.1.0
|
||||
[1.0.0]: https://github.com/urfave/cli/compare/v0.1.0...v1.0.0
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
21
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2016 Jeremy Saenz & Contributors
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
1381
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
1381
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
497
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/app.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
497
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/app.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,497 @@
|
||||
package cli
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
changeLogURL = "https://github.com/urfave/cli/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md"
|
||||
appActionDeprecationURL = fmt.Sprintf("%s#deprecated-cli-app-action-signature", changeLogURL)
|
||||
runAndExitOnErrorDeprecationURL = fmt.Sprintf("%s#deprecated-cli-app-runandexitonerror", changeLogURL)
|
||||
|
||||
contactSysadmin = "This is an error in the application. Please contact the distributor of this application if this is not you."
|
||||
|
||||
errInvalidActionType = NewExitError("ERROR invalid Action type. "+
|
||||
fmt.Sprintf("Must be `func(*Context`)` or `func(*Context) error). %s", contactSysadmin)+
|
||||
fmt.Sprintf("See %s", appActionDeprecationURL), 2)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// App is the main structure of a cli application. It is recommended that
|
||||
// an app be created with the cli.NewApp() function
|
||||
type App struct {
|
||||
// The name of the program. Defaults to path.Base(os.Args[0])
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
// Full name of command for help, defaults to Name
|
||||
HelpName string
|
||||
// Description of the program.
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
// Text to override the USAGE section of help
|
||||
UsageText string
|
||||
// Description of the program argument format.
|
||||
ArgsUsage string
|
||||
// Version of the program
|
||||
Version string
|
||||
// Description of the program
|
||||
Description string
|
||||
// List of commands to execute
|
||||
Commands []Command
|
||||
// List of flags to parse
|
||||
Flags []Flag
|
||||
// Boolean to enable bash completion commands
|
||||
EnableBashCompletion bool
|
||||
// Boolean to hide built-in help command
|
||||
HideHelp bool
|
||||
// Boolean to hide built-in version flag and the VERSION section of help
|
||||
HideVersion bool
|
||||
// Populate on app startup, only gettable through method Categories()
|
||||
categories CommandCategories
|
||||
// An action to execute when the bash-completion flag is set
|
||||
BashComplete BashCompleteFunc
|
||||
// An action to execute before any subcommands are run, but after the context is ready
|
||||
// If a non-nil error is returned, no subcommands are run
|
||||
Before BeforeFunc
|
||||
// An action to execute after any subcommands are run, but after the subcommand has finished
|
||||
// It is run even if Action() panics
|
||||
After AfterFunc
|
||||
|
||||
// The action to execute when no subcommands are specified
|
||||
// Expects a `cli.ActionFunc` but will accept the *deprecated* signature of `func(*cli.Context) {}`
|
||||
// *Note*: support for the deprecated `Action` signature will be removed in a future version
|
||||
Action interface{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Execute this function if the proper command cannot be found
|
||||
CommandNotFound CommandNotFoundFunc
|
||||
// Execute this function if an usage error occurs
|
||||
OnUsageError OnUsageErrorFunc
|
||||
// Compilation date
|
||||
Compiled time.Time
|
||||
// List of all authors who contributed
|
||||
Authors []Author
|
||||
// Copyright of the binary if any
|
||||
Copyright string
|
||||
// Name of Author (Note: Use App.Authors, this is deprecated)
|
||||
Author string
|
||||
// Email of Author (Note: Use App.Authors, this is deprecated)
|
||||
Email string
|
||||
// Writer writer to write output to
|
||||
Writer io.Writer
|
||||
// ErrWriter writes error output
|
||||
ErrWriter io.Writer
|
||||
// Other custom info
|
||||
Metadata map[string]interface{}
|
||||
// Carries a function which returns app specific info.
|
||||
ExtraInfo func() map[string]string
|
||||
// CustomAppHelpTemplate the text template for app help topic.
|
||||
// cli.go uses text/template to render templates. You can
|
||||
// render custom help text by setting this variable.
|
||||
CustomAppHelpTemplate string
|
||||
|
||||
didSetup bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Tries to find out when this binary was compiled.
|
||||
// Returns the current time if it fails to find it.
|
||||
func compileTime() time.Time {
|
||||
info, err := os.Stat(os.Args[0])
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return time.Now()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return info.ModTime()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewApp creates a new cli Application with some reasonable defaults for Name,
|
||||
// Usage, Version and Action.
|
||||
func NewApp() *App {
|
||||
return &App{
|
||||
Name: filepath.Base(os.Args[0]),
|
||||
HelpName: filepath.Base(os.Args[0]),
|
||||
Usage: "A new cli application",
|
||||
UsageText: "",
|
||||
Version: "0.0.0",
|
||||
BashComplete: DefaultAppComplete,
|
||||
Action: helpCommand.Action,
|
||||
Compiled: compileTime(),
|
||||
Writer: os.Stdout,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Setup runs initialization code to ensure all data structures are ready for
|
||||
// `Run` or inspection prior to `Run`. It is internally called by `Run`, but
|
||||
// will return early if setup has already happened.
|
||||
func (a *App) Setup() {
|
||||
if a.didSetup {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a.didSetup = true
|
||||
|
||||
if a.Author != "" || a.Email != "" {
|
||||
a.Authors = append(a.Authors, Author{Name: a.Author, Email: a.Email})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
newCmds := []Command{}
|
||||
for _, c := range a.Commands {
|
||||
if c.HelpName == "" {
|
||||
c.HelpName = fmt.Sprintf("%s %s", a.HelpName, c.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
newCmds = append(newCmds, c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
a.Commands = newCmds
|
||||
|
||||
if a.Command(helpCommand.Name) == nil && !a.HideHelp {
|
||||
a.Commands = append(a.Commands, helpCommand)
|
||||
if (HelpFlag != BoolFlag{}) {
|
||||
a.appendFlag(HelpFlag)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if !a.HideVersion {
|
||||
a.appendFlag(VersionFlag)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a.categories = CommandCategories{}
|
||||
for _, command := range a.Commands {
|
||||
a.categories = a.categories.AddCommand(command.Category, command)
|
||||
}
|
||||
sort.Sort(a.categories)
|
||||
|
||||
if a.Metadata == nil {
|
||||
a.Metadata = make(map[string]interface{})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if a.Writer == nil {
|
||||
a.Writer = os.Stdout
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Run is the entry point to the cli app. Parses the arguments slice and routes
|
||||
// to the proper flag/args combination
|
||||
func (a *App) Run(arguments []string) (err error) {
|
||||
a.Setup()
|
||||
|
||||
// handle the completion flag separately from the flagset since
|
||||
// completion could be attempted after a flag, but before its value was put
|
||||
// on the command line. this causes the flagset to interpret the completion
|
||||
// flag name as the value of the flag before it which is undesirable
|
||||
// note that we can only do this because the shell autocomplete function
|
||||
// always appends the completion flag at the end of the command
|
||||
shellComplete, arguments := checkShellCompleteFlag(a, arguments)
|
||||
|
||||
// parse flags
|
||||
set, err := flagSet(a.Name, a.Flags)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
set.SetOutput(ioutil.Discard)
|
||||
err = set.Parse(arguments[1:])
|
||||
nerr := normalizeFlags(a.Flags, set)
|
||||
context := NewContext(a, set, nil)
|
||||
if nerr != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(a.Writer, nerr)
|
||||
ShowAppHelp(context)
|
||||
return nerr
|
||||
}
|
||||
context.shellComplete = shellComplete
|
||||
|
||||
if checkCompletions(context) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if a.OnUsageError != nil {
|
||||
err := a.OnUsageError(context, err, false)
|
||||
HandleExitCoder(err)
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(a.Writer, "%s %s\n\n", "Incorrect Usage.", err.Error())
|
||||
ShowAppHelp(context)
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if !a.HideHelp && checkHelp(context) {
|
||||
ShowAppHelp(context)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if !a.HideVersion && checkVersion(context) {
|
||||
ShowVersion(context)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if a.After != nil {
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if afterErr := a.After(context); afterErr != nil {
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
err = NewMultiError(err, afterErr)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
err = afterErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if a.Before != nil {
|
||||
beforeErr := a.Before(context)
|
||||
if beforeErr != nil {
|
||||
ShowAppHelp(context)
|
||||
HandleExitCoder(beforeErr)
|
||||
err = beforeErr
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
args := context.Args()
|
||||
if args.Present() {
|
||||
name := args.First()
|
||||
c := a.Command(name)
|
||||
if c != nil {
|
||||
return c.Run(context)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if a.Action == nil {
|
||||
a.Action = helpCommand.Action
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Run default Action
|
||||
err = HandleAction(a.Action, context)
|
||||
|
||||
HandleExitCoder(err)
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RunAndExitOnError calls .Run() and exits non-zero if an error was returned
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: instead you should return an error that fulfills cli.ExitCoder
|
||||
// to cli.App.Run. This will cause the application to exit with the given eror
|
||||
// code in the cli.ExitCoder
|
||||
func (a *App) RunAndExitOnError() {
|
||||
if err := a.Run(os.Args); err != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(a.errWriter(), err)
|
||||
OsExiter(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RunAsSubcommand invokes the subcommand given the context, parses ctx.Args() to
|
||||
// generate command-specific flags
|
||||
func (a *App) RunAsSubcommand(ctx *Context) (err error) {
|
||||
// append help to commands
|
||||
if len(a.Commands) > 0 {
|
||||
if a.Command(helpCommand.Name) == nil && !a.HideHelp {
|
||||
a.Commands = append(a.Commands, helpCommand)
|
||||
if (HelpFlag != BoolFlag{}) {
|
||||
a.appendFlag(HelpFlag)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
newCmds := []Command{}
|
||||
for _, c := range a.Commands {
|
||||
if c.HelpName == "" {
|
||||
c.HelpName = fmt.Sprintf("%s %s", a.HelpName, c.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
newCmds = append(newCmds, c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
a.Commands = newCmds
|
||||
|
||||
// parse flags
|
||||
set, err := flagSet(a.Name, a.Flags)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
set.SetOutput(ioutil.Discard)
|
||||
err = set.Parse(ctx.Args().Tail())
|
||||
nerr := normalizeFlags(a.Flags, set)
|
||||
context := NewContext(a, set, ctx)
|
||||
|
||||
if nerr != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(a.Writer, nerr)
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(a.Writer)
|
||||
if len(a.Commands) > 0 {
|
||||
ShowSubcommandHelp(context)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
ShowCommandHelp(ctx, context.Args().First())
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nerr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if checkCompletions(context) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if a.OnUsageError != nil {
|
||||
err = a.OnUsageError(context, err, true)
|
||||
HandleExitCoder(err)
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(a.Writer, "%s %s\n\n", "Incorrect Usage.", err.Error())
|
||||
ShowSubcommandHelp(context)
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if len(a.Commands) > 0 {
|
||||
if checkSubcommandHelp(context) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if checkCommandHelp(ctx, context.Args().First()) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if a.After != nil {
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
afterErr := a.After(context)
|
||||
if afterErr != nil {
|
||||
HandleExitCoder(err)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
err = NewMultiError(err, afterErr)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
err = afterErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if a.Before != nil {
|
||||
beforeErr := a.Before(context)
|
||||
if beforeErr != nil {
|
||||
HandleExitCoder(beforeErr)
|
||||
err = beforeErr
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
args := context.Args()
|
||||
if args.Present() {
|
||||
name := args.First()
|
||||
c := a.Command(name)
|
||||
if c != nil {
|
||||
return c.Run(context)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Run default Action
|
||||
err = HandleAction(a.Action, context)
|
||||
|
||||
HandleExitCoder(err)
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the named command on App. Returns nil if the command does not exist
|
||||
func (a *App) Command(name string) *Command {
|
||||
for _, c := range a.Commands {
|
||||
if c.HasName(name) {
|
||||
return &c
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Categories returns a slice containing all the categories with the commands they contain
|
||||
func (a *App) Categories() CommandCategories {
|
||||
return a.categories
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VisibleCategories returns a slice of categories and commands that are
|
||||
// Hidden=false
|
||||
func (a *App) VisibleCategories() []*CommandCategory {
|
||||
ret := []*CommandCategory{}
|
||||
for _, category := range a.categories {
|
||||
if visible := func() *CommandCategory {
|
||||
for _, command := range category.Commands {
|
||||
if !command.Hidden {
|
||||
return category
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}(); visible != nil {
|
||||
ret = append(ret, visible)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ret
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VisibleCommands returns a slice of the Commands with Hidden=false
|
||||
func (a *App) VisibleCommands() []Command {
|
||||
ret := []Command{}
|
||||
for _, command := range a.Commands {
|
||||
if !command.Hidden {
|
||||
ret = append(ret, command)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ret
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VisibleFlags returns a slice of the Flags with Hidden=false
|
||||
func (a *App) VisibleFlags() []Flag {
|
||||
return visibleFlags(a.Flags)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *App) hasFlag(flag Flag) bool {
|
||||
for _, f := range a.Flags {
|
||||
if flag == f {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *App) errWriter() io.Writer {
|
||||
|
||||
// When the app ErrWriter is nil use the package level one.
|
||||
if a.ErrWriter == nil {
|
||||
return ErrWriter
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return a.ErrWriter
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (a *App) appendFlag(flag Flag) {
|
||||
if !a.hasFlag(flag) {
|
||||
a.Flags = append(a.Flags, flag)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Author represents someone who has contributed to a cli project.
|
||||
type Author struct {
|
||||
Name string // The Authors name
|
||||
Email string // The Authors email
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String makes Author comply to the Stringer interface, to allow an easy print in the templating process
|
||||
func (a Author) String() string {
|
||||
e := ""
|
||||
if a.Email != "" {
|
||||
e = " <" + a.Email + ">"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%v%v", a.Name, e)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HandleAction attempts to figure out which Action signature was used. If
|
||||
// it's an ActionFunc or a func with the legacy signature for Action, the func
|
||||
// is run!
|
||||
func HandleAction(action interface{}, context *Context) (err error) {
|
||||
if a, ok := action.(ActionFunc); ok {
|
||||
return a(context)
|
||||
} else if a, ok := action.(func(*Context) error); ok {
|
||||
return a(context)
|
||||
} else if a, ok := action.(func(*Context)); ok { // deprecated function signature
|
||||
a(context)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return errInvalidActionType
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
26
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/appveyor.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
26
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/appveyor.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
version: "{build}"
|
||||
|
||||
os: Windows Server 2016
|
||||
|
||||
image: Visual Studio 2017
|
||||
|
||||
clone_folder: c:\gopath\src\github.com\urfave\cli
|
||||
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
GOPATH: C:\gopath
|
||||
GOVERSION: 1.8.x
|
||||
PYTHON: C:\Python36-x64
|
||||
PYTHON_VERSION: 3.6.x
|
||||
PYTHON_ARCH: 64
|
||||
|
||||
install:
|
||||
- set PATH=%GOPATH%\bin;C:\go\bin;%PATH%
|
||||
- go version
|
||||
- go env
|
||||
- go get github.com/urfave/gfmrun/...
|
||||
- go get -v -t ./...
|
||||
|
||||
build_script:
|
||||
- python runtests vet
|
||||
- python runtests test
|
||||
- python runtests gfmrun
|
||||
44
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/category.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
44
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/category.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
package cli
|
||||
|
||||
// CommandCategories is a slice of *CommandCategory.
|
||||
type CommandCategories []*CommandCategory
|
||||
|
||||
// CommandCategory is a category containing commands.
|
||||
type CommandCategory struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Commands Commands
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c CommandCategories) Less(i, j int) bool {
|
||||
return c[i].Name < c[j].Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c CommandCategories) Len() int {
|
||||
return len(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c CommandCategories) Swap(i, j int) {
|
||||
c[i], c[j] = c[j], c[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddCommand adds a command to a category.
|
||||
func (c CommandCategories) AddCommand(category string, command Command) CommandCategories {
|
||||
for _, commandCategory := range c {
|
||||
if commandCategory.Name == category {
|
||||
commandCategory.Commands = append(commandCategory.Commands, command)
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return append(c, &CommandCategory{Name: category, Commands: []Command{command}})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VisibleCommands returns a slice of the Commands with Hidden=false
|
||||
func (c *CommandCategory) VisibleCommands() []Command {
|
||||
ret := []Command{}
|
||||
for _, command := range c.Commands {
|
||||
if !command.Hidden {
|
||||
ret = append(ret, command)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ret
|
||||
}
|
||||
22
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/cli.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
22
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/cli.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
// Package cli provides a minimal framework for creating and organizing command line
|
||||
// Go applications. cli is designed to be easy to understand and write, the most simple
|
||||
// cli application can be written as follows:
|
||||
// func main() {
|
||||
// cli.NewApp().Run(os.Args)
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Of course this application does not do much, so let's make this an actual application:
|
||||
// func main() {
|
||||
// app := cli.NewApp()
|
||||
// app.Name = "greet"
|
||||
// app.Usage = "say a greeting"
|
||||
// app.Action = func(c *cli.Context) error {
|
||||
// println("Greetings")
|
||||
// return nil
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// app.Run(os.Args)
|
||||
// }
|
||||
package cli
|
||||
|
||||
//go:generate python ./generate-flag-types cli -i flag-types.json -o flag_generated.go
|
||||
304
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/command.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
304
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/command.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,304 @@
|
||||
package cli
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io/ioutil"
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Command is a subcommand for a cli.App.
|
||||
type Command struct {
|
||||
// The name of the command
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
// short name of the command. Typically one character (deprecated, use `Aliases`)
|
||||
ShortName string
|
||||
// A list of aliases for the command
|
||||
Aliases []string
|
||||
// A short description of the usage of this command
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
// Custom text to show on USAGE section of help
|
||||
UsageText string
|
||||
// A longer explanation of how the command works
|
||||
Description string
|
||||
// A short description of the arguments of this command
|
||||
ArgsUsage string
|
||||
// The category the command is part of
|
||||
Category string
|
||||
// The function to call when checking for bash command completions
|
||||
BashComplete BashCompleteFunc
|
||||
// An action to execute before any sub-subcommands are run, but after the context is ready
|
||||
// If a non-nil error is returned, no sub-subcommands are run
|
||||
Before BeforeFunc
|
||||
// An action to execute after any subcommands are run, but after the subcommand has finished
|
||||
// It is run even if Action() panics
|
||||
After AfterFunc
|
||||
// The function to call when this command is invoked
|
||||
Action interface{}
|
||||
// TODO: replace `Action: interface{}` with `Action: ActionFunc` once some kind
|
||||
// of deprecation period has passed, maybe?
|
||||
|
||||
// Execute this function if a usage error occurs.
|
||||
OnUsageError OnUsageErrorFunc
|
||||
// List of child commands
|
||||
Subcommands Commands
|
||||
// List of flags to parse
|
||||
Flags []Flag
|
||||
// Treat all flags as normal arguments if true
|
||||
SkipFlagParsing bool
|
||||
// Skip argument reordering which attempts to move flags before arguments,
|
||||
// but only works if all flags appear after all arguments. This behavior was
|
||||
// removed n version 2 since it only works under specific conditions so we
|
||||
// backport here by exposing it as an option for compatibility.
|
||||
SkipArgReorder bool
|
||||
// Boolean to hide built-in help command
|
||||
HideHelp bool
|
||||
// Boolean to hide this command from help or completion
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
|
||||
// Full name of command for help, defaults to full command name, including parent commands.
|
||||
HelpName string
|
||||
commandNamePath []string
|
||||
|
||||
// CustomHelpTemplate the text template for the command help topic.
|
||||
// cli.go uses text/template to render templates. You can
|
||||
// render custom help text by setting this variable.
|
||||
CustomHelpTemplate string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type CommandsByName []Command
|
||||
|
||||
func (c CommandsByName) Len() int {
|
||||
return len(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c CommandsByName) Less(i, j int) bool {
|
||||
return c[i].Name < c[j].Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c CommandsByName) Swap(i, j int) {
|
||||
c[i], c[j] = c[j], c[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// FullName returns the full name of the command.
|
||||
// For subcommands this ensures that parent commands are part of the command path
|
||||
func (c Command) FullName() string {
|
||||
if c.commandNamePath == nil {
|
||||
return c.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
return strings.Join(c.commandNamePath, " ")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Commands is a slice of Command
|
||||
type Commands []Command
|
||||
|
||||
// Run invokes the command given the context, parses ctx.Args() to generate command-specific flags
|
||||
func (c Command) Run(ctx *Context) (err error) {
|
||||
if len(c.Subcommands) > 0 {
|
||||
return c.startApp(ctx)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if !c.HideHelp && (HelpFlag != BoolFlag{}) {
|
||||
// append help to flags
|
||||
c.Flags = append(
|
||||
c.Flags,
|
||||
HelpFlag,
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
set, err := flagSet(c.Name, c.Flags)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
set.SetOutput(ioutil.Discard)
|
||||
|
||||
if c.SkipFlagParsing {
|
||||
err = set.Parse(append([]string{"--"}, ctx.Args().Tail()...))
|
||||
} else if !c.SkipArgReorder {
|
||||
firstFlagIndex := -1
|
||||
terminatorIndex := -1
|
||||
for index, arg := range ctx.Args() {
|
||||
if arg == "--" {
|
||||
terminatorIndex = index
|
||||
break
|
||||
} else if arg == "-" {
|
||||
// Do nothing. A dash alone is not really a flag.
|
||||
continue
|
||||
} else if strings.HasPrefix(arg, "-") && firstFlagIndex == -1 {
|
||||
firstFlagIndex = index
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if firstFlagIndex > -1 {
|
||||
args := ctx.Args()
|
||||
regularArgs := make([]string, len(args[1:firstFlagIndex]))
|
||||
copy(regularArgs, args[1:firstFlagIndex])
|
||||
|
||||
var flagArgs []string
|
||||
if terminatorIndex > -1 {
|
||||
flagArgs = args[firstFlagIndex:terminatorIndex]
|
||||
regularArgs = append(regularArgs, args[terminatorIndex:]...)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
flagArgs = args[firstFlagIndex:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
err = set.Parse(append(flagArgs, regularArgs...))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
err = set.Parse(ctx.Args().Tail())
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
err = set.Parse(ctx.Args().Tail())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
nerr := normalizeFlags(c.Flags, set)
|
||||
if nerr != nil {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(ctx.App.Writer, nerr)
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(ctx.App.Writer)
|
||||
ShowCommandHelp(ctx, c.Name)
|
||||
return nerr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
context := NewContext(ctx.App, set, ctx)
|
||||
context.Command = c
|
||||
if checkCommandCompletions(context, c.Name) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if c.OnUsageError != nil {
|
||||
err := c.OnUsageError(context, err, false)
|
||||
HandleExitCoder(err)
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(context.App.Writer, "Incorrect Usage:", err.Error())
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(context.App.Writer)
|
||||
ShowCommandHelp(context, c.Name)
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if checkCommandHelp(context, c.Name) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if c.After != nil {
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
afterErr := c.After(context)
|
||||
if afterErr != nil {
|
||||
HandleExitCoder(err)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
err = NewMultiError(err, afterErr)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
err = afterErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if c.Before != nil {
|
||||
err = c.Before(context)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
ShowCommandHelp(context, c.Name)
|
||||
HandleExitCoder(err)
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if c.Action == nil {
|
||||
c.Action = helpSubcommand.Action
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
err = HandleAction(c.Action, context)
|
||||
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
HandleExitCoder(err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Names returns the names including short names and aliases.
|
||||
func (c Command) Names() []string {
|
||||
names := []string{c.Name}
|
||||
|
||||
if c.ShortName != "" {
|
||||
names = append(names, c.ShortName)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return append(names, c.Aliases...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasName returns true if Command.Name or Command.ShortName matches given name
|
||||
func (c Command) HasName(name string) bool {
|
||||
for _, n := range c.Names() {
|
||||
if n == name {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c Command) startApp(ctx *Context) error {
|
||||
app := NewApp()
|
||||
app.Metadata = ctx.App.Metadata
|
||||
// set the name and usage
|
||||
app.Name = fmt.Sprintf("%s %s", ctx.App.Name, c.Name)
|
||||
if c.HelpName == "" {
|
||||
app.HelpName = c.HelpName
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
app.HelpName = app.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
app.Usage = c.Usage
|
||||
app.Description = c.Description
|
||||
app.ArgsUsage = c.ArgsUsage
|
||||
|
||||
// set CommandNotFound
|
||||
app.CommandNotFound = ctx.App.CommandNotFound
|
||||
app.CustomAppHelpTemplate = c.CustomHelpTemplate
|
||||
|
||||
// set the flags and commands
|
||||
app.Commands = c.Subcommands
|
||||
app.Flags = c.Flags
|
||||
app.HideHelp = c.HideHelp
|
||||
|
||||
app.Version = ctx.App.Version
|
||||
app.HideVersion = ctx.App.HideVersion
|
||||
app.Compiled = ctx.App.Compiled
|
||||
app.Author = ctx.App.Author
|
||||
app.Email = ctx.App.Email
|
||||
app.Writer = ctx.App.Writer
|
||||
app.ErrWriter = ctx.App.ErrWriter
|
||||
|
||||
app.categories = CommandCategories{}
|
||||
for _, command := range c.Subcommands {
|
||||
app.categories = app.categories.AddCommand(command.Category, command)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sort.Sort(app.categories)
|
||||
|
||||
// bash completion
|
||||
app.EnableBashCompletion = ctx.App.EnableBashCompletion
|
||||
if c.BashComplete != nil {
|
||||
app.BashComplete = c.BashComplete
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// set the actions
|
||||
app.Before = c.Before
|
||||
app.After = c.After
|
||||
if c.Action != nil {
|
||||
app.Action = c.Action
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
app.Action = helpSubcommand.Action
|
||||
}
|
||||
app.OnUsageError = c.OnUsageError
|
||||
|
||||
for index, cc := range app.Commands {
|
||||
app.Commands[index].commandNamePath = []string{c.Name, cc.Name}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return app.RunAsSubcommand(ctx)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VisibleFlags returns a slice of the Flags with Hidden=false
|
||||
func (c Command) VisibleFlags() []Flag {
|
||||
return visibleFlags(c.Flags)
|
||||
}
|
||||
278
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/context.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
278
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/context.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,278 @@
|
||||
package cli
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"flag"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"syscall"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Context is a type that is passed through to
|
||||
// each Handler action in a cli application. Context
|
||||
// can be used to retrieve context-specific Args and
|
||||
// parsed command-line options.
|
||||
type Context struct {
|
||||
App *App
|
||||
Command Command
|
||||
shellComplete bool
|
||||
flagSet *flag.FlagSet
|
||||
setFlags map[string]bool
|
||||
parentContext *Context
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewContext creates a new context. For use in when invoking an App or Command action.
|
||||
func NewContext(app *App, set *flag.FlagSet, parentCtx *Context) *Context {
|
||||
c := &Context{App: app, flagSet: set, parentContext: parentCtx}
|
||||
|
||||
if parentCtx != nil {
|
||||
c.shellComplete = parentCtx.shellComplete
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NumFlags returns the number of flags set
|
||||
func (c *Context) NumFlags() int {
|
||||
return c.flagSet.NFlag()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Set sets a context flag to a value.
|
||||
func (c *Context) Set(name, value string) error {
|
||||
c.setFlags = nil
|
||||
return c.flagSet.Set(name, value)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalSet sets a context flag to a value on the global flagset
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalSet(name, value string) error {
|
||||
globalContext(c).setFlags = nil
|
||||
return globalContext(c).flagSet.Set(name, value)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsSet determines if the flag was actually set
|
||||
func (c *Context) IsSet(name string) bool {
|
||||
if c.setFlags == nil {
|
||||
c.setFlags = make(map[string]bool)
|
||||
|
||||
c.flagSet.Visit(func(f *flag.Flag) {
|
||||
c.setFlags[f.Name] = true
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
c.flagSet.VisitAll(func(f *flag.Flag) {
|
||||
if _, ok := c.setFlags[f.Name]; ok {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
c.setFlags[f.Name] = false
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
// XXX hack to support IsSet for flags with EnvVar
|
||||
//
|
||||
// There isn't an easy way to do this with the current implementation since
|
||||
// whether a flag was set via an environment variable is very difficult to
|
||||
// determine here. Instead, we intend to introduce a backwards incompatible
|
||||
// change in version 2 to add `IsSet` to the Flag interface to push the
|
||||
// responsibility closer to where the information required to determine
|
||||
// whether a flag is set by non-standard means such as environment
|
||||
// variables is avaliable.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://github.com/urfave/cli/issues/294 for additional discussion
|
||||
flags := c.Command.Flags
|
||||
if c.Command.Name == "" { // cannot == Command{} since it contains slice types
|
||||
if c.App != nil {
|
||||
flags = c.App.Flags
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, f := range flags {
|
||||
eachName(f.GetName(), func(name string) {
|
||||
if isSet, ok := c.setFlags[name]; isSet || !ok {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
val := reflect.ValueOf(f)
|
||||
if val.Kind() == reflect.Ptr {
|
||||
val = val.Elem()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
envVarValue := val.FieldByName("EnvVar")
|
||||
if !envVarValue.IsValid() {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
eachName(envVarValue.String(), func(envVar string) {
|
||||
envVar = strings.TrimSpace(envVar)
|
||||
if _, ok := syscall.Getenv(envVar); ok {
|
||||
c.setFlags[name] = true
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
})
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return c.setFlags[name]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalIsSet determines if the global flag was actually set
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalIsSet(name string) bool {
|
||||
ctx := c
|
||||
if ctx.parentContext != nil {
|
||||
ctx = ctx.parentContext
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for ; ctx != nil; ctx = ctx.parentContext {
|
||||
if ctx.IsSet(name) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// FlagNames returns a slice of flag names used in this context.
|
||||
func (c *Context) FlagNames() (names []string) {
|
||||
for _, flag := range c.Command.Flags {
|
||||
name := strings.Split(flag.GetName(), ",")[0]
|
||||
if name == "help" {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
names = append(names, name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalFlagNames returns a slice of global flag names used by the app.
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalFlagNames() (names []string) {
|
||||
for _, flag := range c.App.Flags {
|
||||
name := strings.Split(flag.GetName(), ",")[0]
|
||||
if name == "help" || name == "version" {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
names = append(names, name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parent returns the parent context, if any
|
||||
func (c *Context) Parent() *Context {
|
||||
return c.parentContext
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// value returns the value of the flag coressponding to `name`
|
||||
func (c *Context) value(name string) interface{} {
|
||||
return c.flagSet.Lookup(name).Value.(flag.Getter).Get()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Args contains apps console arguments
|
||||
type Args []string
|
||||
|
||||
// Args returns the command line arguments associated with the context.
|
||||
func (c *Context) Args() Args {
|
||||
args := Args(c.flagSet.Args())
|
||||
return args
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NArg returns the number of the command line arguments.
|
||||
func (c *Context) NArg() int {
|
||||
return len(c.Args())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Get returns the nth argument, or else a blank string
|
||||
func (a Args) Get(n int) string {
|
||||
if len(a) > n {
|
||||
return a[n]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// First returns the first argument, or else a blank string
|
||||
func (a Args) First() string {
|
||||
return a.Get(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Tail returns the rest of the arguments (not the first one)
|
||||
// or else an empty string slice
|
||||
func (a Args) Tail() []string {
|
||||
if len(a) >= 2 {
|
||||
return []string(a)[1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return []string{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Present checks if there are any arguments present
|
||||
func (a Args) Present() bool {
|
||||
return len(a) != 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Swap swaps arguments at the given indexes
|
||||
func (a Args) Swap(from, to int) error {
|
||||
if from >= len(a) || to >= len(a) {
|
||||
return errors.New("index out of range")
|
||||
}
|
||||
a[from], a[to] = a[to], a[from]
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func globalContext(ctx *Context) *Context {
|
||||
if ctx == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for {
|
||||
if ctx.parentContext == nil {
|
||||
return ctx
|
||||
}
|
||||
ctx = ctx.parentContext
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookupGlobalFlagSet(name string, ctx *Context) *flag.FlagSet {
|
||||
if ctx.parentContext != nil {
|
||||
ctx = ctx.parentContext
|
||||
}
|
||||
for ; ctx != nil; ctx = ctx.parentContext {
|
||||
if f := ctx.flagSet.Lookup(name); f != nil {
|
||||
return ctx.flagSet
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func copyFlag(name string, ff *flag.Flag, set *flag.FlagSet) {
|
||||
switch ff.Value.(type) {
|
||||
case *StringSlice:
|
||||
default:
|
||||
set.Set(name, ff.Value.String())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func normalizeFlags(flags []Flag, set *flag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
visited := make(map[string]bool)
|
||||
set.Visit(func(f *flag.Flag) {
|
||||
visited[f.Name] = true
|
||||
})
|
||||
for _, f := range flags {
|
||||
parts := strings.Split(f.GetName(), ",")
|
||||
if len(parts) == 1 {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
var ff *flag.Flag
|
||||
for _, name := range parts {
|
||||
name = strings.Trim(name, " ")
|
||||
if visited[name] {
|
||||
if ff != nil {
|
||||
return errors.New("Cannot use two forms of the same flag: " + name + " " + ff.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
ff = set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if ff == nil {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, name := range parts {
|
||||
name = strings.Trim(name, " ")
|
||||
if !visited[name] {
|
||||
copyFlag(name, ff, set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
115
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/errors.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
115
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/errors.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
|
||||
package cli
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// OsExiter is the function used when the app exits. If not set defaults to os.Exit.
|
||||
var OsExiter = os.Exit
|
||||
|
||||
// ErrWriter is used to write errors to the user. This can be anything
|
||||
// implementing the io.Writer interface and defaults to os.Stderr.
|
||||
var ErrWriter io.Writer = os.Stderr
|
||||
|
||||
// MultiError is an error that wraps multiple errors.
|
||||
type MultiError struct {
|
||||
Errors []error
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewMultiError creates a new MultiError. Pass in one or more errors.
|
||||
func NewMultiError(err ...error) MultiError {
|
||||
return MultiError{Errors: err}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Error implements the error interface.
|
||||
func (m MultiError) Error() string {
|
||||
errs := make([]string, len(m.Errors))
|
||||
for i, err := range m.Errors {
|
||||
errs[i] = err.Error()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return strings.Join(errs, "\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type ErrorFormatter interface {
|
||||
Format(s fmt.State, verb rune)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExitCoder is the interface checked by `App` and `Command` for a custom exit
|
||||
// code
|
||||
type ExitCoder interface {
|
||||
error
|
||||
ExitCode() int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExitError fulfills both the builtin `error` interface and `ExitCoder`
|
||||
type ExitError struct {
|
||||
exitCode int
|
||||
message interface{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewExitError makes a new *ExitError
|
||||
func NewExitError(message interface{}, exitCode int) *ExitError {
|
||||
return &ExitError{
|
||||
exitCode: exitCode,
|
||||
message: message,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Error returns the string message, fulfilling the interface required by
|
||||
// `error`
|
||||
func (ee *ExitError) Error() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%v", ee.message)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExitCode returns the exit code, fulfilling the interface required by
|
||||
// `ExitCoder`
|
||||
func (ee *ExitError) ExitCode() int {
|
||||
return ee.exitCode
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HandleExitCoder checks if the error fulfills the ExitCoder interface, and if
|
||||
// so prints the error to stderr (if it is non-empty) and calls OsExiter with the
|
||||
// given exit code. If the given error is a MultiError, then this func is
|
||||
// called on all members of the Errors slice and calls OsExiter with the last exit code.
|
||||
func HandleExitCoder(err error) {
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if exitErr, ok := err.(ExitCoder); ok {
|
||||
if err.Error() != "" {
|
||||
if _, ok := exitErr.(ErrorFormatter); ok {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(ErrWriter, "%+v\n", err)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(ErrWriter, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
OsExiter(exitErr.ExitCode())
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if multiErr, ok := err.(MultiError); ok {
|
||||
code := handleMultiError(multiErr)
|
||||
OsExiter(code)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func handleMultiError(multiErr MultiError) int {
|
||||
code := 1
|
||||
for _, merr := range multiErr.Errors {
|
||||
if multiErr2, ok := merr.(MultiError); ok {
|
||||
code = handleMultiError(multiErr2)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(ErrWriter, merr)
|
||||
if exitErr, ok := merr.(ExitCoder); ok {
|
||||
code = exitErr.ExitCode()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return code
|
||||
}
|
||||
93
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/flag-types.json
generated
vendored
Normal file
93
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/flag-types.json
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
[
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "Bool",
|
||||
"type": "bool",
|
||||
"value": false,
|
||||
"context_default": "false",
|
||||
"parser": "strconv.ParseBool(f.Value.String())"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "BoolT",
|
||||
"type": "bool",
|
||||
"value": false,
|
||||
"doctail": " that is true by default",
|
||||
"context_default": "false",
|
||||
"parser": "strconv.ParseBool(f.Value.String())"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "Duration",
|
||||
"type": "time.Duration",
|
||||
"doctail": " (see https://golang.org/pkg/time/#ParseDuration)",
|
||||
"context_default": "0",
|
||||
"parser": "time.ParseDuration(f.Value.String())"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "Float64",
|
||||
"type": "float64",
|
||||
"context_default": "0",
|
||||
"parser": "strconv.ParseFloat(f.Value.String(), 64)"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "Generic",
|
||||
"type": "Generic",
|
||||
"dest": false,
|
||||
"context_default": "nil",
|
||||
"context_type": "interface{}"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "Int64",
|
||||
"type": "int64",
|
||||
"context_default": "0",
|
||||
"parser": "strconv.ParseInt(f.Value.String(), 0, 64)"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "Int",
|
||||
"type": "int",
|
||||
"context_default": "0",
|
||||
"parser": "strconv.ParseInt(f.Value.String(), 0, 64)",
|
||||
"parser_cast": "int(parsed)"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "IntSlice",
|
||||
"type": "*IntSlice",
|
||||
"dest": false,
|
||||
"context_default": "nil",
|
||||
"context_type": "[]int",
|
||||
"parser": "(f.Value.(*IntSlice)).Value(), error(nil)"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "Int64Slice",
|
||||
"type": "*Int64Slice",
|
||||
"dest": false,
|
||||
"context_default": "nil",
|
||||
"context_type": "[]int64",
|
||||
"parser": "(f.Value.(*Int64Slice)).Value(), error(nil)"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "String",
|
||||
"type": "string",
|
||||
"context_default": "\"\"",
|
||||
"parser": "f.Value.String(), error(nil)"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "StringSlice",
|
||||
"type": "*StringSlice",
|
||||
"dest": false,
|
||||
"context_default": "nil",
|
||||
"context_type": "[]string",
|
||||
"parser": "(f.Value.(*StringSlice)).Value(), error(nil)"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "Uint64",
|
||||
"type": "uint64",
|
||||
"context_default": "0",
|
||||
"parser": "strconv.ParseUint(f.Value.String(), 0, 64)"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "Uint",
|
||||
"type": "uint",
|
||||
"context_default": "0",
|
||||
"parser": "strconv.ParseUint(f.Value.String(), 0, 64)",
|
||||
"parser_cast": "uint(parsed)"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
799
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/flag.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
799
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/flag.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,799 @@
|
||||
package cli
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"flag"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
"runtime"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"syscall"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const defaultPlaceholder = "value"
|
||||
|
||||
// BashCompletionFlag enables bash-completion for all commands and subcommands
|
||||
var BashCompletionFlag Flag = BoolFlag{
|
||||
Name: "generate-bash-completion",
|
||||
Hidden: true,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VersionFlag prints the version for the application
|
||||
var VersionFlag Flag = BoolFlag{
|
||||
Name: "version, v",
|
||||
Usage: "print the version",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HelpFlag prints the help for all commands and subcommands
|
||||
// Set to the zero value (BoolFlag{}) to disable flag -- keeps subcommand
|
||||
// unless HideHelp is set to true)
|
||||
var HelpFlag Flag = BoolFlag{
|
||||
Name: "help, h",
|
||||
Usage: "show help",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// FlagStringer converts a flag definition to a string. This is used by help
|
||||
// to display a flag.
|
||||
var FlagStringer FlagStringFunc = stringifyFlag
|
||||
|
||||
// FlagsByName is a slice of Flag.
|
||||
type FlagsByName []Flag
|
||||
|
||||
func (f FlagsByName) Len() int {
|
||||
return len(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f FlagsByName) Less(i, j int) bool {
|
||||
return f[i].GetName() < f[j].GetName()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f FlagsByName) Swap(i, j int) {
|
||||
f[i], f[j] = f[j], f[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Flag is a common interface related to parsing flags in cli.
|
||||
// For more advanced flag parsing techniques, it is recommended that
|
||||
// this interface be implemented.
|
||||
type Flag interface {
|
||||
fmt.Stringer
|
||||
// Apply Flag settings to the given flag set
|
||||
Apply(*flag.FlagSet)
|
||||
GetName() string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// errorableFlag is an interface that allows us to return errors during apply
|
||||
// it allows flags defined in this library to return errors in a fashion backwards compatible
|
||||
// TODO remove in v2 and modify the existing Flag interface to return errors
|
||||
type errorableFlag interface {
|
||||
Flag
|
||||
|
||||
ApplyWithError(*flag.FlagSet) error
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func flagSet(name string, flags []Flag) (*flag.FlagSet, error) {
|
||||
set := flag.NewFlagSet(name, flag.ContinueOnError)
|
||||
|
||||
for _, f := range flags {
|
||||
//TODO remove in v2 when errorableFlag is removed
|
||||
if ef, ok := f.(errorableFlag); ok {
|
||||
if err := ef.ApplyWithError(set); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
f.Apply(set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return set, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func eachName(longName string, fn func(string)) {
|
||||
parts := strings.Split(longName, ",")
|
||||
for _, name := range parts {
|
||||
name = strings.Trim(name, " ")
|
||||
fn(name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Generic is a generic parseable type identified by a specific flag
|
||||
type Generic interface {
|
||||
Set(value string) error
|
||||
String() string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply takes the flagset and calls Set on the generic flag with the value
|
||||
// provided by the user for parsing by the flag
|
||||
// Ignores parsing errors
|
||||
func (f GenericFlag) Apply(set *flag.FlagSet) {
|
||||
f.ApplyWithError(set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyWithError takes the flagset and calls Set on the generic flag with the value
|
||||
// provided by the user for parsing by the flag
|
||||
func (f GenericFlag) ApplyWithError(set *flag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
val := f.Value
|
||||
if f.EnvVar != "" {
|
||||
for _, envVar := range strings.Split(f.EnvVar, ",") {
|
||||
envVar = strings.TrimSpace(envVar)
|
||||
if envVal, ok := syscall.Getenv(envVar); ok {
|
||||
if err := val.Set(envVal); err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("could not parse %s as value for flag %s: %s", envVal, f.Name, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
eachName(f.Name, func(name string) {
|
||||
set.Var(f.Value, name, f.Usage)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StringSlice is an opaque type for []string to satisfy flag.Value and flag.Getter
|
||||
type StringSlice []string
|
||||
|
||||
// Set appends the string value to the list of values
|
||||
func (f *StringSlice) Set(value string) error {
|
||||
*f = append(*f, value)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f *StringSlice) String() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%s", *f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Value returns the slice of strings set by this flag
|
||||
func (f *StringSlice) Value() []string {
|
||||
return *f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Get returns the slice of strings set by this flag
|
||||
func (f *StringSlice) Get() interface{} {
|
||||
return *f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
// Ignores errors
|
||||
func (f StringSliceFlag) Apply(set *flag.FlagSet) {
|
||||
f.ApplyWithError(set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyWithError populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
func (f StringSliceFlag) ApplyWithError(set *flag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
if f.EnvVar != "" {
|
||||
for _, envVar := range strings.Split(f.EnvVar, ",") {
|
||||
envVar = strings.TrimSpace(envVar)
|
||||
if envVal, ok := syscall.Getenv(envVar); ok {
|
||||
newVal := &StringSlice{}
|
||||
for _, s := range strings.Split(envVal, ",") {
|
||||
s = strings.TrimSpace(s)
|
||||
if err := newVal.Set(s); err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("could not parse %s as string value for flag %s: %s", envVal, f.Name, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.Value = newVal
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
eachName(f.Name, func(name string) {
|
||||
if f.Value == nil {
|
||||
f.Value = &StringSlice{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
set.Var(f.Value, name, f.Usage)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IntSlice is an opaque type for []int to satisfy flag.Value and flag.Getter
|
||||
type IntSlice []int
|
||||
|
||||
// Set parses the value into an integer and appends it to the list of values
|
||||
func (f *IntSlice) Set(value string) error {
|
||||
tmp, err := strconv.Atoi(value)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
*f = append(*f, tmp)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f *IntSlice) String() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%#v", *f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Value returns the slice of ints set by this flag
|
||||
func (f *IntSlice) Value() []int {
|
||||
return *f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Get returns the slice of ints set by this flag
|
||||
func (f *IntSlice) Get() interface{} {
|
||||
return *f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
// Ignores errors
|
||||
func (f IntSliceFlag) Apply(set *flag.FlagSet) {
|
||||
f.ApplyWithError(set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyWithError populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
func (f IntSliceFlag) ApplyWithError(set *flag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
if f.EnvVar != "" {
|
||||
for _, envVar := range strings.Split(f.EnvVar, ",") {
|
||||
envVar = strings.TrimSpace(envVar)
|
||||
if envVal, ok := syscall.Getenv(envVar); ok {
|
||||
newVal := &IntSlice{}
|
||||
for _, s := range strings.Split(envVal, ",") {
|
||||
s = strings.TrimSpace(s)
|
||||
if err := newVal.Set(s); err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("could not parse %s as int slice value for flag %s: %s", envVal, f.Name, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.Value = newVal
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
eachName(f.Name, func(name string) {
|
||||
if f.Value == nil {
|
||||
f.Value = &IntSlice{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
set.Var(f.Value, name, f.Usage)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Int64Slice is an opaque type for []int to satisfy flag.Value and flag.Getter
|
||||
type Int64Slice []int64
|
||||
|
||||
// Set parses the value into an integer and appends it to the list of values
|
||||
func (f *Int64Slice) Set(value string) error {
|
||||
tmp, err := strconv.ParseInt(value, 10, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
*f = append(*f, tmp)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f *Int64Slice) String() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%#v", *f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Value returns the slice of ints set by this flag
|
||||
func (f *Int64Slice) Value() []int64 {
|
||||
return *f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Get returns the slice of ints set by this flag
|
||||
func (f *Int64Slice) Get() interface{} {
|
||||
return *f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
// Ignores errors
|
||||
func (f Int64SliceFlag) Apply(set *flag.FlagSet) {
|
||||
f.ApplyWithError(set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyWithError populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
func (f Int64SliceFlag) ApplyWithError(set *flag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
if f.EnvVar != "" {
|
||||
for _, envVar := range strings.Split(f.EnvVar, ",") {
|
||||
envVar = strings.TrimSpace(envVar)
|
||||
if envVal, ok := syscall.Getenv(envVar); ok {
|
||||
newVal := &Int64Slice{}
|
||||
for _, s := range strings.Split(envVal, ",") {
|
||||
s = strings.TrimSpace(s)
|
||||
if err := newVal.Set(s); err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("could not parse %s as int64 slice value for flag %s: %s", envVal, f.Name, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.Value = newVal
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
eachName(f.Name, func(name string) {
|
||||
if f.Value == nil {
|
||||
f.Value = &Int64Slice{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
set.Var(f.Value, name, f.Usage)
|
||||
})
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
// Ignores errors
|
||||
func (f BoolFlag) Apply(set *flag.FlagSet) {
|
||||
f.ApplyWithError(set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyWithError populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
func (f BoolFlag) ApplyWithError(set *flag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
val := false
|
||||
if f.EnvVar != "" {
|
||||
for _, envVar := range strings.Split(f.EnvVar, ",") {
|
||||
envVar = strings.TrimSpace(envVar)
|
||||
if envVal, ok := syscall.Getenv(envVar); ok {
|
||||
if envVal == "" {
|
||||
val = false
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
envValBool, err := strconv.ParseBool(envVal)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("could not parse %s as bool value for flag %s: %s", envVal, f.Name, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
val = envValBool
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
eachName(f.Name, func(name string) {
|
||||
if f.Destination != nil {
|
||||
set.BoolVar(f.Destination, name, val, f.Usage)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
set.Bool(name, val, f.Usage)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
// Ignores errors
|
||||
func (f BoolTFlag) Apply(set *flag.FlagSet) {
|
||||
f.ApplyWithError(set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyWithError populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
func (f BoolTFlag) ApplyWithError(set *flag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
val := true
|
||||
if f.EnvVar != "" {
|
||||
for _, envVar := range strings.Split(f.EnvVar, ",") {
|
||||
envVar = strings.TrimSpace(envVar)
|
||||
if envVal, ok := syscall.Getenv(envVar); ok {
|
||||
if envVal == "" {
|
||||
val = false
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
envValBool, err := strconv.ParseBool(envVal)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("could not parse %s as bool value for flag %s: %s", envVal, f.Name, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
val = envValBool
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
eachName(f.Name, func(name string) {
|
||||
if f.Destination != nil {
|
||||
set.BoolVar(f.Destination, name, val, f.Usage)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
set.Bool(name, val, f.Usage)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
// Ignores errors
|
||||
func (f StringFlag) Apply(set *flag.FlagSet) {
|
||||
f.ApplyWithError(set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyWithError populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
func (f StringFlag) ApplyWithError(set *flag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
if f.EnvVar != "" {
|
||||
for _, envVar := range strings.Split(f.EnvVar, ",") {
|
||||
envVar = strings.TrimSpace(envVar)
|
||||
if envVal, ok := syscall.Getenv(envVar); ok {
|
||||
f.Value = envVal
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
eachName(f.Name, func(name string) {
|
||||
if f.Destination != nil {
|
||||
set.StringVar(f.Destination, name, f.Value, f.Usage)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
set.String(name, f.Value, f.Usage)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
// Ignores errors
|
||||
func (f IntFlag) Apply(set *flag.FlagSet) {
|
||||
f.ApplyWithError(set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyWithError populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
func (f IntFlag) ApplyWithError(set *flag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
if f.EnvVar != "" {
|
||||
for _, envVar := range strings.Split(f.EnvVar, ",") {
|
||||
envVar = strings.TrimSpace(envVar)
|
||||
if envVal, ok := syscall.Getenv(envVar); ok {
|
||||
envValInt, err := strconv.ParseInt(envVal, 0, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("could not parse %s as int value for flag %s: %s", envVal, f.Name, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.Value = int(envValInt)
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
eachName(f.Name, func(name string) {
|
||||
if f.Destination != nil {
|
||||
set.IntVar(f.Destination, name, f.Value, f.Usage)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
set.Int(name, f.Value, f.Usage)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
// Ignores errors
|
||||
func (f Int64Flag) Apply(set *flag.FlagSet) {
|
||||
f.ApplyWithError(set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyWithError populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
func (f Int64Flag) ApplyWithError(set *flag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
if f.EnvVar != "" {
|
||||
for _, envVar := range strings.Split(f.EnvVar, ",") {
|
||||
envVar = strings.TrimSpace(envVar)
|
||||
if envVal, ok := syscall.Getenv(envVar); ok {
|
||||
envValInt, err := strconv.ParseInt(envVal, 0, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("could not parse %s as int value for flag %s: %s", envVal, f.Name, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
f.Value = envValInt
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
eachName(f.Name, func(name string) {
|
||||
if f.Destination != nil {
|
||||
set.Int64Var(f.Destination, name, f.Value, f.Usage)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
set.Int64(name, f.Value, f.Usage)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
// Ignores errors
|
||||
func (f UintFlag) Apply(set *flag.FlagSet) {
|
||||
f.ApplyWithError(set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyWithError populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
func (f UintFlag) ApplyWithError(set *flag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
if f.EnvVar != "" {
|
||||
for _, envVar := range strings.Split(f.EnvVar, ",") {
|
||||
envVar = strings.TrimSpace(envVar)
|
||||
if envVal, ok := syscall.Getenv(envVar); ok {
|
||||
envValInt, err := strconv.ParseUint(envVal, 0, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("could not parse %s as uint value for flag %s: %s", envVal, f.Name, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
f.Value = uint(envValInt)
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
eachName(f.Name, func(name string) {
|
||||
if f.Destination != nil {
|
||||
set.UintVar(f.Destination, name, f.Value, f.Usage)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
set.Uint(name, f.Value, f.Usage)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
// Ignores errors
|
||||
func (f Uint64Flag) Apply(set *flag.FlagSet) {
|
||||
f.ApplyWithError(set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyWithError populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
func (f Uint64Flag) ApplyWithError(set *flag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
if f.EnvVar != "" {
|
||||
for _, envVar := range strings.Split(f.EnvVar, ",") {
|
||||
envVar = strings.TrimSpace(envVar)
|
||||
if envVal, ok := syscall.Getenv(envVar); ok {
|
||||
envValInt, err := strconv.ParseUint(envVal, 0, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("could not parse %s as uint64 value for flag %s: %s", envVal, f.Name, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
f.Value = uint64(envValInt)
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
eachName(f.Name, func(name string) {
|
||||
if f.Destination != nil {
|
||||
set.Uint64Var(f.Destination, name, f.Value, f.Usage)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
set.Uint64(name, f.Value, f.Usage)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
// Ignores errors
|
||||
func (f DurationFlag) Apply(set *flag.FlagSet) {
|
||||
f.ApplyWithError(set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyWithError populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
func (f DurationFlag) ApplyWithError(set *flag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
if f.EnvVar != "" {
|
||||
for _, envVar := range strings.Split(f.EnvVar, ",") {
|
||||
envVar = strings.TrimSpace(envVar)
|
||||
if envVal, ok := syscall.Getenv(envVar); ok {
|
||||
envValDuration, err := time.ParseDuration(envVal)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("could not parse %s as duration for flag %s: %s", envVal, f.Name, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
f.Value = envValDuration
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
eachName(f.Name, func(name string) {
|
||||
if f.Destination != nil {
|
||||
set.DurationVar(f.Destination, name, f.Value, f.Usage)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
set.Duration(name, f.Value, f.Usage)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
// Ignores errors
|
||||
func (f Float64Flag) Apply(set *flag.FlagSet) {
|
||||
f.ApplyWithError(set)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyWithError populates the flag given the flag set and environment
|
||||
func (f Float64Flag) ApplyWithError(set *flag.FlagSet) error {
|
||||
if f.EnvVar != "" {
|
||||
for _, envVar := range strings.Split(f.EnvVar, ",") {
|
||||
envVar = strings.TrimSpace(envVar)
|
||||
if envVal, ok := syscall.Getenv(envVar); ok {
|
||||
envValFloat, err := strconv.ParseFloat(envVal, 10)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("could not parse %s as float64 value for flag %s: %s", envVal, f.Name, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
f.Value = float64(envValFloat)
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
eachName(f.Name, func(name string) {
|
||||
if f.Destination != nil {
|
||||
set.Float64Var(f.Destination, name, f.Value, f.Usage)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
set.Float64(name, f.Value, f.Usage)
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func visibleFlags(fl []Flag) []Flag {
|
||||
visible := []Flag{}
|
||||
for _, flag := range fl {
|
||||
field := flagValue(flag).FieldByName("Hidden")
|
||||
if !field.IsValid() || !field.Bool() {
|
||||
visible = append(visible, flag)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return visible
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func prefixFor(name string) (prefix string) {
|
||||
if len(name) == 1 {
|
||||
prefix = "-"
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
prefix = "--"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns the placeholder, if any, and the unquoted usage string.
|
||||
func unquoteUsage(usage string) (string, string) {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(usage); i++ {
|
||||
if usage[i] == '`' {
|
||||
for j := i + 1; j < len(usage); j++ {
|
||||
if usage[j] == '`' {
|
||||
name := usage[i+1 : j]
|
||||
usage = usage[:i] + name + usage[j+1:]
|
||||
return name, usage
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "", usage
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func prefixedNames(fullName, placeholder string) string {
|
||||
var prefixed string
|
||||
parts := strings.Split(fullName, ",")
|
||||
for i, name := range parts {
|
||||
name = strings.Trim(name, " ")
|
||||
prefixed += prefixFor(name) + name
|
||||
if placeholder != "" {
|
||||
prefixed += " " + placeholder
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < len(parts)-1 {
|
||||
prefixed += ", "
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return prefixed
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func withEnvHint(envVar, str string) string {
|
||||
envText := ""
|
||||
if envVar != "" {
|
||||
prefix := "$"
|
||||
suffix := ""
|
||||
sep := ", $"
|
||||
if runtime.GOOS == "windows" {
|
||||
prefix = "%"
|
||||
suffix = "%"
|
||||
sep = "%, %"
|
||||
}
|
||||
envText = fmt.Sprintf(" [%s%s%s]", prefix, strings.Join(strings.Split(envVar, ","), sep), suffix)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return str + envText
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func flagValue(f Flag) reflect.Value {
|
||||
fv := reflect.ValueOf(f)
|
||||
for fv.Kind() == reflect.Ptr {
|
||||
fv = reflect.Indirect(fv)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fv
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func stringifyFlag(f Flag) string {
|
||||
fv := flagValue(f)
|
||||
|
||||
switch f.(type) {
|
||||
case IntSliceFlag:
|
||||
return withEnvHint(fv.FieldByName("EnvVar").String(),
|
||||
stringifyIntSliceFlag(f.(IntSliceFlag)))
|
||||
case Int64SliceFlag:
|
||||
return withEnvHint(fv.FieldByName("EnvVar").String(),
|
||||
stringifyInt64SliceFlag(f.(Int64SliceFlag)))
|
||||
case StringSliceFlag:
|
||||
return withEnvHint(fv.FieldByName("EnvVar").String(),
|
||||
stringifyStringSliceFlag(f.(StringSliceFlag)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
placeholder, usage := unquoteUsage(fv.FieldByName("Usage").String())
|
||||
|
||||
needsPlaceholder := false
|
||||
defaultValueString := ""
|
||||
|
||||
if val := fv.FieldByName("Value"); val.IsValid() {
|
||||
needsPlaceholder = true
|
||||
defaultValueString = fmt.Sprintf(" (default: %v)", val.Interface())
|
||||
|
||||
if val.Kind() == reflect.String && val.String() != "" {
|
||||
defaultValueString = fmt.Sprintf(" (default: %q)", val.String())
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if defaultValueString == " (default: )" {
|
||||
defaultValueString = ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if needsPlaceholder && placeholder == "" {
|
||||
placeholder = defaultPlaceholder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
usageWithDefault := strings.TrimSpace(fmt.Sprintf("%s%s", usage, defaultValueString))
|
||||
|
||||
return withEnvHint(fv.FieldByName("EnvVar").String(),
|
||||
fmt.Sprintf("%s\t%s", prefixedNames(fv.FieldByName("Name").String(), placeholder), usageWithDefault))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func stringifyIntSliceFlag(f IntSliceFlag) string {
|
||||
defaultVals := []string{}
|
||||
if f.Value != nil && len(f.Value.Value()) > 0 {
|
||||
for _, i := range f.Value.Value() {
|
||||
defaultVals = append(defaultVals, fmt.Sprintf("%d", i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return stringifySliceFlag(f.Usage, f.Name, defaultVals)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func stringifyInt64SliceFlag(f Int64SliceFlag) string {
|
||||
defaultVals := []string{}
|
||||
if f.Value != nil && len(f.Value.Value()) > 0 {
|
||||
for _, i := range f.Value.Value() {
|
||||
defaultVals = append(defaultVals, fmt.Sprintf("%d", i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return stringifySliceFlag(f.Usage, f.Name, defaultVals)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func stringifyStringSliceFlag(f StringSliceFlag) string {
|
||||
defaultVals := []string{}
|
||||
if f.Value != nil && len(f.Value.Value()) > 0 {
|
||||
for _, s := range f.Value.Value() {
|
||||
if len(s) > 0 {
|
||||
defaultVals = append(defaultVals, fmt.Sprintf("%q", s))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return stringifySliceFlag(f.Usage, f.Name, defaultVals)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func stringifySliceFlag(usage, name string, defaultVals []string) string {
|
||||
placeholder, usage := unquoteUsage(usage)
|
||||
if placeholder == "" {
|
||||
placeholder = defaultPlaceholder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
defaultVal := ""
|
||||
if len(defaultVals) > 0 {
|
||||
defaultVal = fmt.Sprintf(" (default: %s)", strings.Join(defaultVals, ", "))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
usageWithDefault := strings.TrimSpace(fmt.Sprintf("%s%s", usage, defaultVal))
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%s\t%s", prefixedNames(name, placeholder), usageWithDefault)
|
||||
}
|
||||
627
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/flag_generated.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
627
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/flag_generated.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,627 @@
|
||||
package cli
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"flag"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// WARNING: This file is generated!
|
||||
|
||||
// BoolFlag is a flag with type bool
|
||||
type BoolFlag struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
EnvVar string
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
Destination *bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value
|
||||
// (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f BoolFlag) String() string {
|
||||
return FlagStringer(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetName returns the name of the flag
|
||||
func (f BoolFlag) GetName() string {
|
||||
return f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bool looks up the value of a local BoolFlag, returns
|
||||
// false if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) Bool(name string) bool {
|
||||
return lookupBool(name, c.flagSet)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalBool looks up the value of a global BoolFlag, returns
|
||||
// false if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalBool(name string) bool {
|
||||
if fs := lookupGlobalFlagSet(name, c); fs != nil {
|
||||
return lookupBool(name, fs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookupBool(name string, set *flag.FlagSet) bool {
|
||||
f := set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
parsed, err := strconv.ParseBool(f.Value.String())
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parsed
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BoolTFlag is a flag with type bool that is true by default
|
||||
type BoolTFlag struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
EnvVar string
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
Destination *bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value
|
||||
// (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f BoolTFlag) String() string {
|
||||
return FlagStringer(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetName returns the name of the flag
|
||||
func (f BoolTFlag) GetName() string {
|
||||
return f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BoolT looks up the value of a local BoolTFlag, returns
|
||||
// false if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) BoolT(name string) bool {
|
||||
return lookupBoolT(name, c.flagSet)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalBoolT looks up the value of a global BoolTFlag, returns
|
||||
// false if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalBoolT(name string) bool {
|
||||
if fs := lookupGlobalFlagSet(name, c); fs != nil {
|
||||
return lookupBoolT(name, fs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookupBoolT(name string, set *flag.FlagSet) bool {
|
||||
f := set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
parsed, err := strconv.ParseBool(f.Value.String())
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parsed
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DurationFlag is a flag with type time.Duration (see https://golang.org/pkg/time/#ParseDuration)
|
||||
type DurationFlag struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
EnvVar string
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
Value time.Duration
|
||||
Destination *time.Duration
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value
|
||||
// (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f DurationFlag) String() string {
|
||||
return FlagStringer(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetName returns the name of the flag
|
||||
func (f DurationFlag) GetName() string {
|
||||
return f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Duration looks up the value of a local DurationFlag, returns
|
||||
// 0 if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) Duration(name string) time.Duration {
|
||||
return lookupDuration(name, c.flagSet)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalDuration looks up the value of a global DurationFlag, returns
|
||||
// 0 if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalDuration(name string) time.Duration {
|
||||
if fs := lookupGlobalFlagSet(name, c); fs != nil {
|
||||
return lookupDuration(name, fs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookupDuration(name string, set *flag.FlagSet) time.Duration {
|
||||
f := set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
parsed, err := time.ParseDuration(f.Value.String())
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parsed
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Float64Flag is a flag with type float64
|
||||
type Float64Flag struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
EnvVar string
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
Value float64
|
||||
Destination *float64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value
|
||||
// (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f Float64Flag) String() string {
|
||||
return FlagStringer(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetName returns the name of the flag
|
||||
func (f Float64Flag) GetName() string {
|
||||
return f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Float64 looks up the value of a local Float64Flag, returns
|
||||
// 0 if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) Float64(name string) float64 {
|
||||
return lookupFloat64(name, c.flagSet)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalFloat64 looks up the value of a global Float64Flag, returns
|
||||
// 0 if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalFloat64(name string) float64 {
|
||||
if fs := lookupGlobalFlagSet(name, c); fs != nil {
|
||||
return lookupFloat64(name, fs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookupFloat64(name string, set *flag.FlagSet) float64 {
|
||||
f := set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
parsed, err := strconv.ParseFloat(f.Value.String(), 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parsed
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GenericFlag is a flag with type Generic
|
||||
type GenericFlag struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
EnvVar string
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
Value Generic
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value
|
||||
// (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f GenericFlag) String() string {
|
||||
return FlagStringer(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetName returns the name of the flag
|
||||
func (f GenericFlag) GetName() string {
|
||||
return f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Generic looks up the value of a local GenericFlag, returns
|
||||
// nil if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) Generic(name string) interface{} {
|
||||
return lookupGeneric(name, c.flagSet)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalGeneric looks up the value of a global GenericFlag, returns
|
||||
// nil if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalGeneric(name string) interface{} {
|
||||
if fs := lookupGlobalFlagSet(name, c); fs != nil {
|
||||
return lookupGeneric(name, fs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookupGeneric(name string, set *flag.FlagSet) interface{} {
|
||||
f := set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
parsed, err := f.Value, error(nil)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parsed
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Int64Flag is a flag with type int64
|
||||
type Int64Flag struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
EnvVar string
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
Value int64
|
||||
Destination *int64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value
|
||||
// (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f Int64Flag) String() string {
|
||||
return FlagStringer(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetName returns the name of the flag
|
||||
func (f Int64Flag) GetName() string {
|
||||
return f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Int64 looks up the value of a local Int64Flag, returns
|
||||
// 0 if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) Int64(name string) int64 {
|
||||
return lookupInt64(name, c.flagSet)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalInt64 looks up the value of a global Int64Flag, returns
|
||||
// 0 if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalInt64(name string) int64 {
|
||||
if fs := lookupGlobalFlagSet(name, c); fs != nil {
|
||||
return lookupInt64(name, fs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookupInt64(name string, set *flag.FlagSet) int64 {
|
||||
f := set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
parsed, err := strconv.ParseInt(f.Value.String(), 0, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parsed
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IntFlag is a flag with type int
|
||||
type IntFlag struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
EnvVar string
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
Value int
|
||||
Destination *int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value
|
||||
// (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f IntFlag) String() string {
|
||||
return FlagStringer(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetName returns the name of the flag
|
||||
func (f IntFlag) GetName() string {
|
||||
return f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Int looks up the value of a local IntFlag, returns
|
||||
// 0 if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) Int(name string) int {
|
||||
return lookupInt(name, c.flagSet)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalInt looks up the value of a global IntFlag, returns
|
||||
// 0 if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalInt(name string) int {
|
||||
if fs := lookupGlobalFlagSet(name, c); fs != nil {
|
||||
return lookupInt(name, fs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookupInt(name string, set *flag.FlagSet) int {
|
||||
f := set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
parsed, err := strconv.ParseInt(f.Value.String(), 0, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return int(parsed)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IntSliceFlag is a flag with type *IntSlice
|
||||
type IntSliceFlag struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
EnvVar string
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
Value *IntSlice
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value
|
||||
// (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f IntSliceFlag) String() string {
|
||||
return FlagStringer(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetName returns the name of the flag
|
||||
func (f IntSliceFlag) GetName() string {
|
||||
return f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IntSlice looks up the value of a local IntSliceFlag, returns
|
||||
// nil if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) IntSlice(name string) []int {
|
||||
return lookupIntSlice(name, c.flagSet)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalIntSlice looks up the value of a global IntSliceFlag, returns
|
||||
// nil if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalIntSlice(name string) []int {
|
||||
if fs := lookupGlobalFlagSet(name, c); fs != nil {
|
||||
return lookupIntSlice(name, fs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookupIntSlice(name string, set *flag.FlagSet) []int {
|
||||
f := set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
parsed, err := (f.Value.(*IntSlice)).Value(), error(nil)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parsed
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Int64SliceFlag is a flag with type *Int64Slice
|
||||
type Int64SliceFlag struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
EnvVar string
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
Value *Int64Slice
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value
|
||||
// (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f Int64SliceFlag) String() string {
|
||||
return FlagStringer(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetName returns the name of the flag
|
||||
func (f Int64SliceFlag) GetName() string {
|
||||
return f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Int64Slice looks up the value of a local Int64SliceFlag, returns
|
||||
// nil if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) Int64Slice(name string) []int64 {
|
||||
return lookupInt64Slice(name, c.flagSet)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalInt64Slice looks up the value of a global Int64SliceFlag, returns
|
||||
// nil if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalInt64Slice(name string) []int64 {
|
||||
if fs := lookupGlobalFlagSet(name, c); fs != nil {
|
||||
return lookupInt64Slice(name, fs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookupInt64Slice(name string, set *flag.FlagSet) []int64 {
|
||||
f := set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
parsed, err := (f.Value.(*Int64Slice)).Value(), error(nil)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parsed
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StringFlag is a flag with type string
|
||||
type StringFlag struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
EnvVar string
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
Value string
|
||||
Destination *string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value
|
||||
// (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f StringFlag) String() string {
|
||||
return FlagStringer(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetName returns the name of the flag
|
||||
func (f StringFlag) GetName() string {
|
||||
return f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String looks up the value of a local StringFlag, returns
|
||||
// "" if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) String(name string) string {
|
||||
return lookupString(name, c.flagSet)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalString looks up the value of a global StringFlag, returns
|
||||
// "" if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalString(name string) string {
|
||||
if fs := lookupGlobalFlagSet(name, c); fs != nil {
|
||||
return lookupString(name, fs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookupString(name string, set *flag.FlagSet) string {
|
||||
f := set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
parsed, err := f.Value.String(), error(nil)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parsed
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StringSliceFlag is a flag with type *StringSlice
|
||||
type StringSliceFlag struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
EnvVar string
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
Value *StringSlice
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value
|
||||
// (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f StringSliceFlag) String() string {
|
||||
return FlagStringer(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetName returns the name of the flag
|
||||
func (f StringSliceFlag) GetName() string {
|
||||
return f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StringSlice looks up the value of a local StringSliceFlag, returns
|
||||
// nil if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) StringSlice(name string) []string {
|
||||
return lookupStringSlice(name, c.flagSet)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalStringSlice looks up the value of a global StringSliceFlag, returns
|
||||
// nil if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalStringSlice(name string) []string {
|
||||
if fs := lookupGlobalFlagSet(name, c); fs != nil {
|
||||
return lookupStringSlice(name, fs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookupStringSlice(name string, set *flag.FlagSet) []string {
|
||||
f := set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
parsed, err := (f.Value.(*StringSlice)).Value(), error(nil)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parsed
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Uint64Flag is a flag with type uint64
|
||||
type Uint64Flag struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
EnvVar string
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
Value uint64
|
||||
Destination *uint64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value
|
||||
// (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f Uint64Flag) String() string {
|
||||
return FlagStringer(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetName returns the name of the flag
|
||||
func (f Uint64Flag) GetName() string {
|
||||
return f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Uint64 looks up the value of a local Uint64Flag, returns
|
||||
// 0 if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) Uint64(name string) uint64 {
|
||||
return lookupUint64(name, c.flagSet)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalUint64 looks up the value of a global Uint64Flag, returns
|
||||
// 0 if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalUint64(name string) uint64 {
|
||||
if fs := lookupGlobalFlagSet(name, c); fs != nil {
|
||||
return lookupUint64(name, fs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookupUint64(name string, set *flag.FlagSet) uint64 {
|
||||
f := set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
parsed, err := strconv.ParseUint(f.Value.String(), 0, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return parsed
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UintFlag is a flag with type uint
|
||||
type UintFlag struct {
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
EnvVar string
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
Value uint
|
||||
Destination *uint
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value
|
||||
// (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f UintFlag) String() string {
|
||||
return FlagStringer(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetName returns the name of the flag
|
||||
func (f UintFlag) GetName() string {
|
||||
return f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Uint looks up the value of a local UintFlag, returns
|
||||
// 0 if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) Uint(name string) uint {
|
||||
return lookupUint(name, c.flagSet)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GlobalUint looks up the value of a global UintFlag, returns
|
||||
// 0 if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) GlobalUint(name string) uint {
|
||||
if fs := lookupGlobalFlagSet(name, c); fs != nil {
|
||||
return lookupUint(name, fs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookupUint(name string, set *flag.FlagSet) uint {
|
||||
f := set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
if f != nil {
|
||||
parsed, err := strconv.ParseUint(f.Value.String(), 0, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return uint(parsed)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
28
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/funcs.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
28
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/funcs.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
package cli
|
||||
|
||||
// BashCompleteFunc is an action to execute when the bash-completion flag is set
|
||||
type BashCompleteFunc func(*Context)
|
||||
|
||||
// BeforeFunc is an action to execute before any subcommands are run, but after
|
||||
// the context is ready if a non-nil error is returned, no subcommands are run
|
||||
type BeforeFunc func(*Context) error
|
||||
|
||||
// AfterFunc is an action to execute after any subcommands are run, but after the
|
||||
// subcommand has finished it is run even if Action() panics
|
||||
type AfterFunc func(*Context) error
|
||||
|
||||
// ActionFunc is the action to execute when no subcommands are specified
|
||||
type ActionFunc func(*Context) error
|
||||
|
||||
// CommandNotFoundFunc is executed if the proper command cannot be found
|
||||
type CommandNotFoundFunc func(*Context, string)
|
||||
|
||||
// OnUsageErrorFunc is executed if an usage error occurs. This is useful for displaying
|
||||
// customized usage error messages. This function is able to replace the
|
||||
// original error messages. If this function is not set, the "Incorrect usage"
|
||||
// is displayed and the execution is interrupted.
|
||||
type OnUsageErrorFunc func(context *Context, err error, isSubcommand bool) error
|
||||
|
||||
// FlagStringFunc is used by the help generation to display a flag, which is
|
||||
// expected to be a single line.
|
||||
type FlagStringFunc func(Flag) string
|
||||
255
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/generate-flag-types
generated
vendored
Normal file
255
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/generate-flag-types
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,255 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
"""
|
||||
The flag types that ship with the cli library have many things in common, and
|
||||
so we can take advantage of the `go generate` command to create much of the
|
||||
source code from a list of definitions. These definitions attempt to cover
|
||||
the parts that vary between flag types, and should evolve as needed.
|
||||
|
||||
An example of the minimum definition needed is:
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "SomeType",
|
||||
"type": "sometype",
|
||||
"context_default": "nil"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, the code generated for the `cli` package will include a type
|
||||
named `SomeTypeFlag` that is expected to wrap a value of type `sometype`.
|
||||
Fetching values by name via `*cli.Context` will default to a value of `nil`.
|
||||
|
||||
A more complete, albeit somewhat redundant, example showing all available
|
||||
definition keys is:
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "VeryMuchType",
|
||||
"type": "*VeryMuchType",
|
||||
"value": true,
|
||||
"dest": false,
|
||||
"doctail": " which really only wraps a []float64, oh well!",
|
||||
"context_type": "[]float64",
|
||||
"context_default": "nil",
|
||||
"parser": "parseVeryMuchType(f.Value.String())",
|
||||
"parser_cast": "[]float64(parsed)"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
The meaning of each field is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
name (string) - The type "name", which will be suffixed with
|
||||
`Flag` when generating the type definition
|
||||
for `cli` and the wrapper type for `altsrc`
|
||||
type (string) - The type that the generated `Flag` type for `cli`
|
||||
is expected to "contain" as its `.Value` member
|
||||
value (bool) - Should the generated `cli` type have a `Value`
|
||||
member?
|
||||
dest (bool) - Should the generated `cli` type support a
|
||||
destination pointer?
|
||||
doctail (string) - Additional docs for the `cli` flag type comment
|
||||
context_type (string) - The literal type used in the `*cli.Context`
|
||||
reader func signature
|
||||
context_default (string) - The literal value used as the default by the
|
||||
`*cli.Context` reader funcs when no value is
|
||||
present
|
||||
parser (string) - Literal code used to parse the flag `f`,
|
||||
expected to have a return signature of
|
||||
(value, error)
|
||||
parser_cast (string) - Literal code used to cast the `parsed` value
|
||||
returned from the `parser` code
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function, unicode_literals
|
||||
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import tempfile
|
||||
import textwrap
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class _FancyFormatter(argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter,
|
||||
argparse.RawDescriptionHelpFormatter):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main(sysargs=sys.argv[:]):
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
|
||||
description='Generate flag type code!',
|
||||
formatter_class=_FancyFormatter)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
'package',
|
||||
type=str, default='cli', choices=_WRITEFUNCS.keys(),
|
||||
help='Package for which flag types will be generated'
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
'-i', '--in-json',
|
||||
type=argparse.FileType('r'),
|
||||
default=sys.stdin,
|
||||
help='Input JSON file which defines each type to be generated'
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
'-o', '--out-go',
|
||||
type=argparse.FileType('w'),
|
||||
default=sys.stdout,
|
||||
help='Output file/stream to which generated source will be written'
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.epilog = __doc__
|
||||
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args(sysargs[1:])
|
||||
_generate_flag_types(_WRITEFUNCS[args.package], args.out_go, args.in_json)
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _generate_flag_types(writefunc, output_go, input_json):
|
||||
types = json.load(input_json)
|
||||
|
||||
tmp = tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(suffix='.go', delete=False)
|
||||
writefunc(tmp, types)
|
||||
tmp.close()
|
||||
|
||||
new_content = subprocess.check_output(
|
||||
['goimports', tmp.name]
|
||||
).decode('utf-8')
|
||||
|
||||
print(new_content, file=output_go, end='')
|
||||
output_go.flush()
|
||||
os.remove(tmp.name)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _set_typedef_defaults(typedef):
|
||||
typedef.setdefault('doctail', '')
|
||||
typedef.setdefault('context_type', typedef['type'])
|
||||
typedef.setdefault('dest', True)
|
||||
typedef.setdefault('value', True)
|
||||
typedef.setdefault('parser', 'f.Value, error(nil)')
|
||||
typedef.setdefault('parser_cast', 'parsed')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _write_cli_flag_types(outfile, types):
|
||||
_fwrite(outfile, """\
|
||||
package cli
|
||||
|
||||
// WARNING: This file is generated!
|
||||
|
||||
""")
|
||||
|
||||
for typedef in types:
|
||||
_set_typedef_defaults(typedef)
|
||||
|
||||
_fwrite(outfile, """\
|
||||
// {name}Flag is a flag with type {type}{doctail}
|
||||
type {name}Flag struct {{
|
||||
Name string
|
||||
Usage string
|
||||
EnvVar string
|
||||
Hidden bool
|
||||
""".format(**typedef))
|
||||
|
||||
if typedef['value']:
|
||||
_fwrite(outfile, """\
|
||||
Value {type}
|
||||
""".format(**typedef))
|
||||
|
||||
if typedef['dest']:
|
||||
_fwrite(outfile, """\
|
||||
Destination *{type}
|
||||
""".format(**typedef))
|
||||
|
||||
_fwrite(outfile, "\n}\n\n")
|
||||
|
||||
_fwrite(outfile, """\
|
||||
// String returns a readable representation of this value
|
||||
// (for usage defaults)
|
||||
func (f {name}Flag) String() string {{
|
||||
return FlagStringer(f)
|
||||
}}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetName returns the name of the flag
|
||||
func (f {name}Flag) GetName() string {{
|
||||
return f.Name
|
||||
}}
|
||||
|
||||
// {name} looks up the value of a local {name}Flag, returns
|
||||
// {context_default} if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) {name}(name string) {context_type} {{
|
||||
return lookup{name}(name, c.flagSet)
|
||||
}}
|
||||
|
||||
// Global{name} looks up the value of a global {name}Flag, returns
|
||||
// {context_default} if not found
|
||||
func (c *Context) Global{name}(name string) {context_type} {{
|
||||
if fs := lookupGlobalFlagSet(name, c); fs != nil {{
|
||||
return lookup{name}(name, fs)
|
||||
}}
|
||||
return {context_default}
|
||||
}}
|
||||
|
||||
func lookup{name}(name string, set *flag.FlagSet) {context_type} {{
|
||||
f := set.Lookup(name)
|
||||
if f != nil {{
|
||||
parsed, err := {parser}
|
||||
if err != nil {{
|
||||
return {context_default}
|
||||
}}
|
||||
return {parser_cast}
|
||||
}}
|
||||
return {context_default}
|
||||
}}
|
||||
""".format(**typedef))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _write_altsrc_flag_types(outfile, types):
|
||||
_fwrite(outfile, """\
|
||||
package altsrc
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"gopkg.in/urfave/cli.v1"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// WARNING: This file is generated!
|
||||
|
||||
""")
|
||||
|
||||
for typedef in types:
|
||||
_set_typedef_defaults(typedef)
|
||||
|
||||
_fwrite(outfile, """\
|
||||
// {name}Flag is the flag type that wraps cli.{name}Flag to allow
|
||||
// for other values to be specified
|
||||
type {name}Flag struct {{
|
||||
cli.{name}Flag
|
||||
set *flag.FlagSet
|
||||
}}
|
||||
|
||||
// New{name}Flag creates a new {name}Flag
|
||||
func New{name}Flag(fl cli.{name}Flag) *{name}Flag {{
|
||||
return &{name}Flag{{{name}Flag: fl, set: nil}}
|
||||
}}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply saves the flagSet for later usage calls, then calls the
|
||||
// wrapped {name}Flag.Apply
|
||||
func (f *{name}Flag) Apply(set *flag.FlagSet) {{
|
||||
f.set = set
|
||||
f.{name}Flag.Apply(set)
|
||||
}}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyWithError saves the flagSet for later usage calls, then calls the
|
||||
// wrapped {name}Flag.ApplyWithError
|
||||
func (f *{name}Flag) ApplyWithError(set *flag.FlagSet) error {{
|
||||
f.set = set
|
||||
return f.{name}Flag.ApplyWithError(set)
|
||||
}}
|
||||
""".format(**typedef))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _fwrite(outfile, text):
|
||||
print(textwrap.dedent(text), end='', file=outfile)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
_WRITEFUNCS = {
|
||||
'cli': _write_cli_flag_types,
|
||||
'altsrc': _write_altsrc_flag_types
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
sys.exit(main())
|
||||
338
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/help.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
338
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/help.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,338 @@
|
||||
package cli
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"text/tabwriter"
|
||||
"text/template"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// AppHelpTemplate is the text template for the Default help topic.
|
||||
// cli.go uses text/template to render templates. You can
|
||||
// render custom help text by setting this variable.
|
||||
var AppHelpTemplate = `NAME:
|
||||
{{.Name}}{{if .Usage}} - {{.Usage}}{{end}}
|
||||
|
||||
USAGE:
|
||||
{{if .UsageText}}{{.UsageText}}{{else}}{{.HelpName}} {{if .VisibleFlags}}[global options]{{end}}{{if .Commands}} command [command options]{{end}} {{if .ArgsUsage}}{{.ArgsUsage}}{{else}}[arguments...]{{end}}{{end}}{{if .Version}}{{if not .HideVersion}}
|
||||
|
||||
VERSION:
|
||||
{{.Version}}{{end}}{{end}}{{if .Description}}
|
||||
|
||||
DESCRIPTION:
|
||||
{{.Description}}{{end}}{{if len .Authors}}
|
||||
|
||||
AUTHOR{{with $length := len .Authors}}{{if ne 1 $length}}S{{end}}{{end}}:
|
||||
{{range $index, $author := .Authors}}{{if $index}}
|
||||
{{end}}{{$author}}{{end}}{{end}}{{if .VisibleCommands}}
|
||||
|
||||
COMMANDS:{{range .VisibleCategories}}{{if .Name}}
|
||||
{{.Name}}:{{end}}{{range .VisibleCommands}}
|
||||
{{join .Names ", "}}{{"\t"}}{{.Usage}}{{end}}{{end}}{{end}}{{if .VisibleFlags}}
|
||||
|
||||
GLOBAL OPTIONS:
|
||||
{{range $index, $option := .VisibleFlags}}{{if $index}}
|
||||
{{end}}{{$option}}{{end}}{{end}}{{if .Copyright}}
|
||||
|
||||
COPYRIGHT:
|
||||
{{.Copyright}}{{end}}
|
||||
`
|
||||
|
||||
// CommandHelpTemplate is the text template for the command help topic.
|
||||
// cli.go uses text/template to render templates. You can
|
||||
// render custom help text by setting this variable.
|
||||
var CommandHelpTemplate = `NAME:
|
||||
{{.HelpName}} - {{.Usage}}
|
||||
|
||||
USAGE:
|
||||
{{if .UsageText}}{{.UsageText}}{{else}}{{.HelpName}}{{if .VisibleFlags}} [command options]{{end}} {{if .ArgsUsage}}{{.ArgsUsage}}{{else}}[arguments...]{{end}}{{end}}{{if .Category}}
|
||||
|
||||
CATEGORY:
|
||||
{{.Category}}{{end}}{{if .Description}}
|
||||
|
||||
DESCRIPTION:
|
||||
{{.Description}}{{end}}{{if .VisibleFlags}}
|
||||
|
||||
OPTIONS:
|
||||
{{range .VisibleFlags}}{{.}}
|
||||
{{end}}{{end}}
|
||||
`
|
||||
|
||||
// SubcommandHelpTemplate is the text template for the subcommand help topic.
|
||||
// cli.go uses text/template to render templates. You can
|
||||
// render custom help text by setting this variable.
|
||||
var SubcommandHelpTemplate = `NAME:
|
||||
{{.HelpName}} - {{if .Description}}{{.Description}}{{else}}{{.Usage}}{{end}}
|
||||
|
||||
USAGE:
|
||||
{{if .UsageText}}{{.UsageText}}{{else}}{{.HelpName}} command{{if .VisibleFlags}} [command options]{{end}} {{if .ArgsUsage}}{{.ArgsUsage}}{{else}}[arguments...]{{end}}{{end}}
|
||||
|
||||
COMMANDS:{{range .VisibleCategories}}{{if .Name}}
|
||||
{{.Name}}:{{end}}{{range .VisibleCommands}}
|
||||
{{join .Names ", "}}{{"\t"}}{{.Usage}}{{end}}
|
||||
{{end}}{{if .VisibleFlags}}
|
||||
OPTIONS:
|
||||
{{range .VisibleFlags}}{{.}}
|
||||
{{end}}{{end}}
|
||||
`
|
||||
|
||||
var helpCommand = Command{
|
||||
Name: "help",
|
||||
Aliases: []string{"h"},
|
||||
Usage: "Shows a list of commands or help for one command",
|
||||
ArgsUsage: "[command]",
|
||||
Action: func(c *Context) error {
|
||||
args := c.Args()
|
||||
if args.Present() {
|
||||
return ShowCommandHelp(c, args.First())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ShowAppHelp(c)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var helpSubcommand = Command{
|
||||
Name: "help",
|
||||
Aliases: []string{"h"},
|
||||
Usage: "Shows a list of commands or help for one command",
|
||||
ArgsUsage: "[command]",
|
||||
Action: func(c *Context) error {
|
||||
args := c.Args()
|
||||
if args.Present() {
|
||||
return ShowCommandHelp(c, args.First())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return ShowSubcommandHelp(c)
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Prints help for the App or Command
|
||||
type helpPrinter func(w io.Writer, templ string, data interface{})
|
||||
|
||||
// Prints help for the App or Command with custom template function.
|
||||
type helpPrinterCustom func(w io.Writer, templ string, data interface{}, customFunc map[string]interface{})
|
||||
|
||||
// HelpPrinter is a function that writes the help output. If not set a default
|
||||
// is used. The function signature is:
|
||||
// func(w io.Writer, templ string, data interface{})
|
||||
var HelpPrinter helpPrinter = printHelp
|
||||
|
||||
// HelpPrinterCustom is same as HelpPrinter but
|
||||
// takes a custom function for template function map.
|
||||
var HelpPrinterCustom helpPrinterCustom = printHelpCustom
|
||||
|
||||
// VersionPrinter prints the version for the App
|
||||
var VersionPrinter = printVersion
|
||||
|
||||
// ShowAppHelpAndExit - Prints the list of subcommands for the app and exits with exit code.
|
||||
func ShowAppHelpAndExit(c *Context, exitCode int) {
|
||||
ShowAppHelp(c)
|
||||
os.Exit(exitCode)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ShowAppHelp is an action that displays the help.
|
||||
func ShowAppHelp(c *Context) (err error) {
|
||||
if c.App.CustomAppHelpTemplate == "" {
|
||||
HelpPrinter(c.App.Writer, AppHelpTemplate, c.App)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
customAppData := func() map[string]interface{} {
|
||||
if c.App.ExtraInfo == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return map[string]interface{}{
|
||||
"ExtraInfo": c.App.ExtraInfo,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
HelpPrinterCustom(c.App.Writer, c.App.CustomAppHelpTemplate, c.App, customAppData())
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultAppComplete prints the list of subcommands as the default app completion method
|
||||
func DefaultAppComplete(c *Context) {
|
||||
for _, command := range c.App.Commands {
|
||||
if command.Hidden {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, name := range command.Names() {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintln(c.App.Writer, name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ShowCommandHelpAndExit - exits with code after showing help
|
||||
func ShowCommandHelpAndExit(c *Context, command string, code int) {
|
||||
ShowCommandHelp(c, command)
|
||||
os.Exit(code)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ShowCommandHelp prints help for the given command
|
||||
func ShowCommandHelp(ctx *Context, command string) error {
|
||||
// show the subcommand help for a command with subcommands
|
||||
if command == "" {
|
||||
HelpPrinter(ctx.App.Writer, SubcommandHelpTemplate, ctx.App)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, c := range ctx.App.Commands {
|
||||
if c.HasName(command) {
|
||||
if c.CustomHelpTemplate != "" {
|
||||
HelpPrinterCustom(ctx.App.Writer, c.CustomHelpTemplate, c, nil)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
HelpPrinter(ctx.App.Writer, CommandHelpTemplate, c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if ctx.App.CommandNotFound == nil {
|
||||
return NewExitError(fmt.Sprintf("No help topic for '%v'", command), 3)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ctx.App.CommandNotFound(ctx, command)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ShowSubcommandHelp prints help for the given subcommand
|
||||
func ShowSubcommandHelp(c *Context) error {
|
||||
return ShowCommandHelp(c, c.Command.Name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ShowVersion prints the version number of the App
|
||||
func ShowVersion(c *Context) {
|
||||
VersionPrinter(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func printVersion(c *Context) {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(c.App.Writer, "%v version %v\n", c.App.Name, c.App.Version)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ShowCompletions prints the lists of commands within a given context
|
||||
func ShowCompletions(c *Context) {
|
||||
a := c.App
|
||||
if a != nil && a.BashComplete != nil {
|
||||
a.BashComplete(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ShowCommandCompletions prints the custom completions for a given command
|
||||
func ShowCommandCompletions(ctx *Context, command string) {
|
||||
c := ctx.App.Command(command)
|
||||
if c != nil && c.BashComplete != nil {
|
||||
c.BashComplete(ctx)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func printHelpCustom(out io.Writer, templ string, data interface{}, customFunc map[string]interface{}) {
|
||||
funcMap := template.FuncMap{
|
||||
"join": strings.Join,
|
||||
}
|
||||
if customFunc != nil {
|
||||
for key, value := range customFunc {
|
||||
funcMap[key] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
w := tabwriter.NewWriter(out, 1, 8, 2, ' ', 0)
|
||||
t := template.Must(template.New("help").Funcs(funcMap).Parse(templ))
|
||||
err := t.Execute(w, data)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
// If the writer is closed, t.Execute will fail, and there's nothing
|
||||
// we can do to recover.
|
||||
if os.Getenv("CLI_TEMPLATE_ERROR_DEBUG") != "" {
|
||||
fmt.Fprintf(ErrWriter, "CLI TEMPLATE ERROR: %#v\n", err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.Flush()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func printHelp(out io.Writer, templ string, data interface{}) {
|
||||
printHelpCustom(out, templ, data, nil)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func checkVersion(c *Context) bool {
|
||||
found := false
|
||||
if VersionFlag.GetName() != "" {
|
||||
eachName(VersionFlag.GetName(), func(name string) {
|
||||
if c.GlobalBool(name) || c.Bool(name) {
|
||||
found = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
return found
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func checkHelp(c *Context) bool {
|
||||
found := false
|
||||
if HelpFlag.GetName() != "" {
|
||||
eachName(HelpFlag.GetName(), func(name string) {
|
||||
if c.GlobalBool(name) || c.Bool(name) {
|
||||
found = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
return found
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func checkCommandHelp(c *Context, name string) bool {
|
||||
if c.Bool("h") || c.Bool("help") {
|
||||
ShowCommandHelp(c, name)
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func checkSubcommandHelp(c *Context) bool {
|
||||
if c.Bool("h") || c.Bool("help") {
|
||||
ShowSubcommandHelp(c)
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func checkShellCompleteFlag(a *App, arguments []string) (bool, []string) {
|
||||
if !a.EnableBashCompletion {
|
||||
return false, arguments
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pos := len(arguments) - 1
|
||||
lastArg := arguments[pos]
|
||||
|
||||
if lastArg != "--"+BashCompletionFlag.GetName() {
|
||||
return false, arguments
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return true, arguments[:pos]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func checkCompletions(c *Context) bool {
|
||||
if !c.shellComplete {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if args := c.Args(); args.Present() {
|
||||
name := args.First()
|
||||
if cmd := c.App.Command(name); cmd != nil {
|
||||
// let the command handle the completion
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ShowCompletions(c)
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func checkCommandCompletions(c *Context, name string) bool {
|
||||
if !c.shellComplete {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ShowCommandCompletions(c, name)
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
122
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/runtests
generated
vendored
Normal file
122
vendor/github.com/urfave/cli/runtests
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import tempfile
|
||||
|
||||
from subprocess import check_call, check_output
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PACKAGE_NAME = os.environ.get(
|
||||
'CLI_PACKAGE_NAME', 'github.com/urfave/cli'
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main(sysargs=sys.argv[:]):
|
||||
targets = {
|
||||
'vet': _vet,
|
||||
'test': _test,
|
||||
'gfmrun': _gfmrun,
|
||||
'toc': _toc,
|
||||
'gen': _gen,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
'target', nargs='?', choices=tuple(targets.keys()), default='test'
|
||||
)
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args(sysargs[1:])
|
||||
|
||||
targets[args.target]()
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _test():
|
||||
if check_output('go version'.split()).split()[2] < 'go1.2':
|
||||
_run('go test -v .')
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
coverprofiles = []
|
||||
for subpackage in ['', 'altsrc']:
|
||||
coverprofile = 'cli.coverprofile'
|
||||
if subpackage != '':
|
||||
coverprofile = '{}.coverprofile'.format(subpackage)
|
||||
|
||||
coverprofiles.append(coverprofile)
|
||||
|
||||
_run('go test -v'.split() + [
|
||||
'-coverprofile={}'.format(coverprofile),
|
||||
('{}/{}'.format(PACKAGE_NAME, subpackage)).rstrip('/')
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
combined_name = _combine_coverprofiles(coverprofiles)
|
||||
_run('go tool cover -func={}'.format(combined_name))
|
||||
os.remove(combined_name)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _gfmrun():
|
||||
go_version = check_output('go version'.split()).split()[2]
|
||||
if go_version < 'go1.3':
|
||||
print('runtests: skip on {}'.format(go_version), file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
return
|
||||
_run(['gfmrun', '-c', str(_gfmrun_count()), '-s', 'README.md'])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _vet():
|
||||
_run('go vet ./...')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _toc():
|
||||
_run('node_modules/.bin/markdown-toc -i README.md')
|
||||
_run('git diff --exit-code')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _gen():
|
||||
go_version = check_output('go version'.split()).split()[2]
|
||||
if go_version < 'go1.5':
|
||||
print('runtests: skip on {}'.format(go_version), file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
_run('go generate ./...')
|
||||
_run('git diff --exit-code')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _run(command):
|
||||
if hasattr(command, 'split'):
|
||||
command = command.split()
|
||||
print('runtests: {}'.format(' '.join(command)), file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
check_call(command)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _gfmrun_count():
|
||||
with open('README.md') as infile:
|
||||
lines = infile.read().splitlines()
|
||||
return len(filter(_is_go_runnable, lines))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _is_go_runnable(line):
|
||||
return line.startswith('package main')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _combine_coverprofiles(coverprofiles):
|
||||
combined = tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(
|
||||
suffix='.coverprofile', delete=False
|
||||
)
|
||||
combined.write('mode: set\n')
|
||||
|
||||
for coverprofile in coverprofiles:
|
||||
with open(coverprofile, 'r') as infile:
|
||||
for line in infile.readlines():
|
||||
if not line.startswith('mode: '):
|
||||
combined.write(line)
|
||||
|
||||
combined.flush()
|
||||
name = combined.name
|
||||
combined.close()
|
||||
return name
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
sys.exit(main())
|
||||
56
vendor/golang.org/x/net/context/context.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
56
vendor/golang.org/x/net/context/context.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2014 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package context defines the Context type, which carries deadlines,
|
||||
// cancelation signals, and other request-scoped values across API boundaries
|
||||
// and between processes.
|
||||
// As of Go 1.7 this package is available in the standard library under the
|
||||
// name context. https://golang.org/pkg/context.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Incoming requests to a server should create a Context, and outgoing calls to
|
||||
// servers should accept a Context. The chain of function calls between must
|
||||
// propagate the Context, optionally replacing it with a modified copy created
|
||||
// using WithDeadline, WithTimeout, WithCancel, or WithValue.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Programs that use Contexts should follow these rules to keep interfaces
|
||||
// consistent across packages and enable static analysis tools to check context
|
||||
// propagation:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Do not store Contexts inside a struct type; instead, pass a Context
|
||||
// explicitly to each function that needs it. The Context should be the first
|
||||
// parameter, typically named ctx:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func DoSomething(ctx context.Context, arg Arg) error {
|
||||
// // ... use ctx ...
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Do not pass a nil Context, even if a function permits it. Pass context.TODO
|
||||
// if you are unsure about which Context to use.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use context Values only for request-scoped data that transits processes and
|
||||
// APIs, not for passing optional parameters to functions.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The same Context may be passed to functions running in different goroutines;
|
||||
// Contexts are safe for simultaneous use by multiple goroutines.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See http://blog.golang.org/context for example code for a server that uses
|
||||
// Contexts.
|
||||
package context // import "golang.org/x/net/context"
|
||||
|
||||
// Background returns a non-nil, empty Context. It is never canceled, has no
|
||||
// values, and has no deadline. It is typically used by the main function,
|
||||
// initialization, and tests, and as the top-level Context for incoming
|
||||
// requests.
|
||||
func Background() Context {
|
||||
return background
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO returns a non-nil, empty Context. Code should use context.TODO when
|
||||
// it's unclear which Context to use or it is not yet available (because the
|
||||
// surrounding function has not yet been extended to accept a Context
|
||||
// parameter). TODO is recognized by static analysis tools that determine
|
||||
// whether Contexts are propagated correctly in a program.
|
||||
func TODO() Context {
|
||||
return todo
|
||||
}
|
||||
72
vendor/golang.org/x/net/context/go17.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
72
vendor/golang.org/x/net/context/go17.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2016 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build go1.7
|
||||
|
||||
package context
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"context" // standard library's context, as of Go 1.7
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
todo = context.TODO()
|
||||
background = context.Background()
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Canceled is the error returned by Context.Err when the context is canceled.
|
||||
var Canceled = context.Canceled
|
||||
|
||||
// DeadlineExceeded is the error returned by Context.Err when the context's
|
||||
// deadline passes.
|
||||
var DeadlineExceeded = context.DeadlineExceeded
|
||||
|
||||
// WithCancel returns a copy of parent with a new Done channel. The returned
|
||||
// context's Done channel is closed when the returned cancel function is called
|
||||
// or when the parent context's Done channel is closed, whichever happens first.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Canceling this context releases resources associated with it, so code should
|
||||
// call cancel as soon as the operations running in this Context complete.
|
||||
func WithCancel(parent Context) (ctx Context, cancel CancelFunc) {
|
||||
ctx, f := context.WithCancel(parent)
|
||||
return ctx, CancelFunc(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithDeadline returns a copy of the parent context with the deadline adjusted
|
||||
// to be no later than d. If the parent's deadline is already earlier than d,
|
||||
// WithDeadline(parent, d) is semantically equivalent to parent. The returned
|
||||
// context's Done channel is closed when the deadline expires, when the returned
|
||||
// cancel function is called, or when the parent context's Done channel is
|
||||
// closed, whichever happens first.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Canceling this context releases resources associated with it, so code should
|
||||
// call cancel as soon as the operations running in this Context complete.
|
||||
func WithDeadline(parent Context, deadline time.Time) (Context, CancelFunc) {
|
||||
ctx, f := context.WithDeadline(parent, deadline)
|
||||
return ctx, CancelFunc(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithTimeout returns WithDeadline(parent, time.Now().Add(timeout)).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Canceling this context releases resources associated with it, so code should
|
||||
// call cancel as soon as the operations running in this Context complete:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func slowOperationWithTimeout(ctx context.Context) (Result, error) {
|
||||
// ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 100*time.Millisecond)
|
||||
// defer cancel() // releases resources if slowOperation completes before timeout elapses
|
||||
// return slowOperation(ctx)
|
||||
// }
|
||||
func WithTimeout(parent Context, timeout time.Duration) (Context, CancelFunc) {
|
||||
return WithDeadline(parent, time.Now().Add(timeout))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithValue returns a copy of parent in which the value associated with key is
|
||||
// val.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use context Values only for request-scoped data that transits processes and
|
||||
// APIs, not for passing optional parameters to functions.
|
||||
func WithValue(parent Context, key interface{}, val interface{}) Context {
|
||||
return context.WithValue(parent, key, val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
20
vendor/golang.org/x/net/context/go19.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
20
vendor/golang.org/x/net/context/go19.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2017 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build go1.9
|
||||
|
||||
package context
|
||||
|
||||
import "context" // standard library's context, as of Go 1.7
|
||||
|
||||
// A Context carries a deadline, a cancelation signal, and other values across
|
||||
// API boundaries.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Context's methods may be called by multiple goroutines simultaneously.
|
||||
type Context = context.Context
|
||||
|
||||
// A CancelFunc tells an operation to abandon its work.
|
||||
// A CancelFunc does not wait for the work to stop.
|
||||
// After the first call, subsequent calls to a CancelFunc do nothing.
|
||||
type CancelFunc = context.CancelFunc
|
||||
300
vendor/golang.org/x/net/context/pre_go17.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
300
vendor/golang.org/x/net/context/pre_go17.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,300 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2014 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build !go1.7
|
||||
|
||||
package context
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// An emptyCtx is never canceled, has no values, and has no deadline. It is not
|
||||
// struct{}, since vars of this type must have distinct addresses.
|
||||
type emptyCtx int
|
||||
|
||||
func (*emptyCtx) Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool) {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (*emptyCtx) Done() <-chan struct{} {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (*emptyCtx) Err() error {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (*emptyCtx) Value(key interface{}) interface{} {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *emptyCtx) String() string {
|
||||
switch e {
|
||||
case background:
|
||||
return "context.Background"
|
||||
case todo:
|
||||
return "context.TODO"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "unknown empty Context"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
background = new(emptyCtx)
|
||||
todo = new(emptyCtx)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Canceled is the error returned by Context.Err when the context is canceled.
|
||||
var Canceled = errors.New("context canceled")
|
||||
|
||||
// DeadlineExceeded is the error returned by Context.Err when the context's
|
||||
// deadline passes.
|
||||
var DeadlineExceeded = errors.New("context deadline exceeded")
|
||||
|
||||
// WithCancel returns a copy of parent with a new Done channel. The returned
|
||||
// context's Done channel is closed when the returned cancel function is called
|
||||
// or when the parent context's Done channel is closed, whichever happens first.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Canceling this context releases resources associated with it, so code should
|
||||
// call cancel as soon as the operations running in this Context complete.
|
||||
func WithCancel(parent Context) (ctx Context, cancel CancelFunc) {
|
||||
c := newCancelCtx(parent)
|
||||
propagateCancel(parent, c)
|
||||
return c, func() { c.cancel(true, Canceled) }
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// newCancelCtx returns an initialized cancelCtx.
|
||||
func newCancelCtx(parent Context) *cancelCtx {
|
||||
return &cancelCtx{
|
||||
Context: parent,
|
||||
done: make(chan struct{}),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// propagateCancel arranges for child to be canceled when parent is.
|
||||
func propagateCancel(parent Context, child canceler) {
|
||||
if parent.Done() == nil {
|
||||
return // parent is never canceled
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p, ok := parentCancelCtx(parent); ok {
|
||||
p.mu.Lock()
|
||||
if p.err != nil {
|
||||
// parent has already been canceled
|
||||
child.cancel(false, p.err)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if p.children == nil {
|
||||
p.children = make(map[canceler]bool)
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.children[child] = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
go func() {
|
||||
select {
|
||||
case <-parent.Done():
|
||||
child.cancel(false, parent.Err())
|
||||
case <-child.Done():
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// parentCancelCtx follows a chain of parent references until it finds a
|
||||
// *cancelCtx. This function understands how each of the concrete types in this
|
||||
// package represents its parent.
|
||||
func parentCancelCtx(parent Context) (*cancelCtx, bool) {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
switch c := parent.(type) {
|
||||
case *cancelCtx:
|
||||
return c, true
|
||||
case *timerCtx:
|
||||
return c.cancelCtx, true
|
||||
case *valueCtx:
|
||||
parent = c.Context
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return nil, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// removeChild removes a context from its parent.
|
||||
func removeChild(parent Context, child canceler) {
|
||||
p, ok := parentCancelCtx(parent)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.mu.Lock()
|
||||
if p.children != nil {
|
||||
delete(p.children, child)
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A canceler is a context type that can be canceled directly. The
|
||||
// implementations are *cancelCtx and *timerCtx.
|
||||
type canceler interface {
|
||||
cancel(removeFromParent bool, err error)
|
||||
Done() <-chan struct{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A cancelCtx can be canceled. When canceled, it also cancels any children
|
||||
// that implement canceler.
|
||||
type cancelCtx struct {
|
||||
Context
|
||||
|
||||
done chan struct{} // closed by the first cancel call.
|
||||
|
||||
mu sync.Mutex
|
||||
children map[canceler]bool // set to nil by the first cancel call
|
||||
err error // set to non-nil by the first cancel call
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *cancelCtx) Done() <-chan struct{} {
|
||||
return c.done
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *cancelCtx) Err() error {
|
||||
c.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer c.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
return c.err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *cancelCtx) String() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%v.WithCancel", c.Context)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// cancel closes c.done, cancels each of c's children, and, if
|
||||
// removeFromParent is true, removes c from its parent's children.
|
||||
func (c *cancelCtx) cancel(removeFromParent bool, err error) {
|
||||
if err == nil {
|
||||
panic("context: internal error: missing cancel error")
|
||||
}
|
||||
c.mu.Lock()
|
||||
if c.err != nil {
|
||||
c.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
return // already canceled
|
||||
}
|
||||
c.err = err
|
||||
close(c.done)
|
||||
for child := range c.children {
|
||||
// NOTE: acquiring the child's lock while holding parent's lock.
|
||||
child.cancel(false, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
c.children = nil
|
||||
c.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
if removeFromParent {
|
||||
removeChild(c.Context, c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithDeadline returns a copy of the parent context with the deadline adjusted
|
||||
// to be no later than d. If the parent's deadline is already earlier than d,
|
||||
// WithDeadline(parent, d) is semantically equivalent to parent. The returned
|
||||
// context's Done channel is closed when the deadline expires, when the returned
|
||||
// cancel function is called, or when the parent context's Done channel is
|
||||
// closed, whichever happens first.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Canceling this context releases resources associated with it, so code should
|
||||
// call cancel as soon as the operations running in this Context complete.
|
||||
func WithDeadline(parent Context, deadline time.Time) (Context, CancelFunc) {
|
||||
if cur, ok := parent.Deadline(); ok && cur.Before(deadline) {
|
||||
// The current deadline is already sooner than the new one.
|
||||
return WithCancel(parent)
|
||||
}
|
||||
c := &timerCtx{
|
||||
cancelCtx: newCancelCtx(parent),
|
||||
deadline: deadline,
|
||||
}
|
||||
propagateCancel(parent, c)
|
||||
d := deadline.Sub(time.Now())
|
||||
if d <= 0 {
|
||||
c.cancel(true, DeadlineExceeded) // deadline has already passed
|
||||
return c, func() { c.cancel(true, Canceled) }
|
||||
}
|
||||
c.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer c.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
if c.err == nil {
|
||||
c.timer = time.AfterFunc(d, func() {
|
||||
c.cancel(true, DeadlineExceeded)
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
return c, func() { c.cancel(true, Canceled) }
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A timerCtx carries a timer and a deadline. It embeds a cancelCtx to
|
||||
// implement Done and Err. It implements cancel by stopping its timer then
|
||||
// delegating to cancelCtx.cancel.
|
||||
type timerCtx struct {
|
||||
*cancelCtx
|
||||
timer *time.Timer // Under cancelCtx.mu.
|
||||
|
||||
deadline time.Time
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *timerCtx) Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool) {
|
||||
return c.deadline, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *timerCtx) String() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%v.WithDeadline(%s [%s])", c.cancelCtx.Context, c.deadline, c.deadline.Sub(time.Now()))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *timerCtx) cancel(removeFromParent bool, err error) {
|
||||
c.cancelCtx.cancel(false, err)
|
||||
if removeFromParent {
|
||||
// Remove this timerCtx from its parent cancelCtx's children.
|
||||
removeChild(c.cancelCtx.Context, c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
c.mu.Lock()
|
||||
if c.timer != nil {
|
||||
c.timer.Stop()
|
||||
c.timer = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
c.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithTimeout returns WithDeadline(parent, time.Now().Add(timeout)).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Canceling this context releases resources associated with it, so code should
|
||||
// call cancel as soon as the operations running in this Context complete:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// func slowOperationWithTimeout(ctx context.Context) (Result, error) {
|
||||
// ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 100*time.Millisecond)
|
||||
// defer cancel() // releases resources if slowOperation completes before timeout elapses
|
||||
// return slowOperation(ctx)
|
||||
// }
|
||||
func WithTimeout(parent Context, timeout time.Duration) (Context, CancelFunc) {
|
||||
return WithDeadline(parent, time.Now().Add(timeout))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithValue returns a copy of parent in which the value associated with key is
|
||||
// val.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use context Values only for request-scoped data that transits processes and
|
||||
// APIs, not for passing optional parameters to functions.
|
||||
func WithValue(parent Context, key interface{}, val interface{}) Context {
|
||||
return &valueCtx{parent, key, val}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A valueCtx carries a key-value pair. It implements Value for that key and
|
||||
// delegates all other calls to the embedded Context.
|
||||
type valueCtx struct {
|
||||
Context
|
||||
key, val interface{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *valueCtx) String() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%v.WithValue(%#v, %#v)", c.Context, c.key, c.val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *valueCtx) Value(key interface{}) interface{} {
|
||||
if c.key == key {
|
||||
return c.val
|
||||
}
|
||||
return c.Context.Value(key)
|
||||
}
|
||||
109
vendor/golang.org/x/net/context/pre_go19.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
109
vendor/golang.org/x/net/context/pre_go19.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2014 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build !go1.9
|
||||
|
||||
package context
|
||||
|
||||
import "time"
|
||||
|
||||
// A Context carries a deadline, a cancelation signal, and other values across
|
||||
// API boundaries.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Context's methods may be called by multiple goroutines simultaneously.
|
||||
type Context interface {
|
||||
// Deadline returns the time when work done on behalf of this context
|
||||
// should be canceled. Deadline returns ok==false when no deadline is
|
||||
// set. Successive calls to Deadline return the same results.
|
||||
Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool)
|
||||
|
||||
// Done returns a channel that's closed when work done on behalf of this
|
||||
// context should be canceled. Done may return nil if this context can
|
||||
// never be canceled. Successive calls to Done return the same value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// WithCancel arranges for Done to be closed when cancel is called;
|
||||
// WithDeadline arranges for Done to be closed when the deadline
|
||||
// expires; WithTimeout arranges for Done to be closed when the timeout
|
||||
// elapses.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Done is provided for use in select statements:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Stream generates values with DoSomething and sends them to out
|
||||
// // until DoSomething returns an error or ctx.Done is closed.
|
||||
// func Stream(ctx context.Context, out chan<- Value) error {
|
||||
// for {
|
||||
// v, err := DoSomething(ctx)
|
||||
// if err != nil {
|
||||
// return err
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// select {
|
||||
// case <-ctx.Done():
|
||||
// return ctx.Err()
|
||||
// case out <- v:
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See http://blog.golang.org/pipelines for more examples of how to use
|
||||
// a Done channel for cancelation.
|
||||
Done() <-chan struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Err returns a non-nil error value after Done is closed. Err returns
|
||||
// Canceled if the context was canceled or DeadlineExceeded if the
|
||||
// context's deadline passed. No other values for Err are defined.
|
||||
// After Done is closed, successive calls to Err return the same value.
|
||||
Err() error
|
||||
|
||||
// Value returns the value associated with this context for key, or nil
|
||||
// if no value is associated with key. Successive calls to Value with
|
||||
// the same key returns the same result.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Use context values only for request-scoped data that transits
|
||||
// processes and API boundaries, not for passing optional parameters to
|
||||
// functions.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A key identifies a specific value in a Context. Functions that wish
|
||||
// to store values in Context typically allocate a key in a global
|
||||
// variable then use that key as the argument to context.WithValue and
|
||||
// Context.Value. A key can be any type that supports equality;
|
||||
// packages should define keys as an unexported type to avoid
|
||||
// collisions.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Packages that define a Context key should provide type-safe accessors
|
||||
// for the values stores using that key:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Package user defines a User type that's stored in Contexts.
|
||||
// package user
|
||||
//
|
||||
// import "golang.org/x/net/context"
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // User is the type of value stored in the Contexts.
|
||||
// type User struct {...}
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // key is an unexported type for keys defined in this package.
|
||||
// // This prevents collisions with keys defined in other packages.
|
||||
// type key int
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // userKey is the key for user.User values in Contexts. It is
|
||||
// // unexported; clients use user.NewContext and user.FromContext
|
||||
// // instead of using this key directly.
|
||||
// var userKey key = 0
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // NewContext returns a new Context that carries value u.
|
||||
// func NewContext(ctx context.Context, u *User) context.Context {
|
||||
// return context.WithValue(ctx, userKey, u)
|
||||
// }
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // FromContext returns the User value stored in ctx, if any.
|
||||
// func FromContext(ctx context.Context) (*User, bool) {
|
||||
// u, ok := ctx.Value(userKey).(*User)
|
||||
// return u, ok
|
||||
// }
|
||||
Value(key interface{}) interface{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A CancelFunc tells an operation to abandon its work.
|
||||
// A CancelFunc does not wait for the work to stop.
|
||||
// After the first call, subsequent calls to a CancelFunc do nothing.
|
||||
type CancelFunc func()
|
||||
796
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/file.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
796
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/file.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,796 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2014 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package webdav
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"encoding/xml"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/net/context"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// slashClean is equivalent to but slightly more efficient than
|
||||
// path.Clean("/" + name).
|
||||
func slashClean(name string) string {
|
||||
if name == "" || name[0] != '/' {
|
||||
name = "/" + name
|
||||
}
|
||||
return path.Clean(name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A FileSystem implements access to a collection of named files. The elements
|
||||
// in a file path are separated by slash ('/', U+002F) characters, regardless
|
||||
// of host operating system convention.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Each method has the same semantics as the os package's function of the same
|
||||
// name.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that the os.Rename documentation says that "OS-specific restrictions
|
||||
// might apply". In particular, whether or not renaming a file or directory
|
||||
// overwriting another existing file or directory is an error is OS-dependent.
|
||||
type FileSystem interface {
|
||||
Mkdir(ctx context.Context, name string, perm os.FileMode) error
|
||||
OpenFile(ctx context.Context, name string, flag int, perm os.FileMode) (File, error)
|
||||
RemoveAll(ctx context.Context, name string) error
|
||||
Rename(ctx context.Context, oldName, newName string) error
|
||||
Stat(ctx context.Context, name string) (os.FileInfo, error)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A File is returned by a FileSystem's OpenFile method and can be served by a
|
||||
// Handler.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A File may optionally implement the DeadPropsHolder interface, if it can
|
||||
// load and save dead properties.
|
||||
type File interface {
|
||||
http.File
|
||||
io.Writer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A Dir implements FileSystem using the native file system restricted to a
|
||||
// specific directory tree.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// While the FileSystem.OpenFile method takes '/'-separated paths, a Dir's
|
||||
// string value is a filename on the native file system, not a URL, so it is
|
||||
// separated by filepath.Separator, which isn't necessarily '/'.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// An empty Dir is treated as ".".
|
||||
type Dir string
|
||||
|
||||
func (d Dir) resolve(name string) string {
|
||||
// This implementation is based on Dir.Open's code in the standard net/http package.
|
||||
if filepath.Separator != '/' && strings.IndexRune(name, filepath.Separator) >= 0 ||
|
||||
strings.Contains(name, "\x00") {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
dir := string(d)
|
||||
if dir == "" {
|
||||
dir = "."
|
||||
}
|
||||
return filepath.Join(dir, filepath.FromSlash(slashClean(name)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d Dir) Mkdir(ctx context.Context, name string, perm os.FileMode) error {
|
||||
if name = d.resolve(name); name == "" {
|
||||
return os.ErrNotExist
|
||||
}
|
||||
return os.Mkdir(name, perm)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d Dir) OpenFile(ctx context.Context, name string, flag int, perm os.FileMode) (File, error) {
|
||||
if name = d.resolve(name); name == "" {
|
||||
return nil, os.ErrNotExist
|
||||
}
|
||||
f, err := os.OpenFile(name, flag, perm)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return f, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d Dir) RemoveAll(ctx context.Context, name string) error {
|
||||
if name = d.resolve(name); name == "" {
|
||||
return os.ErrNotExist
|
||||
}
|
||||
if name == filepath.Clean(string(d)) {
|
||||
// Prohibit removing the virtual root directory.
|
||||
return os.ErrInvalid
|
||||
}
|
||||
return os.RemoveAll(name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d Dir) Rename(ctx context.Context, oldName, newName string) error {
|
||||
if oldName = d.resolve(oldName); oldName == "" {
|
||||
return os.ErrNotExist
|
||||
}
|
||||
if newName = d.resolve(newName); newName == "" {
|
||||
return os.ErrNotExist
|
||||
}
|
||||
if root := filepath.Clean(string(d)); root == oldName || root == newName {
|
||||
// Prohibit renaming from or to the virtual root directory.
|
||||
return os.ErrInvalid
|
||||
}
|
||||
return os.Rename(oldName, newName)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (d Dir) Stat(ctx context.Context, name string) (os.FileInfo, error) {
|
||||
if name = d.resolve(name); name == "" {
|
||||
return nil, os.ErrNotExist
|
||||
}
|
||||
return os.Stat(name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewMemFS returns a new in-memory FileSystem implementation.
|
||||
func NewMemFS() FileSystem {
|
||||
return &memFS{
|
||||
root: memFSNode{
|
||||
children: make(map[string]*memFSNode),
|
||||
mode: 0660 | os.ModeDir,
|
||||
modTime: time.Now(),
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A memFS implements FileSystem, storing all metadata and actual file data
|
||||
// in-memory. No limits on filesystem size are used, so it is not recommended
|
||||
// this be used where the clients are untrusted.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Concurrent access is permitted. The tree structure is protected by a mutex,
|
||||
// and each node's contents and metadata are protected by a per-node mutex.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// TODO: Enforce file permissions.
|
||||
type memFS struct {
|
||||
mu sync.Mutex
|
||||
root memFSNode
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: clean up and rationalize the walk/find code.
|
||||
|
||||
// walk walks the directory tree for the fullname, calling f at each step. If f
|
||||
// returns an error, the walk will be aborted and return that same error.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// dir is the directory at that step, frag is the name fragment, and final is
|
||||
// whether it is the final step. For example, walking "/foo/bar/x" will result
|
||||
// in 3 calls to f:
|
||||
// - "/", "foo", false
|
||||
// - "/foo/", "bar", false
|
||||
// - "/foo/bar/", "x", true
|
||||
// The frag argument will be empty only if dir is the root node and the walk
|
||||
// ends at that root node.
|
||||
func (fs *memFS) walk(op, fullname string, f func(dir *memFSNode, frag string, final bool) error) error {
|
||||
original := fullname
|
||||
fullname = slashClean(fullname)
|
||||
|
||||
// Strip any leading "/"s to make fullname a relative path, as the walk
|
||||
// starts at fs.root.
|
||||
if fullname[0] == '/' {
|
||||
fullname = fullname[1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
dir := &fs.root
|
||||
|
||||
for {
|
||||
frag, remaining := fullname, ""
|
||||
i := strings.IndexRune(fullname, '/')
|
||||
final := i < 0
|
||||
if !final {
|
||||
frag, remaining = fullname[:i], fullname[i+1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if frag == "" && dir != &fs.root {
|
||||
panic("webdav: empty path fragment for a clean path")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err := f(dir, frag, final); err != nil {
|
||||
return &os.PathError{
|
||||
Op: op,
|
||||
Path: original,
|
||||
Err: err,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if final {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
child := dir.children[frag]
|
||||
if child == nil {
|
||||
return &os.PathError{
|
||||
Op: op,
|
||||
Path: original,
|
||||
Err: os.ErrNotExist,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !child.mode.IsDir() {
|
||||
return &os.PathError{
|
||||
Op: op,
|
||||
Path: original,
|
||||
Err: os.ErrInvalid,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
dir, fullname = child, remaining
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// find returns the parent of the named node and the relative name fragment
|
||||
// from the parent to the child. For example, if finding "/foo/bar/baz" then
|
||||
// parent will be the node for "/foo/bar" and frag will be "baz".
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the fullname names the root node, then parent, frag and err will be zero.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// find returns an error if the parent does not already exist or the parent
|
||||
// isn't a directory, but it will not return an error per se if the child does
|
||||
// not already exist. The error returned is either nil or an *os.PathError
|
||||
// whose Op is op.
|
||||
func (fs *memFS) find(op, fullname string) (parent *memFSNode, frag string, err error) {
|
||||
err = fs.walk(op, fullname, func(parent0 *memFSNode, frag0 string, final bool) error {
|
||||
if !final {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if frag0 != "" {
|
||||
parent, frag = parent0, frag0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
})
|
||||
return parent, frag, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (fs *memFS) Mkdir(ctx context.Context, name string, perm os.FileMode) error {
|
||||
fs.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer fs.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
dir, frag, err := fs.find("mkdir", name)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dir == nil {
|
||||
// We can't create the root.
|
||||
return os.ErrInvalid
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, ok := dir.children[frag]; ok {
|
||||
return os.ErrExist
|
||||
}
|
||||
dir.children[frag] = &memFSNode{
|
||||
children: make(map[string]*memFSNode),
|
||||
mode: perm.Perm() | os.ModeDir,
|
||||
modTime: time.Now(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (fs *memFS) OpenFile(ctx context.Context, name string, flag int, perm os.FileMode) (File, error) {
|
||||
fs.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer fs.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
dir, frag, err := fs.find("open", name)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
var n *memFSNode
|
||||
if dir == nil {
|
||||
// We're opening the root.
|
||||
if flag&(os.O_WRONLY|os.O_RDWR) != 0 {
|
||||
return nil, os.ErrPermission
|
||||
}
|
||||
n, frag = &fs.root, "/"
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
n = dir.children[frag]
|
||||
if flag&(os.O_SYNC|os.O_APPEND) != 0 {
|
||||
// memFile doesn't support these flags yet.
|
||||
return nil, os.ErrInvalid
|
||||
}
|
||||
if flag&os.O_CREATE != 0 {
|
||||
if flag&os.O_EXCL != 0 && n != nil {
|
||||
return nil, os.ErrExist
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n == nil {
|
||||
n = &memFSNode{
|
||||
mode: perm.Perm(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
dir.children[frag] = n
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n == nil {
|
||||
return nil, os.ErrNotExist
|
||||
}
|
||||
if flag&(os.O_WRONLY|os.O_RDWR) != 0 && flag&os.O_TRUNC != 0 {
|
||||
n.mu.Lock()
|
||||
n.data = nil
|
||||
n.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
children := make([]os.FileInfo, 0, len(n.children))
|
||||
for cName, c := range n.children {
|
||||
children = append(children, c.stat(cName))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return &memFile{
|
||||
n: n,
|
||||
nameSnapshot: frag,
|
||||
childrenSnapshot: children,
|
||||
}, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (fs *memFS) RemoveAll(ctx context.Context, name string) error {
|
||||
fs.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer fs.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
dir, frag, err := fs.find("remove", name)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dir == nil {
|
||||
// We can't remove the root.
|
||||
return os.ErrInvalid
|
||||
}
|
||||
delete(dir.children, frag)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (fs *memFS) Rename(ctx context.Context, oldName, newName string) error {
|
||||
fs.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer fs.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
oldName = slashClean(oldName)
|
||||
newName = slashClean(newName)
|
||||
if oldName == newName {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if strings.HasPrefix(newName, oldName+"/") {
|
||||
// We can't rename oldName to be a sub-directory of itself.
|
||||
return os.ErrInvalid
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
oDir, oFrag, err := fs.find("rename", oldName)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if oDir == nil {
|
||||
// We can't rename from the root.
|
||||
return os.ErrInvalid
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
nDir, nFrag, err := fs.find("rename", newName)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if nDir == nil {
|
||||
// We can't rename to the root.
|
||||
return os.ErrInvalid
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
oNode, ok := oDir.children[oFrag]
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return os.ErrNotExist
|
||||
}
|
||||
if oNode.children != nil {
|
||||
if nNode, ok := nDir.children[nFrag]; ok {
|
||||
if nNode.children == nil {
|
||||
return errNotADirectory
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(nNode.children) != 0 {
|
||||
return errDirectoryNotEmpty
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
delete(oDir.children, oFrag)
|
||||
nDir.children[nFrag] = oNode
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (fs *memFS) Stat(ctx context.Context, name string) (os.FileInfo, error) {
|
||||
fs.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer fs.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
dir, frag, err := fs.find("stat", name)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dir == nil {
|
||||
// We're stat'ting the root.
|
||||
return fs.root.stat("/"), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n, ok := dir.children[frag]; ok {
|
||||
return n.stat(path.Base(name)), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, os.ErrNotExist
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A memFSNode represents a single entry in the in-memory filesystem and also
|
||||
// implements os.FileInfo.
|
||||
type memFSNode struct {
|
||||
// children is protected by memFS.mu.
|
||||
children map[string]*memFSNode
|
||||
|
||||
mu sync.Mutex
|
||||
data []byte
|
||||
mode os.FileMode
|
||||
modTime time.Time
|
||||
deadProps map[xml.Name]Property
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (n *memFSNode) stat(name string) *memFileInfo {
|
||||
n.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer n.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
return &memFileInfo{
|
||||
name: name,
|
||||
size: int64(len(n.data)),
|
||||
mode: n.mode,
|
||||
modTime: n.modTime,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (n *memFSNode) DeadProps() (map[xml.Name]Property, error) {
|
||||
n.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer n.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
if len(n.deadProps) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
ret := make(map[xml.Name]Property, len(n.deadProps))
|
||||
for k, v := range n.deadProps {
|
||||
ret[k] = v
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ret, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (n *memFSNode) Patch(patches []Proppatch) ([]Propstat, error) {
|
||||
n.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer n.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
pstat := Propstat{Status: http.StatusOK}
|
||||
for _, patch := range patches {
|
||||
for _, p := range patch.Props {
|
||||
pstat.Props = append(pstat.Props, Property{XMLName: p.XMLName})
|
||||
if patch.Remove {
|
||||
delete(n.deadProps, p.XMLName)
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n.deadProps == nil {
|
||||
n.deadProps = map[xml.Name]Property{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
n.deadProps[p.XMLName] = p
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return []Propstat{pstat}, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type memFileInfo struct {
|
||||
name string
|
||||
size int64
|
||||
mode os.FileMode
|
||||
modTime time.Time
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *memFileInfo) Name() string { return f.name }
|
||||
func (f *memFileInfo) Size() int64 { return f.size }
|
||||
func (f *memFileInfo) Mode() os.FileMode { return f.mode }
|
||||
func (f *memFileInfo) ModTime() time.Time { return f.modTime }
|
||||
func (f *memFileInfo) IsDir() bool { return f.mode.IsDir() }
|
||||
func (f *memFileInfo) Sys() interface{} { return nil }
|
||||
|
||||
// A memFile is a File implementation for a memFSNode. It is a per-file (not
|
||||
// per-node) read/write position, and a snapshot of the memFS' tree structure
|
||||
// (a node's name and children) for that node.
|
||||
type memFile struct {
|
||||
n *memFSNode
|
||||
nameSnapshot string
|
||||
childrenSnapshot []os.FileInfo
|
||||
// pos is protected by n.mu.
|
||||
pos int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A *memFile implements the optional DeadPropsHolder interface.
|
||||
var _ DeadPropsHolder = (*memFile)(nil)
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *memFile) DeadProps() (map[xml.Name]Property, error) { return f.n.DeadProps() }
|
||||
func (f *memFile) Patch(patches []Proppatch) ([]Propstat, error) { return f.n.Patch(patches) }
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *memFile) Close() error {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *memFile) Read(p []byte) (int, error) {
|
||||
f.n.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer f.n.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
if f.n.mode.IsDir() {
|
||||
return 0, os.ErrInvalid
|
||||
}
|
||||
if f.pos >= len(f.n.data) {
|
||||
return 0, io.EOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
n := copy(p, f.n.data[f.pos:])
|
||||
f.pos += n
|
||||
return n, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *memFile) Readdir(count int) ([]os.FileInfo, error) {
|
||||
f.n.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer f.n.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
if !f.n.mode.IsDir() {
|
||||
return nil, os.ErrInvalid
|
||||
}
|
||||
old := f.pos
|
||||
if old >= len(f.childrenSnapshot) {
|
||||
// The os.File Readdir docs say that at the end of a directory,
|
||||
// the error is io.EOF if count > 0 and nil if count <= 0.
|
||||
if count > 0 {
|
||||
return nil, io.EOF
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if count > 0 {
|
||||
f.pos += count
|
||||
if f.pos > len(f.childrenSnapshot) {
|
||||
f.pos = len(f.childrenSnapshot)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
f.pos = len(f.childrenSnapshot)
|
||||
old = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return f.childrenSnapshot[old:f.pos], nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *memFile) Seek(offset int64, whence int) (int64, error) {
|
||||
f.n.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer f.n.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
npos := f.pos
|
||||
// TODO: How to handle offsets greater than the size of system int?
|
||||
switch whence {
|
||||
case os.SEEK_SET:
|
||||
npos = int(offset)
|
||||
case os.SEEK_CUR:
|
||||
npos += int(offset)
|
||||
case os.SEEK_END:
|
||||
npos = len(f.n.data) + int(offset)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
npos = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if npos < 0 {
|
||||
return 0, os.ErrInvalid
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.pos = npos
|
||||
return int64(f.pos), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *memFile) Stat() (os.FileInfo, error) {
|
||||
return f.n.stat(f.nameSnapshot), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (f *memFile) Write(p []byte) (int, error) {
|
||||
lenp := len(p)
|
||||
f.n.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer f.n.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
if f.n.mode.IsDir() {
|
||||
return 0, os.ErrInvalid
|
||||
}
|
||||
if f.pos < len(f.n.data) {
|
||||
n := copy(f.n.data[f.pos:], p)
|
||||
f.pos += n
|
||||
p = p[n:]
|
||||
} else if f.pos > len(f.n.data) {
|
||||
// Write permits the creation of holes, if we've seek'ed past the
|
||||
// existing end of file.
|
||||
if f.pos <= cap(f.n.data) {
|
||||
oldLen := len(f.n.data)
|
||||
f.n.data = f.n.data[:f.pos]
|
||||
hole := f.n.data[oldLen:]
|
||||
for i := range hole {
|
||||
hole[i] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
d := make([]byte, f.pos, f.pos+len(p))
|
||||
copy(d, f.n.data)
|
||||
f.n.data = d
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if len(p) > 0 {
|
||||
// We should only get here if f.pos == len(f.n.data).
|
||||
f.n.data = append(f.n.data, p...)
|
||||
f.pos = len(f.n.data)
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.n.modTime = time.Now()
|
||||
return lenp, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// moveFiles moves files and/or directories from src to dst.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See section 9.9.4 for when various HTTP status codes apply.
|
||||
func moveFiles(ctx context.Context, fs FileSystem, src, dst string, overwrite bool) (status int, err error) {
|
||||
created := false
|
||||
if _, err := fs.Stat(ctx, dst); err != nil {
|
||||
if !os.IsNotExist(err) {
|
||||
return http.StatusForbidden, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
created = true
|
||||
} else if overwrite {
|
||||
// Section 9.9.3 says that "If a resource exists at the destination
|
||||
// and the Overwrite header is "T", then prior to performing the move,
|
||||
// the server must perform a DELETE with "Depth: infinity" on the
|
||||
// destination resource.
|
||||
if err := fs.RemoveAll(ctx, dst); err != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusForbidden, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return http.StatusPreconditionFailed, os.ErrExist
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err := fs.Rename(ctx, src, dst); err != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusForbidden, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if created {
|
||||
return http.StatusCreated, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return http.StatusNoContent, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func copyProps(dst, src File) error {
|
||||
d, ok := dst.(DeadPropsHolder)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
s, ok := src.(DeadPropsHolder)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
m, err := s.DeadProps()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
props := make([]Property, 0, len(m))
|
||||
for _, prop := range m {
|
||||
props = append(props, prop)
|
||||
}
|
||||
_, err = d.Patch([]Proppatch{{Props: props}})
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// copyFiles copies files and/or directories from src to dst.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See section 9.8.5 for when various HTTP status codes apply.
|
||||
func copyFiles(ctx context.Context, fs FileSystem, src, dst string, overwrite bool, depth int, recursion int) (status int, err error) {
|
||||
if recursion == 1000 {
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, errRecursionTooDeep
|
||||
}
|
||||
recursion++
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: section 9.8.3 says that "Note that an infinite-depth COPY of /A/
|
||||
// into /A/B/ could lead to infinite recursion if not handled correctly."
|
||||
|
||||
srcFile, err := fs.OpenFile(ctx, src, os.O_RDONLY, 0)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
|
||||
return http.StatusNotFound, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer srcFile.Close()
|
||||
srcStat, err := srcFile.Stat()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
|
||||
return http.StatusNotFound, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
srcPerm := srcStat.Mode() & os.ModePerm
|
||||
|
||||
created := false
|
||||
if _, err := fs.Stat(ctx, dst); err != nil {
|
||||
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
|
||||
created = true
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return http.StatusForbidden, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if !overwrite {
|
||||
return http.StatusPreconditionFailed, os.ErrExist
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err := fs.RemoveAll(ctx, dst); err != nil && !os.IsNotExist(err) {
|
||||
return http.StatusForbidden, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if srcStat.IsDir() {
|
||||
if err := fs.Mkdir(ctx, dst, srcPerm); err != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusForbidden, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if depth == infiniteDepth {
|
||||
children, err := srcFile.Readdir(-1)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusForbidden, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, c := range children {
|
||||
name := c.Name()
|
||||
s := path.Join(src, name)
|
||||
d := path.Join(dst, name)
|
||||
cStatus, cErr := copyFiles(ctx, fs, s, d, overwrite, depth, recursion)
|
||||
if cErr != nil {
|
||||
// TODO: MultiStatus.
|
||||
return cStatus, cErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
dstFile, err := fs.OpenFile(ctx, dst, os.O_RDWR|os.O_CREATE|os.O_TRUNC, srcPerm)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
|
||||
return http.StatusConflict, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return http.StatusForbidden, err
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
_, copyErr := io.Copy(dstFile, srcFile)
|
||||
propsErr := copyProps(dstFile, srcFile)
|
||||
closeErr := dstFile.Close()
|
||||
if copyErr != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, copyErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
if propsErr != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, propsErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
if closeErr != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, closeErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if created {
|
||||
return http.StatusCreated, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return http.StatusNoContent, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// walkFS traverses filesystem fs starting at name up to depth levels.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Allowed values for depth are 0, 1 or infiniteDepth. For each visited node,
|
||||
// walkFS calls walkFn. If a visited file system node is a directory and
|
||||
// walkFn returns filepath.SkipDir, walkFS will skip traversal of this node.
|
||||
func walkFS(ctx context.Context, fs FileSystem, depth int, name string, info os.FileInfo, walkFn filepath.WalkFunc) error {
|
||||
// This implementation is based on Walk's code in the standard path/filepath package.
|
||||
err := walkFn(name, info, nil)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if info.IsDir() && err == filepath.SkipDir {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !info.IsDir() || depth == 0 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if depth == 1 {
|
||||
depth = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Read directory names.
|
||||
f, err := fs.OpenFile(ctx, name, os.O_RDONLY, 0)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return walkFn(name, info, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
fileInfos, err := f.Readdir(0)
|
||||
f.Close()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return walkFn(name, info, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, fileInfo := range fileInfos {
|
||||
filename := path.Join(name, fileInfo.Name())
|
||||
fileInfo, err := fs.Stat(ctx, filename)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if err := walkFn(filename, fileInfo, err); err != nil && err != filepath.SkipDir {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
err = walkFS(ctx, fs, depth, filename, fileInfo, walkFn)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if !fileInfo.IsDir() || err != filepath.SkipDir {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
17
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/file_go1.6.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
17
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/file_go1.6.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2016 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build !go1.7
|
||||
|
||||
package webdav
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/net/context"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func getContext(r *http.Request) context.Context {
|
||||
return context.Background()
|
||||
}
|
||||
16
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/file_go1.7.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
16
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/file_go1.7.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2016 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build go1.7
|
||||
|
||||
package webdav
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"context"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func getContext(r *http.Request) context.Context {
|
||||
return r.Context()
|
||||
}
|
||||
173
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/if.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
173
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/if.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,173 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2014 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package webdav
|
||||
|
||||
// The If header is covered by Section 10.4.
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#HEADER_If
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ifHeader is a disjunction (OR) of ifLists.
|
||||
type ifHeader struct {
|
||||
lists []ifList
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ifList is a conjunction (AND) of Conditions, and an optional resource tag.
|
||||
type ifList struct {
|
||||
resourceTag string
|
||||
conditions []Condition
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// parseIfHeader parses the "If: foo bar" HTTP header. The httpHeader string
|
||||
// should omit the "If:" prefix and have any "\r\n"s collapsed to a " ", as is
|
||||
// returned by req.Header.Get("If") for a http.Request req.
|
||||
func parseIfHeader(httpHeader string) (h ifHeader, ok bool) {
|
||||
s := strings.TrimSpace(httpHeader)
|
||||
switch tokenType, _, _ := lex(s); tokenType {
|
||||
case '(':
|
||||
return parseNoTagLists(s)
|
||||
case angleTokenType:
|
||||
return parseTaggedLists(s)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return ifHeader{}, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func parseNoTagLists(s string) (h ifHeader, ok bool) {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
l, remaining, ok := parseList(s)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return ifHeader{}, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
h.lists = append(h.lists, l)
|
||||
if remaining == "" {
|
||||
return h, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
s = remaining
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func parseTaggedLists(s string) (h ifHeader, ok bool) {
|
||||
resourceTag, n := "", 0
|
||||
for first := true; ; first = false {
|
||||
tokenType, tokenStr, remaining := lex(s)
|
||||
switch tokenType {
|
||||
case angleTokenType:
|
||||
if !first && n == 0 {
|
||||
return ifHeader{}, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
resourceTag, n = tokenStr, 0
|
||||
s = remaining
|
||||
case '(':
|
||||
n++
|
||||
l, remaining, ok := parseList(s)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return ifHeader{}, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.resourceTag = resourceTag
|
||||
h.lists = append(h.lists, l)
|
||||
if remaining == "" {
|
||||
return h, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
s = remaining
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return ifHeader{}, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func parseList(s string) (l ifList, remaining string, ok bool) {
|
||||
tokenType, _, s := lex(s)
|
||||
if tokenType != '(' {
|
||||
return ifList{}, "", false
|
||||
}
|
||||
for {
|
||||
tokenType, _, remaining = lex(s)
|
||||
if tokenType == ')' {
|
||||
if len(l.conditions) == 0 {
|
||||
return ifList{}, "", false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return l, remaining, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
c, remaining, ok := parseCondition(s)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return ifList{}, "", false
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.conditions = append(l.conditions, c)
|
||||
s = remaining
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func parseCondition(s string) (c Condition, remaining string, ok bool) {
|
||||
tokenType, tokenStr, s := lex(s)
|
||||
if tokenType == notTokenType {
|
||||
c.Not = true
|
||||
tokenType, tokenStr, s = lex(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch tokenType {
|
||||
case strTokenType, angleTokenType:
|
||||
c.Token = tokenStr
|
||||
case squareTokenType:
|
||||
c.ETag = tokenStr
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return Condition{}, "", false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return c, s, true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Single-rune tokens like '(' or ')' have a token type equal to their rune.
|
||||
// All other tokens have a negative token type.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
errTokenType = rune(-1)
|
||||
eofTokenType = rune(-2)
|
||||
strTokenType = rune(-3)
|
||||
notTokenType = rune(-4)
|
||||
angleTokenType = rune(-5)
|
||||
squareTokenType = rune(-6)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func lex(s string) (tokenType rune, tokenStr string, remaining string) {
|
||||
// The net/textproto Reader that parses the HTTP header will collapse
|
||||
// Linear White Space that spans multiple "\r\n" lines to a single " ",
|
||||
// so we don't need to look for '\r' or '\n'.
|
||||
for len(s) > 0 && (s[0] == '\t' || s[0] == ' ') {
|
||||
s = s[1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(s) == 0 {
|
||||
return eofTokenType, "", ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
loop:
|
||||
for ; i < len(s); i++ {
|
||||
switch s[i] {
|
||||
case '\t', ' ', '(', ')', '<', '>', '[', ']':
|
||||
break loop
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if i != 0 {
|
||||
tokenStr, remaining = s[:i], s[i:]
|
||||
if tokenStr == "Not" {
|
||||
return notTokenType, "", remaining
|
||||
}
|
||||
return strTokenType, tokenStr, remaining
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
j := 0
|
||||
switch s[0] {
|
||||
case '<':
|
||||
j, tokenType = strings.IndexByte(s, '>'), angleTokenType
|
||||
case '[':
|
||||
j, tokenType = strings.IndexByte(s, ']'), squareTokenType
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return rune(s[0]), "", s[1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
if j < 0 {
|
||||
return errTokenType, "", ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
return tokenType, s[1:j], s[j+1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
11
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/internal/xml/README
generated
vendored
Normal file
11
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/internal/xml/README
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
This is a fork of the encoding/xml package at ca1d6c4, the last commit before
|
||||
https://go.googlesource.com/go/+/c0d6d33 "encoding/xml: restore Go 1.4 name
|
||||
space behavior" made late in the lead-up to the Go 1.5 release.
|
||||
|
||||
The list of encoding/xml changes is at
|
||||
https://go.googlesource.com/go/+log/master/src/encoding/xml
|
||||
|
||||
This fork is temporary, and I (nigeltao) expect to revert it after Go 1.6 is
|
||||
released.
|
||||
|
||||
See http://golang.org/issue/11841
|
||||
1223
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/internal/xml/marshal.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
1223
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/internal/xml/marshal.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
692
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/internal/xml/read.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
692
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/internal/xml/read.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,692 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2009 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package xml
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"encoding"
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// BUG(rsc): Mapping between XML elements and data structures is inherently flawed:
|
||||
// an XML element is an order-dependent collection of anonymous
|
||||
// values, while a data structure is an order-independent collection
|
||||
// of named values.
|
||||
// See package json for a textual representation more suitable
|
||||
// to data structures.
|
||||
|
||||
// Unmarshal parses the XML-encoded data and stores the result in
|
||||
// the value pointed to by v, which must be an arbitrary struct,
|
||||
// slice, or string. Well-formed data that does not fit into v is
|
||||
// discarded.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Because Unmarshal uses the reflect package, it can only assign
|
||||
// to exported (upper case) fields. Unmarshal uses a case-sensitive
|
||||
// comparison to match XML element names to tag values and struct
|
||||
// field names.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unmarshal maps an XML element to a struct using the following rules.
|
||||
// In the rules, the tag of a field refers to the value associated with the
|
||||
// key 'xml' in the struct field's tag (see the example above).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// * If the struct has a field of type []byte or string with tag
|
||||
// ",innerxml", Unmarshal accumulates the raw XML nested inside the
|
||||
// element in that field. The rest of the rules still apply.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// * If the struct has a field named XMLName of type xml.Name,
|
||||
// Unmarshal records the element name in that field.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// * If the XMLName field has an associated tag of the form
|
||||
// "name" or "namespace-URL name", the XML element must have
|
||||
// the given name (and, optionally, name space) or else Unmarshal
|
||||
// returns an error.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// * If the XML element has an attribute whose name matches a
|
||||
// struct field name with an associated tag containing ",attr" or
|
||||
// the explicit name in a struct field tag of the form "name,attr",
|
||||
// Unmarshal records the attribute value in that field.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// * If the XML element contains character data, that data is
|
||||
// accumulated in the first struct field that has tag ",chardata".
|
||||
// The struct field may have type []byte or string.
|
||||
// If there is no such field, the character data is discarded.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// * If the XML element contains comments, they are accumulated in
|
||||
// the first struct field that has tag ",comment". The struct
|
||||
// field may have type []byte or string. If there is no such
|
||||
// field, the comments are discarded.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// * If the XML element contains a sub-element whose name matches
|
||||
// the prefix of a tag formatted as "a" or "a>b>c", unmarshal
|
||||
// will descend into the XML structure looking for elements with the
|
||||
// given names, and will map the innermost elements to that struct
|
||||
// field. A tag starting with ">" is equivalent to one starting
|
||||
// with the field name followed by ">".
|
||||
//
|
||||
// * If the XML element contains a sub-element whose name matches
|
||||
// a struct field's XMLName tag and the struct field has no
|
||||
// explicit name tag as per the previous rule, unmarshal maps
|
||||
// the sub-element to that struct field.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// * If the XML element contains a sub-element whose name matches a
|
||||
// field without any mode flags (",attr", ",chardata", etc), Unmarshal
|
||||
// maps the sub-element to that struct field.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// * If the XML element contains a sub-element that hasn't matched any
|
||||
// of the above rules and the struct has a field with tag ",any",
|
||||
// unmarshal maps the sub-element to that struct field.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// * An anonymous struct field is handled as if the fields of its
|
||||
// value were part of the outer struct.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// * A struct field with tag "-" is never unmarshalled into.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unmarshal maps an XML element to a string or []byte by saving the
|
||||
// concatenation of that element's character data in the string or
|
||||
// []byte. The saved []byte is never nil.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unmarshal maps an attribute value to a string or []byte by saving
|
||||
// the value in the string or slice.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unmarshal maps an XML element to a slice by extending the length of
|
||||
// the slice and mapping the element to the newly created value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unmarshal maps an XML element or attribute value to a bool by
|
||||
// setting it to the boolean value represented by the string.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unmarshal maps an XML element or attribute value to an integer or
|
||||
// floating-point field by setting the field to the result of
|
||||
// interpreting the string value in decimal. There is no check for
|
||||
// overflow.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unmarshal maps an XML element to an xml.Name by recording the
|
||||
// element name.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Unmarshal maps an XML element to a pointer by setting the pointer
|
||||
// to a freshly allocated value and then mapping the element to that value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
func Unmarshal(data []byte, v interface{}) error {
|
||||
return NewDecoder(bytes.NewReader(data)).Decode(v)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Decode works like xml.Unmarshal, except it reads the decoder
|
||||
// stream to find the start element.
|
||||
func (d *Decoder) Decode(v interface{}) error {
|
||||
return d.DecodeElement(v, nil)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DecodeElement works like xml.Unmarshal except that it takes
|
||||
// a pointer to the start XML element to decode into v.
|
||||
// It is useful when a client reads some raw XML tokens itself
|
||||
// but also wants to defer to Unmarshal for some elements.
|
||||
func (d *Decoder) DecodeElement(v interface{}, start *StartElement) error {
|
||||
val := reflect.ValueOf(v)
|
||||
if val.Kind() != reflect.Ptr {
|
||||
return errors.New("non-pointer passed to Unmarshal")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return d.unmarshal(val.Elem(), start)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// An UnmarshalError represents an error in the unmarshalling process.
|
||||
type UnmarshalError string
|
||||
|
||||
func (e UnmarshalError) Error() string { return string(e) }
|
||||
|
||||
// Unmarshaler is the interface implemented by objects that can unmarshal
|
||||
// an XML element description of themselves.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// UnmarshalXML decodes a single XML element
|
||||
// beginning with the given start element.
|
||||
// If it returns an error, the outer call to Unmarshal stops and
|
||||
// returns that error.
|
||||
// UnmarshalXML must consume exactly one XML element.
|
||||
// One common implementation strategy is to unmarshal into
|
||||
// a separate value with a layout matching the expected XML
|
||||
// using d.DecodeElement, and then to copy the data from
|
||||
// that value into the receiver.
|
||||
// Another common strategy is to use d.Token to process the
|
||||
// XML object one token at a time.
|
||||
// UnmarshalXML may not use d.RawToken.
|
||||
type Unmarshaler interface {
|
||||
UnmarshalXML(d *Decoder, start StartElement) error
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnmarshalerAttr is the interface implemented by objects that can unmarshal
|
||||
// an XML attribute description of themselves.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// UnmarshalXMLAttr decodes a single XML attribute.
|
||||
// If it returns an error, the outer call to Unmarshal stops and
|
||||
// returns that error.
|
||||
// UnmarshalXMLAttr is used only for struct fields with the
|
||||
// "attr" option in the field tag.
|
||||
type UnmarshalerAttr interface {
|
||||
UnmarshalXMLAttr(attr Attr) error
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// receiverType returns the receiver type to use in an expression like "%s.MethodName".
|
||||
func receiverType(val interface{}) string {
|
||||
t := reflect.TypeOf(val)
|
||||
if t.Name() != "" {
|
||||
return t.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "(" + t.String() + ")"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// unmarshalInterface unmarshals a single XML element into val.
|
||||
// start is the opening tag of the element.
|
||||
func (p *Decoder) unmarshalInterface(val Unmarshaler, start *StartElement) error {
|
||||
// Record that decoder must stop at end tag corresponding to start.
|
||||
p.pushEOF()
|
||||
|
||||
p.unmarshalDepth++
|
||||
err := val.UnmarshalXML(p, *start)
|
||||
p.unmarshalDepth--
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
p.popEOF()
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if !p.popEOF() {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("xml: %s.UnmarshalXML did not consume entire <%s> element", receiverType(val), start.Name.Local)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// unmarshalTextInterface unmarshals a single XML element into val.
|
||||
// The chardata contained in the element (but not its children)
|
||||
// is passed to the text unmarshaler.
|
||||
func (p *Decoder) unmarshalTextInterface(val encoding.TextUnmarshaler, start *StartElement) error {
|
||||
var buf []byte
|
||||
depth := 1
|
||||
for depth > 0 {
|
||||
t, err := p.Token()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch t := t.(type) {
|
||||
case CharData:
|
||||
if depth == 1 {
|
||||
buf = append(buf, t...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case StartElement:
|
||||
depth++
|
||||
case EndElement:
|
||||
depth--
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return val.UnmarshalText(buf)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// unmarshalAttr unmarshals a single XML attribute into val.
|
||||
func (p *Decoder) unmarshalAttr(val reflect.Value, attr Attr) error {
|
||||
if val.Kind() == reflect.Ptr {
|
||||
if val.IsNil() {
|
||||
val.Set(reflect.New(val.Type().Elem()))
|
||||
}
|
||||
val = val.Elem()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if val.CanInterface() && val.Type().Implements(unmarshalerAttrType) {
|
||||
// This is an unmarshaler with a non-pointer receiver,
|
||||
// so it's likely to be incorrect, but we do what we're told.
|
||||
return val.Interface().(UnmarshalerAttr).UnmarshalXMLAttr(attr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if val.CanAddr() {
|
||||
pv := val.Addr()
|
||||
if pv.CanInterface() && pv.Type().Implements(unmarshalerAttrType) {
|
||||
return pv.Interface().(UnmarshalerAttr).UnmarshalXMLAttr(attr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Not an UnmarshalerAttr; try encoding.TextUnmarshaler.
|
||||
if val.CanInterface() && val.Type().Implements(textUnmarshalerType) {
|
||||
// This is an unmarshaler with a non-pointer receiver,
|
||||
// so it's likely to be incorrect, but we do what we're told.
|
||||
return val.Interface().(encoding.TextUnmarshaler).UnmarshalText([]byte(attr.Value))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if val.CanAddr() {
|
||||
pv := val.Addr()
|
||||
if pv.CanInterface() && pv.Type().Implements(textUnmarshalerType) {
|
||||
return pv.Interface().(encoding.TextUnmarshaler).UnmarshalText([]byte(attr.Value))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
copyValue(val, []byte(attr.Value))
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
unmarshalerType = reflect.TypeOf((*Unmarshaler)(nil)).Elem()
|
||||
unmarshalerAttrType = reflect.TypeOf((*UnmarshalerAttr)(nil)).Elem()
|
||||
textUnmarshalerType = reflect.TypeOf((*encoding.TextUnmarshaler)(nil)).Elem()
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Unmarshal a single XML element into val.
|
||||
func (p *Decoder) unmarshal(val reflect.Value, start *StartElement) error {
|
||||
// Find start element if we need it.
|
||||
if start == nil {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
tok, err := p.Token()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t, ok := tok.(StartElement); ok {
|
||||
start = &t
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Load value from interface, but only if the result will be
|
||||
// usefully addressable.
|
||||
if val.Kind() == reflect.Interface && !val.IsNil() {
|
||||
e := val.Elem()
|
||||
if e.Kind() == reflect.Ptr && !e.IsNil() {
|
||||
val = e
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if val.Kind() == reflect.Ptr {
|
||||
if val.IsNil() {
|
||||
val.Set(reflect.New(val.Type().Elem()))
|
||||
}
|
||||
val = val.Elem()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if val.CanInterface() && val.Type().Implements(unmarshalerType) {
|
||||
// This is an unmarshaler with a non-pointer receiver,
|
||||
// so it's likely to be incorrect, but we do what we're told.
|
||||
return p.unmarshalInterface(val.Interface().(Unmarshaler), start)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if val.CanAddr() {
|
||||
pv := val.Addr()
|
||||
if pv.CanInterface() && pv.Type().Implements(unmarshalerType) {
|
||||
return p.unmarshalInterface(pv.Interface().(Unmarshaler), start)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if val.CanInterface() && val.Type().Implements(textUnmarshalerType) {
|
||||
return p.unmarshalTextInterface(val.Interface().(encoding.TextUnmarshaler), start)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if val.CanAddr() {
|
||||
pv := val.Addr()
|
||||
if pv.CanInterface() && pv.Type().Implements(textUnmarshalerType) {
|
||||
return p.unmarshalTextInterface(pv.Interface().(encoding.TextUnmarshaler), start)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
data []byte
|
||||
saveData reflect.Value
|
||||
comment []byte
|
||||
saveComment reflect.Value
|
||||
saveXML reflect.Value
|
||||
saveXMLIndex int
|
||||
saveXMLData []byte
|
||||
saveAny reflect.Value
|
||||
sv reflect.Value
|
||||
tinfo *typeInfo
|
||||
err error
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
switch v := val; v.Kind() {
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return errors.New("unknown type " + v.Type().String())
|
||||
|
||||
case reflect.Interface:
|
||||
// TODO: For now, simply ignore the field. In the near
|
||||
// future we may choose to unmarshal the start
|
||||
// element on it, if not nil.
|
||||
return p.Skip()
|
||||
|
||||
case reflect.Slice:
|
||||
typ := v.Type()
|
||||
if typ.Elem().Kind() == reflect.Uint8 {
|
||||
// []byte
|
||||
saveData = v
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Slice of element values.
|
||||
// Grow slice.
|
||||
n := v.Len()
|
||||
if n >= v.Cap() {
|
||||
ncap := 2 * n
|
||||
if ncap < 4 {
|
||||
ncap = 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
new := reflect.MakeSlice(typ, n, ncap)
|
||||
reflect.Copy(new, v)
|
||||
v.Set(new)
|
||||
}
|
||||
v.SetLen(n + 1)
|
||||
|
||||
// Recur to read element into slice.
|
||||
if err := p.unmarshal(v.Index(n), start); err != nil {
|
||||
v.SetLen(n)
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
|
||||
case reflect.Bool, reflect.Float32, reflect.Float64, reflect.Int, reflect.Int8, reflect.Int16, reflect.Int32, reflect.Int64, reflect.Uint, reflect.Uint8, reflect.Uint16, reflect.Uint32, reflect.Uint64, reflect.Uintptr, reflect.String:
|
||||
saveData = v
|
||||
|
||||
case reflect.Struct:
|
||||
typ := v.Type()
|
||||
if typ == nameType {
|
||||
v.Set(reflect.ValueOf(start.Name))
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sv = v
|
||||
tinfo, err = getTypeInfo(typ)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Validate and assign element name.
|
||||
if tinfo.xmlname != nil {
|
||||
finfo := tinfo.xmlname
|
||||
if finfo.name != "" && finfo.name != start.Name.Local {
|
||||
return UnmarshalError("expected element type <" + finfo.name + "> but have <" + start.Name.Local + ">")
|
||||
}
|
||||
if finfo.xmlns != "" && finfo.xmlns != start.Name.Space {
|
||||
e := "expected element <" + finfo.name + "> in name space " + finfo.xmlns + " but have "
|
||||
if start.Name.Space == "" {
|
||||
e += "no name space"
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
e += start.Name.Space
|
||||
}
|
||||
return UnmarshalError(e)
|
||||
}
|
||||
fv := finfo.value(sv)
|
||||
if _, ok := fv.Interface().(Name); ok {
|
||||
fv.Set(reflect.ValueOf(start.Name))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Assign attributes.
|
||||
// Also, determine whether we need to save character data or comments.
|
||||
for i := range tinfo.fields {
|
||||
finfo := &tinfo.fields[i]
|
||||
switch finfo.flags & fMode {
|
||||
case fAttr:
|
||||
strv := finfo.value(sv)
|
||||
// Look for attribute.
|
||||
for _, a := range start.Attr {
|
||||
if a.Name.Local == finfo.name && (finfo.xmlns == "" || finfo.xmlns == a.Name.Space) {
|
||||
if err := p.unmarshalAttr(strv, a); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case fCharData:
|
||||
if !saveData.IsValid() {
|
||||
saveData = finfo.value(sv)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case fComment:
|
||||
if !saveComment.IsValid() {
|
||||
saveComment = finfo.value(sv)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case fAny, fAny | fElement:
|
||||
if !saveAny.IsValid() {
|
||||
saveAny = finfo.value(sv)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case fInnerXml:
|
||||
if !saveXML.IsValid() {
|
||||
saveXML = finfo.value(sv)
|
||||
if p.saved == nil {
|
||||
saveXMLIndex = 0
|
||||
p.saved = new(bytes.Buffer)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
saveXMLIndex = p.savedOffset()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Find end element.
|
||||
// Process sub-elements along the way.
|
||||
Loop:
|
||||
for {
|
||||
var savedOffset int
|
||||
if saveXML.IsValid() {
|
||||
savedOffset = p.savedOffset()
|
||||
}
|
||||
tok, err := p.Token()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch t := tok.(type) {
|
||||
case StartElement:
|
||||
consumed := false
|
||||
if sv.IsValid() {
|
||||
consumed, err = p.unmarshalPath(tinfo, sv, nil, &t)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !consumed && saveAny.IsValid() {
|
||||
consumed = true
|
||||
if err := p.unmarshal(saveAny, &t); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !consumed {
|
||||
if err := p.Skip(); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case EndElement:
|
||||
if saveXML.IsValid() {
|
||||
saveXMLData = p.saved.Bytes()[saveXMLIndex:savedOffset]
|
||||
if saveXMLIndex == 0 {
|
||||
p.saved = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
break Loop
|
||||
|
||||
case CharData:
|
||||
if saveData.IsValid() {
|
||||
data = append(data, t...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case Comment:
|
||||
if saveComment.IsValid() {
|
||||
comment = append(comment, t...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if saveData.IsValid() && saveData.CanInterface() && saveData.Type().Implements(textUnmarshalerType) {
|
||||
if err := saveData.Interface().(encoding.TextUnmarshaler).UnmarshalText(data); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
saveData = reflect.Value{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if saveData.IsValid() && saveData.CanAddr() {
|
||||
pv := saveData.Addr()
|
||||
if pv.CanInterface() && pv.Type().Implements(textUnmarshalerType) {
|
||||
if err := pv.Interface().(encoding.TextUnmarshaler).UnmarshalText(data); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
saveData = reflect.Value{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if err := copyValue(saveData, data); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch t := saveComment; t.Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.String:
|
||||
t.SetString(string(comment))
|
||||
case reflect.Slice:
|
||||
t.Set(reflect.ValueOf(comment))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch t := saveXML; t.Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.String:
|
||||
t.SetString(string(saveXMLData))
|
||||
case reflect.Slice:
|
||||
t.Set(reflect.ValueOf(saveXMLData))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func copyValue(dst reflect.Value, src []byte) (err error) {
|
||||
dst0 := dst
|
||||
|
||||
if dst.Kind() == reflect.Ptr {
|
||||
if dst.IsNil() {
|
||||
dst.Set(reflect.New(dst.Type().Elem()))
|
||||
}
|
||||
dst = dst.Elem()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Save accumulated data.
|
||||
switch dst.Kind() {
|
||||
case reflect.Invalid:
|
||||
// Probably a comment.
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return errors.New("cannot unmarshal into " + dst0.Type().String())
|
||||
case reflect.Int, reflect.Int8, reflect.Int16, reflect.Int32, reflect.Int64:
|
||||
itmp, err := strconv.ParseInt(string(src), 10, dst.Type().Bits())
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
dst.SetInt(itmp)
|
||||
case reflect.Uint, reflect.Uint8, reflect.Uint16, reflect.Uint32, reflect.Uint64, reflect.Uintptr:
|
||||
utmp, err := strconv.ParseUint(string(src), 10, dst.Type().Bits())
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
dst.SetUint(utmp)
|
||||
case reflect.Float32, reflect.Float64:
|
||||
ftmp, err := strconv.ParseFloat(string(src), dst.Type().Bits())
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
dst.SetFloat(ftmp)
|
||||
case reflect.Bool:
|
||||
value, err := strconv.ParseBool(strings.TrimSpace(string(src)))
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
dst.SetBool(value)
|
||||
case reflect.String:
|
||||
dst.SetString(string(src))
|
||||
case reflect.Slice:
|
||||
if len(src) == 0 {
|
||||
// non-nil to flag presence
|
||||
src = []byte{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
dst.SetBytes(src)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// unmarshalPath walks down an XML structure looking for wanted
|
||||
// paths, and calls unmarshal on them.
|
||||
// The consumed result tells whether XML elements have been consumed
|
||||
// from the Decoder until start's matching end element, or if it's
|
||||
// still untouched because start is uninteresting for sv's fields.
|
||||
func (p *Decoder) unmarshalPath(tinfo *typeInfo, sv reflect.Value, parents []string, start *StartElement) (consumed bool, err error) {
|
||||
recurse := false
|
||||
Loop:
|
||||
for i := range tinfo.fields {
|
||||
finfo := &tinfo.fields[i]
|
||||
if finfo.flags&fElement == 0 || len(finfo.parents) < len(parents) || finfo.xmlns != "" && finfo.xmlns != start.Name.Space {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
for j := range parents {
|
||||
if parents[j] != finfo.parents[j] {
|
||||
continue Loop
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(finfo.parents) == len(parents) && finfo.name == start.Name.Local {
|
||||
// It's a perfect match, unmarshal the field.
|
||||
return true, p.unmarshal(finfo.value(sv), start)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(finfo.parents) > len(parents) && finfo.parents[len(parents)] == start.Name.Local {
|
||||
// It's a prefix for the field. Break and recurse
|
||||
// since it's not ok for one field path to be itself
|
||||
// the prefix for another field path.
|
||||
recurse = true
|
||||
|
||||
// We can reuse the same slice as long as we
|
||||
// don't try to append to it.
|
||||
parents = finfo.parents[:len(parents)+1]
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !recurse {
|
||||
// We have no business with this element.
|
||||
return false, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
// The element is not a perfect match for any field, but one
|
||||
// or more fields have the path to this element as a parent
|
||||
// prefix. Recurse and attempt to match these.
|
||||
for {
|
||||
var tok Token
|
||||
tok, err = p.Token()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return true, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch t := tok.(type) {
|
||||
case StartElement:
|
||||
consumed2, err := p.unmarshalPath(tinfo, sv, parents, &t)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return true, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !consumed2 {
|
||||
if err := p.Skip(); err != nil {
|
||||
return true, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
case EndElement:
|
||||
return true, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Skip reads tokens until it has consumed the end element
|
||||
// matching the most recent start element already consumed.
|
||||
// It recurs if it encounters a start element, so it can be used to
|
||||
// skip nested structures.
|
||||
// It returns nil if it finds an end element matching the start
|
||||
// element; otherwise it returns an error describing the problem.
|
||||
func (d *Decoder) Skip() error {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
tok, err := d.Token()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch tok.(type) {
|
||||
case StartElement:
|
||||
if err := d.Skip(); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
case EndElement:
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
371
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/internal/xml/typeinfo.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
371
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/internal/xml/typeinfo.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,371 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2011 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package xml
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"reflect"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// typeInfo holds details for the xml representation of a type.
|
||||
type typeInfo struct {
|
||||
xmlname *fieldInfo
|
||||
fields []fieldInfo
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// fieldInfo holds details for the xml representation of a single field.
|
||||
type fieldInfo struct {
|
||||
idx []int
|
||||
name string
|
||||
xmlns string
|
||||
flags fieldFlags
|
||||
parents []string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type fieldFlags int
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
fElement fieldFlags = 1 << iota
|
||||
fAttr
|
||||
fCharData
|
||||
fInnerXml
|
||||
fComment
|
||||
fAny
|
||||
|
||||
fOmitEmpty
|
||||
|
||||
fMode = fElement | fAttr | fCharData | fInnerXml | fComment | fAny
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var tinfoMap = make(map[reflect.Type]*typeInfo)
|
||||
var tinfoLock sync.RWMutex
|
||||
|
||||
var nameType = reflect.TypeOf(Name{})
|
||||
|
||||
// getTypeInfo returns the typeInfo structure with details necessary
|
||||
// for marshalling and unmarshalling typ.
|
||||
func getTypeInfo(typ reflect.Type) (*typeInfo, error) {
|
||||
tinfoLock.RLock()
|
||||
tinfo, ok := tinfoMap[typ]
|
||||
tinfoLock.RUnlock()
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
return tinfo, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
tinfo = &typeInfo{}
|
||||
if typ.Kind() == reflect.Struct && typ != nameType {
|
||||
n := typ.NumField()
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
|
||||
f := typ.Field(i)
|
||||
if f.PkgPath != "" || f.Tag.Get("xml") == "-" {
|
||||
continue // Private field
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// For embedded structs, embed its fields.
|
||||
if f.Anonymous {
|
||||
t := f.Type
|
||||
if t.Kind() == reflect.Ptr {
|
||||
t = t.Elem()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t.Kind() == reflect.Struct {
|
||||
inner, err := getTypeInfo(t)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if tinfo.xmlname == nil {
|
||||
tinfo.xmlname = inner.xmlname
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, finfo := range inner.fields {
|
||||
finfo.idx = append([]int{i}, finfo.idx...)
|
||||
if err := addFieldInfo(typ, tinfo, &finfo); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
finfo, err := structFieldInfo(typ, &f)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if f.Name == "XMLName" {
|
||||
tinfo.xmlname = finfo
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add the field if it doesn't conflict with other fields.
|
||||
if err := addFieldInfo(typ, tinfo, finfo); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
tinfoLock.Lock()
|
||||
tinfoMap[typ] = tinfo
|
||||
tinfoLock.Unlock()
|
||||
return tinfo, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// structFieldInfo builds and returns a fieldInfo for f.
|
||||
func structFieldInfo(typ reflect.Type, f *reflect.StructField) (*fieldInfo, error) {
|
||||
finfo := &fieldInfo{idx: f.Index}
|
||||
|
||||
// Split the tag from the xml namespace if necessary.
|
||||
tag := f.Tag.Get("xml")
|
||||
if i := strings.Index(tag, " "); i >= 0 {
|
||||
finfo.xmlns, tag = tag[:i], tag[i+1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse flags.
|
||||
tokens := strings.Split(tag, ",")
|
||||
if len(tokens) == 1 {
|
||||
finfo.flags = fElement
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
tag = tokens[0]
|
||||
for _, flag := range tokens[1:] {
|
||||
switch flag {
|
||||
case "attr":
|
||||
finfo.flags |= fAttr
|
||||
case "chardata":
|
||||
finfo.flags |= fCharData
|
||||
case "innerxml":
|
||||
finfo.flags |= fInnerXml
|
||||
case "comment":
|
||||
finfo.flags |= fComment
|
||||
case "any":
|
||||
finfo.flags |= fAny
|
||||
case "omitempty":
|
||||
finfo.flags |= fOmitEmpty
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Validate the flags used.
|
||||
valid := true
|
||||
switch mode := finfo.flags & fMode; mode {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
finfo.flags |= fElement
|
||||
case fAttr, fCharData, fInnerXml, fComment, fAny:
|
||||
if f.Name == "XMLName" || tag != "" && mode != fAttr {
|
||||
valid = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
// This will also catch multiple modes in a single field.
|
||||
valid = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if finfo.flags&fMode == fAny {
|
||||
finfo.flags |= fElement
|
||||
}
|
||||
if finfo.flags&fOmitEmpty != 0 && finfo.flags&(fElement|fAttr) == 0 {
|
||||
valid = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !valid {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("xml: invalid tag in field %s of type %s: %q",
|
||||
f.Name, typ, f.Tag.Get("xml"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Use of xmlns without a name is not allowed.
|
||||
if finfo.xmlns != "" && tag == "" {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("xml: namespace without name in field %s of type %s: %q",
|
||||
f.Name, typ, f.Tag.Get("xml"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if f.Name == "XMLName" {
|
||||
// The XMLName field records the XML element name. Don't
|
||||
// process it as usual because its name should default to
|
||||
// empty rather than to the field name.
|
||||
finfo.name = tag
|
||||
return finfo, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if tag == "" {
|
||||
// If the name part of the tag is completely empty, get
|
||||
// default from XMLName of underlying struct if feasible,
|
||||
// or field name otherwise.
|
||||
if xmlname := lookupXMLName(f.Type); xmlname != nil {
|
||||
finfo.xmlns, finfo.name = xmlname.xmlns, xmlname.name
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
finfo.name = f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
return finfo, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if finfo.xmlns == "" && finfo.flags&fAttr == 0 {
|
||||
// If it's an element no namespace specified, get the default
|
||||
// from the XMLName of enclosing struct if possible.
|
||||
if xmlname := lookupXMLName(typ); xmlname != nil {
|
||||
finfo.xmlns = xmlname.xmlns
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Prepare field name and parents.
|
||||
parents := strings.Split(tag, ">")
|
||||
if parents[0] == "" {
|
||||
parents[0] = f.Name
|
||||
}
|
||||
if parents[len(parents)-1] == "" {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("xml: trailing '>' in field %s of type %s", f.Name, typ)
|
||||
}
|
||||
finfo.name = parents[len(parents)-1]
|
||||
if len(parents) > 1 {
|
||||
if (finfo.flags & fElement) == 0 {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("xml: %s chain not valid with %s flag", tag, strings.Join(tokens[1:], ","))
|
||||
}
|
||||
finfo.parents = parents[:len(parents)-1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If the field type has an XMLName field, the names must match
|
||||
// so that the behavior of both marshalling and unmarshalling
|
||||
// is straightforward and unambiguous.
|
||||
if finfo.flags&fElement != 0 {
|
||||
ftyp := f.Type
|
||||
xmlname := lookupXMLName(ftyp)
|
||||
if xmlname != nil && xmlname.name != finfo.name {
|
||||
return nil, fmt.Errorf("xml: name %q in tag of %s.%s conflicts with name %q in %s.XMLName",
|
||||
finfo.name, typ, f.Name, xmlname.name, ftyp)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return finfo, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lookupXMLName returns the fieldInfo for typ's XMLName field
|
||||
// in case it exists and has a valid xml field tag, otherwise
|
||||
// it returns nil.
|
||||
func lookupXMLName(typ reflect.Type) (xmlname *fieldInfo) {
|
||||
for typ.Kind() == reflect.Ptr {
|
||||
typ = typ.Elem()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if typ.Kind() != reflect.Struct {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i, n := 0, typ.NumField(); i < n; i++ {
|
||||
f := typ.Field(i)
|
||||
if f.Name != "XMLName" {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
finfo, err := structFieldInfo(typ, &f)
|
||||
if finfo.name != "" && err == nil {
|
||||
return finfo
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Also consider errors as a non-existent field tag
|
||||
// and let getTypeInfo itself report the error.
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func min(a, b int) int {
|
||||
if a <= b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// addFieldInfo adds finfo to tinfo.fields if there are no
|
||||
// conflicts, or if conflicts arise from previous fields that were
|
||||
// obtained from deeper embedded structures than finfo. In the latter
|
||||
// case, the conflicting entries are dropped.
|
||||
// A conflict occurs when the path (parent + name) to a field is
|
||||
// itself a prefix of another path, or when two paths match exactly.
|
||||
// It is okay for field paths to share a common, shorter prefix.
|
||||
func addFieldInfo(typ reflect.Type, tinfo *typeInfo, newf *fieldInfo) error {
|
||||
var conflicts []int
|
||||
Loop:
|
||||
// First, figure all conflicts. Most working code will have none.
|
||||
for i := range tinfo.fields {
|
||||
oldf := &tinfo.fields[i]
|
||||
if oldf.flags&fMode != newf.flags&fMode {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if oldf.xmlns != "" && newf.xmlns != "" && oldf.xmlns != newf.xmlns {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
minl := min(len(newf.parents), len(oldf.parents))
|
||||
for p := 0; p < minl; p++ {
|
||||
if oldf.parents[p] != newf.parents[p] {
|
||||
continue Loop
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(oldf.parents) > len(newf.parents) {
|
||||
if oldf.parents[len(newf.parents)] == newf.name {
|
||||
conflicts = append(conflicts, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if len(oldf.parents) < len(newf.parents) {
|
||||
if newf.parents[len(oldf.parents)] == oldf.name {
|
||||
conflicts = append(conflicts, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if newf.name == oldf.name {
|
||||
conflicts = append(conflicts, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Without conflicts, add the new field and return.
|
||||
if conflicts == nil {
|
||||
tinfo.fields = append(tinfo.fields, *newf)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If any conflict is shallower, ignore the new field.
|
||||
// This matches the Go field resolution on embedding.
|
||||
for _, i := range conflicts {
|
||||
if len(tinfo.fields[i].idx) < len(newf.idx) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, if any of them is at the same depth level, it's an error.
|
||||
for _, i := range conflicts {
|
||||
oldf := &tinfo.fields[i]
|
||||
if len(oldf.idx) == len(newf.idx) {
|
||||
f1 := typ.FieldByIndex(oldf.idx)
|
||||
f2 := typ.FieldByIndex(newf.idx)
|
||||
return &TagPathError{typ, f1.Name, f1.Tag.Get("xml"), f2.Name, f2.Tag.Get("xml")}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, the new field is shallower, and thus takes precedence,
|
||||
// so drop the conflicting fields from tinfo and append the new one.
|
||||
for c := len(conflicts) - 1; c >= 0; c-- {
|
||||
i := conflicts[c]
|
||||
copy(tinfo.fields[i:], tinfo.fields[i+1:])
|
||||
tinfo.fields = tinfo.fields[:len(tinfo.fields)-1]
|
||||
}
|
||||
tinfo.fields = append(tinfo.fields, *newf)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// A TagPathError represents an error in the unmarshalling process
|
||||
// caused by the use of field tags with conflicting paths.
|
||||
type TagPathError struct {
|
||||
Struct reflect.Type
|
||||
Field1, Tag1 string
|
||||
Field2, Tag2 string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (e *TagPathError) Error() string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%s field %q with tag %q conflicts with field %q with tag %q", e.Struct, e.Field1, e.Tag1, e.Field2, e.Tag2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// value returns v's field value corresponding to finfo.
|
||||
// It's equivalent to v.FieldByIndex(finfo.idx), but initializes
|
||||
// and dereferences pointers as necessary.
|
||||
func (finfo *fieldInfo) value(v reflect.Value) reflect.Value {
|
||||
for i, x := range finfo.idx {
|
||||
if i > 0 {
|
||||
t := v.Type()
|
||||
if t.Kind() == reflect.Ptr && t.Elem().Kind() == reflect.Struct {
|
||||
if v.IsNil() {
|
||||
v.Set(reflect.New(v.Type().Elem()))
|
||||
}
|
||||
v = v.Elem()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
v = v.Field(x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
1998
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/internal/xml/xml.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
1998
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/internal/xml/xml.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
94
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/litmus_test_server.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
94
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/litmus_test_server.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// +build ignore
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
This program is a server for the WebDAV 'litmus' compliance test at
|
||||
http://www.webdav.org/neon/litmus/
|
||||
To run the test:
|
||||
|
||||
go run litmus_test_server.go
|
||||
|
||||
and separately, from the downloaded litmus-xxx directory:
|
||||
|
||||
make URL=http://localhost:9999/ check
|
||||
*/
|
||||
package main
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"flag"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"net/url"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/net/webdav"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var port = flag.Int("port", 9999, "server port")
|
||||
|
||||
func main() {
|
||||
flag.Parse()
|
||||
log.SetFlags(0)
|
||||
h := &webdav.Handler{
|
||||
FileSystem: webdav.NewMemFS(),
|
||||
LockSystem: webdav.NewMemLS(),
|
||||
Logger: func(r *http.Request, err error) {
|
||||
litmus := r.Header.Get("X-Litmus")
|
||||
if len(litmus) > 19 {
|
||||
litmus = litmus[:16] + "..."
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch r.Method {
|
||||
case "COPY", "MOVE":
|
||||
dst := ""
|
||||
if u, err := url.Parse(r.Header.Get("Destination")); err == nil {
|
||||
dst = u.Path
|
||||
}
|
||||
o := r.Header.Get("Overwrite")
|
||||
log.Printf("%-20s%-10s%-30s%-30so=%-2s%v", litmus, r.Method, r.URL.Path, dst, o, err)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
log.Printf("%-20s%-10s%-30s%v", litmus, r.Method, r.URL.Path, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// The next line would normally be:
|
||||
// http.Handle("/", h)
|
||||
// but we wrap that HTTP handler h to cater for a special case.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The propfind_invalid2 litmus test case expects an empty namespace prefix
|
||||
// declaration to be an error. The FAQ in the webdav litmus test says:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// "What does the "propfind_invalid2" test check for?...
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If a request was sent with an XML body which included an empty namespace
|
||||
// prefix declaration (xmlns:ns1=""), then the server must reject that with
|
||||
// a "400 Bad Request" response, as it is invalid according to the XML
|
||||
// Namespace specification."
|
||||
//
|
||||
// On the other hand, the Go standard library's encoding/xml package
|
||||
// accepts an empty xmlns namespace, as per the discussion at
|
||||
// https://github.com/golang/go/issues/8068
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Empty namespaces seem disallowed in the second (2006) edition of the XML
|
||||
// standard, but allowed in a later edition. The grammar differs between
|
||||
// http://www.w3.org/TR/2006/REC-xml-names-20060816/#ns-decl and
|
||||
// http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml-names/#dt-prefix
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Thus, we assume that the propfind_invalid2 test is obsolete, and
|
||||
// hard-code the 400 Bad Request response that the test expects.
|
||||
http.Handle("/", http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
|
||||
if r.Header.Get("X-Litmus") == "props: 3 (propfind_invalid2)" {
|
||||
http.Error(w, "400 Bad Request", http.StatusBadRequest)
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
h.ServeHTTP(w, r)
|
||||
}))
|
||||
|
||||
addr := fmt.Sprintf(":%d", *port)
|
||||
log.Printf("Serving %v", addr)
|
||||
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(addr, nil))
|
||||
}
|
||||
445
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/lock.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
445
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/lock.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,445 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2014 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package webdav
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"container/heap"
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
// ErrConfirmationFailed is returned by a LockSystem's Confirm method.
|
||||
ErrConfirmationFailed = errors.New("webdav: confirmation failed")
|
||||
// ErrForbidden is returned by a LockSystem's Unlock method.
|
||||
ErrForbidden = errors.New("webdav: forbidden")
|
||||
// ErrLocked is returned by a LockSystem's Create, Refresh and Unlock methods.
|
||||
ErrLocked = errors.New("webdav: locked")
|
||||
// ErrNoSuchLock is returned by a LockSystem's Refresh and Unlock methods.
|
||||
ErrNoSuchLock = errors.New("webdav: no such lock")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Condition can match a WebDAV resource, based on a token or ETag.
|
||||
// Exactly one of Token and ETag should be non-empty.
|
||||
type Condition struct {
|
||||
Not bool
|
||||
Token string
|
||||
ETag string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LockSystem manages access to a collection of named resources. The elements
|
||||
// in a lock name are separated by slash ('/', U+002F) characters, regardless
|
||||
// of host operating system convention.
|
||||
type LockSystem interface {
|
||||
// Confirm confirms that the caller can claim all of the locks specified by
|
||||
// the given conditions, and that holding the union of all of those locks
|
||||
// gives exclusive access to all of the named resources. Up to two resources
|
||||
// can be named. Empty names are ignored.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Exactly one of release and err will be non-nil. If release is non-nil,
|
||||
// all of the requested locks are held until release is called. Calling
|
||||
// release does not unlock the lock, in the WebDAV UNLOCK sense, but once
|
||||
// Confirm has confirmed that a lock claim is valid, that lock cannot be
|
||||
// Confirmed again until it has been released.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If Confirm returns ErrConfirmationFailed then the Handler will continue
|
||||
// to try any other set of locks presented (a WebDAV HTTP request can
|
||||
// present more than one set of locks). If it returns any other non-nil
|
||||
// error, the Handler will write a "500 Internal Server Error" HTTP status.
|
||||
Confirm(now time.Time, name0, name1 string, conditions ...Condition) (release func(), err error)
|
||||
|
||||
// Create creates a lock with the given depth, duration, owner and root
|
||||
// (name). The depth will either be negative (meaning infinite) or zero.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If Create returns ErrLocked then the Handler will write a "423 Locked"
|
||||
// HTTP status. If it returns any other non-nil error, the Handler will
|
||||
// write a "500 Internal Server Error" HTTP status.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#rfc.section.9.10.6 for
|
||||
// when to use each error.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The token returned identifies the created lock. It should be an absolute
|
||||
// URI as defined by RFC 3986, Section 4.3. In particular, it should not
|
||||
// contain whitespace.
|
||||
Create(now time.Time, details LockDetails) (token string, err error)
|
||||
|
||||
// Refresh refreshes the lock with the given token.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If Refresh returns ErrLocked then the Handler will write a "423 Locked"
|
||||
// HTTP Status. If Refresh returns ErrNoSuchLock then the Handler will write
|
||||
// a "412 Precondition Failed" HTTP Status. If it returns any other non-nil
|
||||
// error, the Handler will write a "500 Internal Server Error" HTTP status.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#rfc.section.9.10.6 for
|
||||
// when to use each error.
|
||||
Refresh(now time.Time, token string, duration time.Duration) (LockDetails, error)
|
||||
|
||||
// Unlock unlocks the lock with the given token.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If Unlock returns ErrForbidden then the Handler will write a "403
|
||||
// Forbidden" HTTP Status. If Unlock returns ErrLocked then the Handler
|
||||
// will write a "423 Locked" HTTP status. If Unlock returns ErrNoSuchLock
|
||||
// then the Handler will write a "409 Conflict" HTTP Status. If it returns
|
||||
// any other non-nil error, the Handler will write a "500 Internal Server
|
||||
// Error" HTTP status.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#rfc.section.9.11.1 for
|
||||
// when to use each error.
|
||||
Unlock(now time.Time, token string) error
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LockDetails are a lock's metadata.
|
||||
type LockDetails struct {
|
||||
// Root is the root resource name being locked. For a zero-depth lock, the
|
||||
// root is the only resource being locked.
|
||||
Root string
|
||||
// Duration is the lock timeout. A negative duration means infinite.
|
||||
Duration time.Duration
|
||||
// OwnerXML is the verbatim <owner> XML given in a LOCK HTTP request.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// TODO: does the "verbatim" nature play well with XML namespaces?
|
||||
// Does the OwnerXML field need to have more structure? See
|
||||
// https://codereview.appspot.com/175140043/#msg2
|
||||
OwnerXML string
|
||||
// ZeroDepth is whether the lock has zero depth. If it does not have zero
|
||||
// depth, it has infinite depth.
|
||||
ZeroDepth bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewMemLS returns a new in-memory LockSystem.
|
||||
func NewMemLS() LockSystem {
|
||||
return &memLS{
|
||||
byName: make(map[string]*memLSNode),
|
||||
byToken: make(map[string]*memLSNode),
|
||||
gen: uint64(time.Now().Unix()),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type memLS struct {
|
||||
mu sync.Mutex
|
||||
byName map[string]*memLSNode
|
||||
byToken map[string]*memLSNode
|
||||
gen uint64
|
||||
// byExpiry only contains those nodes whose LockDetails have a finite
|
||||
// Duration and are yet to expire.
|
||||
byExpiry byExpiry
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *memLS) nextToken() string {
|
||||
m.gen++
|
||||
return strconv.FormatUint(m.gen, 10)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *memLS) collectExpiredNodes(now time.Time) {
|
||||
for len(m.byExpiry) > 0 {
|
||||
if now.Before(m.byExpiry[0].expiry) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
m.remove(m.byExpiry[0])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *memLS) Confirm(now time.Time, name0, name1 string, conditions ...Condition) (func(), error) {
|
||||
m.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer m.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
m.collectExpiredNodes(now)
|
||||
|
||||
var n0, n1 *memLSNode
|
||||
if name0 != "" {
|
||||
if n0 = m.lookup(slashClean(name0), conditions...); n0 == nil {
|
||||
return nil, ErrConfirmationFailed
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if name1 != "" {
|
||||
if n1 = m.lookup(slashClean(name1), conditions...); n1 == nil {
|
||||
return nil, ErrConfirmationFailed
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Don't hold the same node twice.
|
||||
if n1 == n0 {
|
||||
n1 = nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if n0 != nil {
|
||||
m.hold(n0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n1 != nil {
|
||||
m.hold(n1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return func() {
|
||||
m.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer m.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
if n1 != nil {
|
||||
m.unhold(n1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n0 != nil {
|
||||
m.unhold(n0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// lookup returns the node n that locks the named resource, provided that n
|
||||
// matches at least one of the given conditions and that lock isn't held by
|
||||
// another party. Otherwise, it returns nil.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// n may be a parent of the named resource, if n is an infinite depth lock.
|
||||
func (m *memLS) lookup(name string, conditions ...Condition) (n *memLSNode) {
|
||||
// TODO: support Condition.Not and Condition.ETag.
|
||||
for _, c := range conditions {
|
||||
n = m.byToken[c.Token]
|
||||
if n == nil || n.held {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if name == n.details.Root {
|
||||
return n
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n.details.ZeroDepth {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n.details.Root == "/" || strings.HasPrefix(name, n.details.Root+"/") {
|
||||
return n
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *memLS) hold(n *memLSNode) {
|
||||
if n.held {
|
||||
panic("webdav: memLS inconsistent held state")
|
||||
}
|
||||
n.held = true
|
||||
if n.details.Duration >= 0 && n.byExpiryIndex >= 0 {
|
||||
heap.Remove(&m.byExpiry, n.byExpiryIndex)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *memLS) unhold(n *memLSNode) {
|
||||
if !n.held {
|
||||
panic("webdav: memLS inconsistent held state")
|
||||
}
|
||||
n.held = false
|
||||
if n.details.Duration >= 0 {
|
||||
heap.Push(&m.byExpiry, n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *memLS) Create(now time.Time, details LockDetails) (string, error) {
|
||||
m.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer m.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
m.collectExpiredNodes(now)
|
||||
details.Root = slashClean(details.Root)
|
||||
|
||||
if !m.canCreate(details.Root, details.ZeroDepth) {
|
||||
return "", ErrLocked
|
||||
}
|
||||
n := m.create(details.Root)
|
||||
n.token = m.nextToken()
|
||||
m.byToken[n.token] = n
|
||||
n.details = details
|
||||
if n.details.Duration >= 0 {
|
||||
n.expiry = now.Add(n.details.Duration)
|
||||
heap.Push(&m.byExpiry, n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n.token, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *memLS) Refresh(now time.Time, token string, duration time.Duration) (LockDetails, error) {
|
||||
m.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer m.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
m.collectExpiredNodes(now)
|
||||
|
||||
n := m.byToken[token]
|
||||
if n == nil {
|
||||
return LockDetails{}, ErrNoSuchLock
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n.held {
|
||||
return LockDetails{}, ErrLocked
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n.byExpiryIndex >= 0 {
|
||||
heap.Remove(&m.byExpiry, n.byExpiryIndex)
|
||||
}
|
||||
n.details.Duration = duration
|
||||
if n.details.Duration >= 0 {
|
||||
n.expiry = now.Add(n.details.Duration)
|
||||
heap.Push(&m.byExpiry, n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n.details, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *memLS) Unlock(now time.Time, token string) error {
|
||||
m.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer m.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
m.collectExpiredNodes(now)
|
||||
|
||||
n := m.byToken[token]
|
||||
if n == nil {
|
||||
return ErrNoSuchLock
|
||||
}
|
||||
if n.held {
|
||||
return ErrLocked
|
||||
}
|
||||
m.remove(n)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *memLS) canCreate(name string, zeroDepth bool) bool {
|
||||
return walkToRoot(name, func(name0 string, first bool) bool {
|
||||
n := m.byName[name0]
|
||||
if n == nil {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
if first {
|
||||
if n.token != "" {
|
||||
// The target node is already locked.
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !zeroDepth {
|
||||
// The requested lock depth is infinite, and the fact that n exists
|
||||
// (n != nil) means that a descendent of the target node is locked.
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if n.token != "" && !n.details.ZeroDepth {
|
||||
// An ancestor of the target node is locked with infinite depth.
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *memLS) create(name string) (ret *memLSNode) {
|
||||
walkToRoot(name, func(name0 string, first bool) bool {
|
||||
n := m.byName[name0]
|
||||
if n == nil {
|
||||
n = &memLSNode{
|
||||
details: LockDetails{
|
||||
Root: name0,
|
||||
},
|
||||
byExpiryIndex: -1,
|
||||
}
|
||||
m.byName[name0] = n
|
||||
}
|
||||
n.refCount++
|
||||
if first {
|
||||
ret = n
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
})
|
||||
return ret
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (m *memLS) remove(n *memLSNode) {
|
||||
delete(m.byToken, n.token)
|
||||
n.token = ""
|
||||
walkToRoot(n.details.Root, func(name0 string, first bool) bool {
|
||||
x := m.byName[name0]
|
||||
x.refCount--
|
||||
if x.refCount == 0 {
|
||||
delete(m.byName, name0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
})
|
||||
if n.byExpiryIndex >= 0 {
|
||||
heap.Remove(&m.byExpiry, n.byExpiryIndex)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func walkToRoot(name string, f func(name0 string, first bool) bool) bool {
|
||||
for first := true; ; first = false {
|
||||
if !f(name, first) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
if name == "/" {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
name = name[:strings.LastIndex(name, "/")]
|
||||
if name == "" {
|
||||
name = "/"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type memLSNode struct {
|
||||
// details are the lock metadata. Even if this node's name is not explicitly locked,
|
||||
// details.Root will still equal the node's name.
|
||||
details LockDetails
|
||||
// token is the unique identifier for this node's lock. An empty token means that
|
||||
// this node is not explicitly locked.
|
||||
token string
|
||||
// refCount is the number of self-or-descendent nodes that are explicitly locked.
|
||||
refCount int
|
||||
// expiry is when this node's lock expires.
|
||||
expiry time.Time
|
||||
// byExpiryIndex is the index of this node in memLS.byExpiry. It is -1
|
||||
// if this node does not expire, or has expired.
|
||||
byExpiryIndex int
|
||||
// held is whether this node's lock is actively held by a Confirm call.
|
||||
held bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type byExpiry []*memLSNode
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *byExpiry) Len() int {
|
||||
return len(*b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *byExpiry) Less(i, j int) bool {
|
||||
return (*b)[i].expiry.Before((*b)[j].expiry)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *byExpiry) Swap(i, j int) {
|
||||
(*b)[i], (*b)[j] = (*b)[j], (*b)[i]
|
||||
(*b)[i].byExpiryIndex = i
|
||||
(*b)[j].byExpiryIndex = j
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *byExpiry) Push(x interface{}) {
|
||||
n := x.(*memLSNode)
|
||||
n.byExpiryIndex = len(*b)
|
||||
*b = append(*b, n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (b *byExpiry) Pop() interface{} {
|
||||
i := len(*b) - 1
|
||||
n := (*b)[i]
|
||||
(*b)[i] = nil
|
||||
n.byExpiryIndex = -1
|
||||
*b = (*b)[:i]
|
||||
return n
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const infiniteTimeout = -1
|
||||
|
||||
// parseTimeout parses the Timeout HTTP header, as per section 10.7. If s is
|
||||
// empty, an infiniteTimeout is returned.
|
||||
func parseTimeout(s string) (time.Duration, error) {
|
||||
if s == "" {
|
||||
return infiniteTimeout, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i := strings.IndexByte(s, ','); i >= 0 {
|
||||
s = s[:i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
s = strings.TrimSpace(s)
|
||||
if s == "Infinite" {
|
||||
return infiniteTimeout, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
const pre = "Second-"
|
||||
if !strings.HasPrefix(s, pre) {
|
||||
return 0, errInvalidTimeout
|
||||
}
|
||||
s = s[len(pre):]
|
||||
if s == "" || s[0] < '0' || '9' < s[0] {
|
||||
return 0, errInvalidTimeout
|
||||
}
|
||||
n, err := strconv.ParseInt(s, 10, 64)
|
||||
if err != nil || 1<<32-1 < n {
|
||||
return 0, errInvalidTimeout
|
||||
}
|
||||
return time.Duration(n) * time.Second, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
470
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/prop.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
470
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/prop.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,470 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2015 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package webdav
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"encoding/xml"
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"mime"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path/filepath"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/net/context"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Proppatch describes a property update instruction as defined in RFC 4918.
|
||||
// See http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#METHOD_PROPPATCH
|
||||
type Proppatch struct {
|
||||
// Remove specifies whether this patch removes properties. If it does not
|
||||
// remove them, it sets them.
|
||||
Remove bool
|
||||
// Props contains the properties to be set or removed.
|
||||
Props []Property
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Propstat describes a XML propstat element as defined in RFC 4918.
|
||||
// See http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#ELEMENT_propstat
|
||||
type Propstat struct {
|
||||
// Props contains the properties for which Status applies.
|
||||
Props []Property
|
||||
|
||||
// Status defines the HTTP status code of the properties in Prop.
|
||||
// Allowed values include, but are not limited to the WebDAV status
|
||||
// code extensions for HTTP/1.1.
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#status.code.extensions.to.http11
|
||||
Status int
|
||||
|
||||
// XMLError contains the XML representation of the optional error element.
|
||||
// XML content within this field must not rely on any predefined
|
||||
// namespace declarations or prefixes. If empty, the XML error element
|
||||
// is omitted.
|
||||
XMLError string
|
||||
|
||||
// ResponseDescription contains the contents of the optional
|
||||
// responsedescription field. If empty, the XML element is omitted.
|
||||
ResponseDescription string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// makePropstats returns a slice containing those of x and y whose Props slice
|
||||
// is non-empty. If both are empty, it returns a slice containing an otherwise
|
||||
// zero Propstat whose HTTP status code is 200 OK.
|
||||
func makePropstats(x, y Propstat) []Propstat {
|
||||
pstats := make([]Propstat, 0, 2)
|
||||
if len(x.Props) != 0 {
|
||||
pstats = append(pstats, x)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(y.Props) != 0 {
|
||||
pstats = append(pstats, y)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(pstats) == 0 {
|
||||
pstats = append(pstats, Propstat{
|
||||
Status: http.StatusOK,
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
return pstats
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DeadPropsHolder holds the dead properties of a resource.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Dead properties are those properties that are explicitly defined. In
|
||||
// comparison, live properties, such as DAV:getcontentlength, are implicitly
|
||||
// defined by the underlying resource, and cannot be explicitly overridden or
|
||||
// removed. See the Terminology section of
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#rfc.section.3
|
||||
//
|
||||
// There is a whitelist of the names of live properties. This package handles
|
||||
// all live properties, and will only pass non-whitelisted names to the Patch
|
||||
// method of DeadPropsHolder implementations.
|
||||
type DeadPropsHolder interface {
|
||||
// DeadProps returns a copy of the dead properties held.
|
||||
DeadProps() (map[xml.Name]Property, error)
|
||||
|
||||
// Patch patches the dead properties held.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Patching is atomic; either all or no patches succeed. It returns (nil,
|
||||
// non-nil) if an internal server error occurred, otherwise the Propstats
|
||||
// collectively contain one Property for each proposed patch Property. If
|
||||
// all patches succeed, Patch returns a slice of length one and a Propstat
|
||||
// element with a 200 OK HTTP status code. If none succeed, for reasons
|
||||
// other than an internal server error, no Propstat has status 200 OK.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For more details on when various HTTP status codes apply, see
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#PROPPATCH-status
|
||||
Patch([]Proppatch) ([]Propstat, error)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// liveProps contains all supported, protected DAV: properties.
|
||||
var liveProps = map[xml.Name]struct {
|
||||
// findFn implements the propfind function of this property. If nil,
|
||||
// it indicates a hidden property.
|
||||
findFn func(context.Context, FileSystem, LockSystem, string, os.FileInfo) (string, error)
|
||||
// dir is true if the property applies to directories.
|
||||
dir bool
|
||||
}{
|
||||
{Space: "DAV:", Local: "resourcetype"}: {
|
||||
findFn: findResourceType,
|
||||
dir: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
{Space: "DAV:", Local: "displayname"}: {
|
||||
findFn: findDisplayName,
|
||||
dir: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
{Space: "DAV:", Local: "getcontentlength"}: {
|
||||
findFn: findContentLength,
|
||||
dir: false,
|
||||
},
|
||||
{Space: "DAV:", Local: "getlastmodified"}: {
|
||||
findFn: findLastModified,
|
||||
// http://webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#PROPERTY_getlastmodified
|
||||
// suggests that getlastmodified should only apply to GETable
|
||||
// resources, and this package does not support GET on directories.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Nonetheless, some WebDAV clients expect child directories to be
|
||||
// sortable by getlastmodified date, so this value is true, not false.
|
||||
// See golang.org/issue/15334.
|
||||
dir: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
{Space: "DAV:", Local: "creationdate"}: {
|
||||
findFn: nil,
|
||||
dir: false,
|
||||
},
|
||||
{Space: "DAV:", Local: "getcontentlanguage"}: {
|
||||
findFn: nil,
|
||||
dir: false,
|
||||
},
|
||||
{Space: "DAV:", Local: "getcontenttype"}: {
|
||||
findFn: findContentType,
|
||||
dir: false,
|
||||
},
|
||||
{Space: "DAV:", Local: "getetag"}: {
|
||||
findFn: findETag,
|
||||
// findETag implements ETag as the concatenated hex values of a file's
|
||||
// modification time and size. This is not a reliable synchronization
|
||||
// mechanism for directories, so we do not advertise getetag for DAV
|
||||
// collections.
|
||||
dir: false,
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: The lockdiscovery property requires LockSystem to list the
|
||||
// active locks on a resource.
|
||||
{Space: "DAV:", Local: "lockdiscovery"}: {},
|
||||
{Space: "DAV:", Local: "supportedlock"}: {
|
||||
findFn: findSupportedLock,
|
||||
dir: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO(nigeltao) merge props and allprop?
|
||||
|
||||
// Props returns the status of the properties named pnames for resource name.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Each Propstat has a unique status and each property name will only be part
|
||||
// of one Propstat element.
|
||||
func props(ctx context.Context, fs FileSystem, ls LockSystem, name string, pnames []xml.Name) ([]Propstat, error) {
|
||||
f, err := fs.OpenFile(ctx, name, os.O_RDONLY, 0)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
fi, err := f.Stat()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
isDir := fi.IsDir()
|
||||
|
||||
var deadProps map[xml.Name]Property
|
||||
if dph, ok := f.(DeadPropsHolder); ok {
|
||||
deadProps, err = dph.DeadProps()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pstatOK := Propstat{Status: http.StatusOK}
|
||||
pstatNotFound := Propstat{Status: http.StatusNotFound}
|
||||
for _, pn := range pnames {
|
||||
// If this file has dead properties, check if they contain pn.
|
||||
if dp, ok := deadProps[pn]; ok {
|
||||
pstatOK.Props = append(pstatOK.Props, dp)
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Otherwise, it must either be a live property or we don't know it.
|
||||
if prop := liveProps[pn]; prop.findFn != nil && (prop.dir || !isDir) {
|
||||
innerXML, err := prop.findFn(ctx, fs, ls, name, fi)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
pstatOK.Props = append(pstatOK.Props, Property{
|
||||
XMLName: pn,
|
||||
InnerXML: []byte(innerXML),
|
||||
})
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
pstatNotFound.Props = append(pstatNotFound.Props, Property{
|
||||
XMLName: pn,
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return makePropstats(pstatOK, pstatNotFound), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Propnames returns the property names defined for resource name.
|
||||
func propnames(ctx context.Context, fs FileSystem, ls LockSystem, name string) ([]xml.Name, error) {
|
||||
f, err := fs.OpenFile(ctx, name, os.O_RDONLY, 0)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
fi, err := f.Stat()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
isDir := fi.IsDir()
|
||||
|
||||
var deadProps map[xml.Name]Property
|
||||
if dph, ok := f.(DeadPropsHolder); ok {
|
||||
deadProps, err = dph.DeadProps()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pnames := make([]xml.Name, 0, len(liveProps)+len(deadProps))
|
||||
for pn, prop := range liveProps {
|
||||
if prop.findFn != nil && (prop.dir || !isDir) {
|
||||
pnames = append(pnames, pn)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
for pn := range deadProps {
|
||||
pnames = append(pnames, pn)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return pnames, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Allprop returns the properties defined for resource name and the properties
|
||||
// named in include.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that RFC 4918 defines 'allprop' to return the DAV: properties defined
|
||||
// within the RFC plus dead properties. Other live properties should only be
|
||||
// returned if they are named in 'include'.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#METHOD_PROPFIND
|
||||
func allprop(ctx context.Context, fs FileSystem, ls LockSystem, name string, include []xml.Name) ([]Propstat, error) {
|
||||
pnames, err := propnames(ctx, fs, ls, name)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Add names from include if they are not already covered in pnames.
|
||||
nameset := make(map[xml.Name]bool)
|
||||
for _, pn := range pnames {
|
||||
nameset[pn] = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, pn := range include {
|
||||
if !nameset[pn] {
|
||||
pnames = append(pnames, pn)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return props(ctx, fs, ls, name, pnames)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Patch patches the properties of resource name. The return values are
|
||||
// constrained in the same manner as DeadPropsHolder.Patch.
|
||||
func patch(ctx context.Context, fs FileSystem, ls LockSystem, name string, patches []Proppatch) ([]Propstat, error) {
|
||||
conflict := false
|
||||
loop:
|
||||
for _, patch := range patches {
|
||||
for _, p := range patch.Props {
|
||||
if _, ok := liveProps[p.XMLName]; ok {
|
||||
conflict = true
|
||||
break loop
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if conflict {
|
||||
pstatForbidden := Propstat{
|
||||
Status: http.StatusForbidden,
|
||||
XMLError: `<D:cannot-modify-protected-property xmlns:D="DAV:"/>`,
|
||||
}
|
||||
pstatFailedDep := Propstat{
|
||||
Status: StatusFailedDependency,
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, patch := range patches {
|
||||
for _, p := range patch.Props {
|
||||
if _, ok := liveProps[p.XMLName]; ok {
|
||||
pstatForbidden.Props = append(pstatForbidden.Props, Property{XMLName: p.XMLName})
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
pstatFailedDep.Props = append(pstatFailedDep.Props, Property{XMLName: p.XMLName})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return makePropstats(pstatForbidden, pstatFailedDep), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
f, err := fs.OpenFile(ctx, name, os.O_RDWR, 0)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
if dph, ok := f.(DeadPropsHolder); ok {
|
||||
ret, err := dph.Patch(patches)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#ELEMENT_propstat says that
|
||||
// "The contents of the prop XML element must only list the names of
|
||||
// properties to which the result in the status element applies."
|
||||
for _, pstat := range ret {
|
||||
for i, p := range pstat.Props {
|
||||
pstat.Props[i] = Property{XMLName: p.XMLName}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ret, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
// The file doesn't implement the optional DeadPropsHolder interface, so
|
||||
// all patches are forbidden.
|
||||
pstat := Propstat{Status: http.StatusForbidden}
|
||||
for _, patch := range patches {
|
||||
for _, p := range patch.Props {
|
||||
pstat.Props = append(pstat.Props, Property{XMLName: p.XMLName})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return []Propstat{pstat}, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func escapeXML(s string) string {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
|
||||
// As an optimization, if s contains only ASCII letters, digits or a
|
||||
// few special characters, the escaped value is s itself and we don't
|
||||
// need to allocate a buffer and convert between string and []byte.
|
||||
switch c := s[i]; {
|
||||
case c == ' ' || c == '_' ||
|
||||
('+' <= c && c <= '9') || // Digits as well as + , - . and /
|
||||
('A' <= c && c <= 'Z') ||
|
||||
('a' <= c && c <= 'z'):
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Otherwise, go through the full escaping process.
|
||||
var buf bytes.Buffer
|
||||
xml.EscapeText(&buf, []byte(s))
|
||||
return buf.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func findResourceType(ctx context.Context, fs FileSystem, ls LockSystem, name string, fi os.FileInfo) (string, error) {
|
||||
if fi.IsDir() {
|
||||
return `<D:collection xmlns:D="DAV:"/>`, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "", nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func findDisplayName(ctx context.Context, fs FileSystem, ls LockSystem, name string, fi os.FileInfo) (string, error) {
|
||||
if slashClean(name) == "/" {
|
||||
// Hide the real name of a possibly prefixed root directory.
|
||||
return "", nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return escapeXML(fi.Name()), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func findContentLength(ctx context.Context, fs FileSystem, ls LockSystem, name string, fi os.FileInfo) (string, error) {
|
||||
return strconv.FormatInt(fi.Size(), 10), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func findLastModified(ctx context.Context, fs FileSystem, ls LockSystem, name string, fi os.FileInfo) (string, error) {
|
||||
return fi.ModTime().UTC().Format(http.TimeFormat), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ErrNotImplemented should be returned by optional interfaces if they
|
||||
// want the original implementation to be used.
|
||||
var ErrNotImplemented = errors.New("not implemented")
|
||||
|
||||
// ContentTyper is an optional interface for the os.FileInfo
|
||||
// objects returned by the FileSystem.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If this interface is defined then it will be used to read the
|
||||
// content type from the object.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If this interface is not defined the file will be opened and the
|
||||
// content type will be guessed from the initial contents of the file.
|
||||
type ContentTyper interface {
|
||||
// ContentType returns the content type for the file.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If this returns error ErrNotImplemented then the error will
|
||||
// be ignored and the base implementation will be used
|
||||
// instead.
|
||||
ContentType(ctx context.Context) (string, error)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func findContentType(ctx context.Context, fs FileSystem, ls LockSystem, name string, fi os.FileInfo) (string, error) {
|
||||
if do, ok := fi.(ContentTyper); ok {
|
||||
ctype, err := do.ContentType(ctx)
|
||||
if err != ErrNotImplemented {
|
||||
return ctype, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
f, err := fs.OpenFile(ctx, name, os.O_RDONLY, 0)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return "", err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
// This implementation is based on serveContent's code in the standard net/http package.
|
||||
ctype := mime.TypeByExtension(filepath.Ext(name))
|
||||
if ctype != "" {
|
||||
return ctype, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Read a chunk to decide between utf-8 text and binary.
|
||||
var buf [512]byte
|
||||
n, err := io.ReadFull(f, buf[:])
|
||||
if err != nil && err != io.EOF && err != io.ErrUnexpectedEOF {
|
||||
return "", err
|
||||
}
|
||||
ctype = http.DetectContentType(buf[:n])
|
||||
// Rewind file.
|
||||
_, err = f.Seek(0, os.SEEK_SET)
|
||||
return ctype, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ETager is an optional interface for the os.FileInfo objects
|
||||
// returned by the FileSystem.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If this interface is defined then it will be used to read the ETag
|
||||
// for the object.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If this interface is not defined an ETag will be computed using the
|
||||
// ModTime() and the Size() methods of the os.FileInfo object.
|
||||
type ETager interface {
|
||||
// ETag returns an ETag for the file. This should be of the
|
||||
// form "value" or W/"value"
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If this returns error ErrNotImplemented then the error will
|
||||
// be ignored and the base implementation will be used
|
||||
// instead.
|
||||
ETag(ctx context.Context) (string, error)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func findETag(ctx context.Context, fs FileSystem, ls LockSystem, name string, fi os.FileInfo) (string, error) {
|
||||
if do, ok := fi.(ETager); ok {
|
||||
etag, err := do.ETag(ctx)
|
||||
if err != ErrNotImplemented {
|
||||
return etag, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// The Apache http 2.4 web server by default concatenates the
|
||||
// modification time and size of a file. We replicate the heuristic
|
||||
// with nanosecond granularity.
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf(`"%x%x"`, fi.ModTime().UnixNano(), fi.Size()), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func findSupportedLock(ctx context.Context, fs FileSystem, ls LockSystem, name string, fi os.FileInfo) (string, error) {
|
||||
return `` +
|
||||
`<D:lockentry xmlns:D="DAV:">` +
|
||||
`<D:lockscope><D:exclusive/></D:lockscope>` +
|
||||
`<D:locktype><D:write/></D:locktype>` +
|
||||
`</D:lockentry>`, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
702
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/webdav.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
702
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/webdav.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,702 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2014 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
// Package webdav provides a WebDAV server implementation.
|
||||
package webdav // import "golang.org/x/net/webdav"
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"net/url"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"path"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type Handler struct {
|
||||
// Prefix is the URL path prefix to strip from WebDAV resource paths.
|
||||
Prefix string
|
||||
// FileSystem is the virtual file system.
|
||||
FileSystem FileSystem
|
||||
// LockSystem is the lock management system.
|
||||
LockSystem LockSystem
|
||||
// Logger is an optional error logger. If non-nil, it will be called
|
||||
// for all HTTP requests.
|
||||
Logger func(*http.Request, error)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *Handler) stripPrefix(p string) (string, int, error) {
|
||||
if h.Prefix == "" {
|
||||
return p, http.StatusOK, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if r := strings.TrimPrefix(p, h.Prefix); len(r) < len(p) {
|
||||
return r, http.StatusOK, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return p, http.StatusNotFound, errPrefixMismatch
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *Handler) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
|
||||
status, err := http.StatusBadRequest, errUnsupportedMethod
|
||||
if h.FileSystem == nil {
|
||||
status, err = http.StatusInternalServerError, errNoFileSystem
|
||||
} else if h.LockSystem == nil {
|
||||
status, err = http.StatusInternalServerError, errNoLockSystem
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
switch r.Method {
|
||||
case "OPTIONS":
|
||||
status, err = h.handleOptions(w, r)
|
||||
case "GET", "HEAD", "POST":
|
||||
status, err = h.handleGetHeadPost(w, r)
|
||||
case "DELETE":
|
||||
status, err = h.handleDelete(w, r)
|
||||
case "PUT":
|
||||
status, err = h.handlePut(w, r)
|
||||
case "MKCOL":
|
||||
status, err = h.handleMkcol(w, r)
|
||||
case "COPY", "MOVE":
|
||||
status, err = h.handleCopyMove(w, r)
|
||||
case "LOCK":
|
||||
status, err = h.handleLock(w, r)
|
||||
case "UNLOCK":
|
||||
status, err = h.handleUnlock(w, r)
|
||||
case "PROPFIND":
|
||||
status, err = h.handlePropfind(w, r)
|
||||
case "PROPPATCH":
|
||||
status, err = h.handleProppatch(w, r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if status != 0 {
|
||||
w.WriteHeader(status)
|
||||
if status != http.StatusNoContent {
|
||||
w.Write([]byte(StatusText(status)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if h.Logger != nil {
|
||||
h.Logger(r, err)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *Handler) lock(now time.Time, root string) (token string, status int, err error) {
|
||||
token, err = h.LockSystem.Create(now, LockDetails{
|
||||
Root: root,
|
||||
Duration: infiniteTimeout,
|
||||
ZeroDepth: true,
|
||||
})
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if err == ErrLocked {
|
||||
return "", StatusLocked, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "", http.StatusInternalServerError, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return token, 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *Handler) confirmLocks(r *http.Request, src, dst string) (release func(), status int, err error) {
|
||||
hdr := r.Header.Get("If")
|
||||
if hdr == "" {
|
||||
// An empty If header means that the client hasn't previously created locks.
|
||||
// Even if this client doesn't care about locks, we still need to check that
|
||||
// the resources aren't locked by another client, so we create temporary
|
||||
// locks that would conflict with another client's locks. These temporary
|
||||
// locks are unlocked at the end of the HTTP request.
|
||||
now, srcToken, dstToken := time.Now(), "", ""
|
||||
if src != "" {
|
||||
srcToken, status, err = h.lock(now, src)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dst != "" {
|
||||
dstToken, status, err = h.lock(now, dst)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if srcToken != "" {
|
||||
h.LockSystem.Unlock(now, srcToken)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil, status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return func() {
|
||||
if dstToken != "" {
|
||||
h.LockSystem.Unlock(now, dstToken)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if srcToken != "" {
|
||||
h.LockSystem.Unlock(now, srcToken)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ih, ok := parseIfHeader(hdr)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return nil, http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidIfHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
// ih is a disjunction (OR) of ifLists, so any ifList will do.
|
||||
for _, l := range ih.lists {
|
||||
lsrc := l.resourceTag
|
||||
if lsrc == "" {
|
||||
lsrc = src
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
u, err := url.Parse(lsrc)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if u.Host != r.Host {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
lsrc, status, err = h.stripPrefix(u.Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
release, err = h.LockSystem.Confirm(time.Now(), lsrc, dst, l.conditions...)
|
||||
if err == ErrConfirmationFailed {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, http.StatusInternalServerError, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return release, 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Section 10.4.1 says that "If this header is evaluated and all state lists
|
||||
// fail, then the request must fail with a 412 (Precondition Failed) status."
|
||||
// We follow the spec even though the cond_put_corrupt_token test case from
|
||||
// the litmus test warns on seeing a 412 instead of a 423 (Locked).
|
||||
return nil, http.StatusPreconditionFailed, ErrLocked
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *Handler) handleOptions(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) (status int, err error) {
|
||||
reqPath, status, err := h.stripPrefix(r.URL.Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
ctx := getContext(r)
|
||||
allow := "OPTIONS, LOCK, PUT, MKCOL"
|
||||
if fi, err := h.FileSystem.Stat(ctx, reqPath); err == nil {
|
||||
if fi.IsDir() {
|
||||
allow = "OPTIONS, LOCK, DELETE, PROPPATCH, COPY, MOVE, UNLOCK, PROPFIND"
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
allow = "OPTIONS, LOCK, GET, HEAD, POST, DELETE, PROPPATCH, COPY, MOVE, UNLOCK, PROPFIND, PUT"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.Header().Set("Allow", allow)
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#dav.compliance.classes
|
||||
w.Header().Set("DAV", "1, 2")
|
||||
// http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-au/library/cc250217.aspx
|
||||
w.Header().Set("MS-Author-Via", "DAV")
|
||||
return 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *Handler) handleGetHeadPost(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) (status int, err error) {
|
||||
reqPath, status, err := h.stripPrefix(r.URL.Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
// TODO: check locks for read-only access??
|
||||
ctx := getContext(r)
|
||||
f, err := h.FileSystem.OpenFile(ctx, reqPath, os.O_RDONLY, 0)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusNotFound, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer f.Close()
|
||||
fi, err := f.Stat()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusNotFound, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if fi.IsDir() {
|
||||
return http.StatusMethodNotAllowed, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
etag, err := findETag(ctx, h.FileSystem, h.LockSystem, reqPath, fi)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.Header().Set("ETag", etag)
|
||||
// Let ServeContent determine the Content-Type header.
|
||||
http.ServeContent(w, r, reqPath, fi.ModTime(), f)
|
||||
return 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *Handler) handleDelete(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) (status int, err error) {
|
||||
reqPath, status, err := h.stripPrefix(r.URL.Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
release, status, err := h.confirmLocks(r, reqPath, "")
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer release()
|
||||
|
||||
ctx := getContext(r)
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: return MultiStatus where appropriate.
|
||||
|
||||
// "godoc os RemoveAll" says that "If the path does not exist, RemoveAll
|
||||
// returns nil (no error)." WebDAV semantics are that it should return a
|
||||
// "404 Not Found". We therefore have to Stat before we RemoveAll.
|
||||
if _, err := h.FileSystem.Stat(ctx, reqPath); err != nil {
|
||||
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
|
||||
return http.StatusNotFound, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return http.StatusMethodNotAllowed, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err := h.FileSystem.RemoveAll(ctx, reqPath); err != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusMethodNotAllowed, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return http.StatusNoContent, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *Handler) handlePut(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) (status int, err error) {
|
||||
reqPath, status, err := h.stripPrefix(r.URL.Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
release, status, err := h.confirmLocks(r, reqPath, "")
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer release()
|
||||
// TODO(rost): Support the If-Match, If-None-Match headers? See bradfitz'
|
||||
// comments in http.checkEtag.
|
||||
ctx := getContext(r)
|
||||
|
||||
f, err := h.FileSystem.OpenFile(ctx, reqPath, os.O_RDWR|os.O_CREATE|os.O_TRUNC, 0666)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusNotFound, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
_, copyErr := io.Copy(f, r.Body)
|
||||
fi, statErr := f.Stat()
|
||||
closeErr := f.Close()
|
||||
// TODO(rost): Returning 405 Method Not Allowed might not be appropriate.
|
||||
if copyErr != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusMethodNotAllowed, copyErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
if statErr != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusMethodNotAllowed, statErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
if closeErr != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusMethodNotAllowed, closeErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
etag, err := findETag(ctx, h.FileSystem, h.LockSystem, reqPath, fi)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.Header().Set("ETag", etag)
|
||||
return http.StatusCreated, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *Handler) handleMkcol(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) (status int, err error) {
|
||||
reqPath, status, err := h.stripPrefix(r.URL.Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
release, status, err := h.confirmLocks(r, reqPath, "")
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer release()
|
||||
|
||||
ctx := getContext(r)
|
||||
|
||||
if r.ContentLength > 0 {
|
||||
return http.StatusUnsupportedMediaType, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err := h.FileSystem.Mkdir(ctx, reqPath, 0777); err != nil {
|
||||
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
|
||||
return http.StatusConflict, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return http.StatusMethodNotAllowed, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return http.StatusCreated, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *Handler) handleCopyMove(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) (status int, err error) {
|
||||
hdr := r.Header.Get("Destination")
|
||||
if hdr == "" {
|
||||
return http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidDestination
|
||||
}
|
||||
u, err := url.Parse(hdr)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidDestination
|
||||
}
|
||||
if u.Host != r.Host {
|
||||
return http.StatusBadGateway, errInvalidDestination
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
src, status, err := h.stripPrefix(r.URL.Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dst, status, err := h.stripPrefix(u.Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if dst == "" {
|
||||
return http.StatusBadGateway, errInvalidDestination
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dst == src {
|
||||
return http.StatusForbidden, errDestinationEqualsSource
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ctx := getContext(r)
|
||||
|
||||
if r.Method == "COPY" {
|
||||
// Section 7.5.1 says that a COPY only needs to lock the destination,
|
||||
// not both destination and source. Strictly speaking, this is racy,
|
||||
// even though a COPY doesn't modify the source, if a concurrent
|
||||
// operation modifies the source. However, the litmus test explicitly
|
||||
// checks that COPYing a locked-by-another source is OK.
|
||||
release, status, err := h.confirmLocks(r, "", dst)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer release()
|
||||
|
||||
// Section 9.8.3 says that "The COPY method on a collection without a Depth
|
||||
// header must act as if a Depth header with value "infinity" was included".
|
||||
depth := infiniteDepth
|
||||
if hdr := r.Header.Get("Depth"); hdr != "" {
|
||||
depth = parseDepth(hdr)
|
||||
if depth != 0 && depth != infiniteDepth {
|
||||
// Section 9.8.3 says that "A client may submit a Depth header on a
|
||||
// COPY on a collection with a value of "0" or "infinity"."
|
||||
return http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidDepth
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return copyFiles(ctx, h.FileSystem, src, dst, r.Header.Get("Overwrite") != "F", depth, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
release, status, err := h.confirmLocks(r, src, dst)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer release()
|
||||
|
||||
// Section 9.9.2 says that "The MOVE method on a collection must act as if
|
||||
// a "Depth: infinity" header was used on it. A client must not submit a
|
||||
// Depth header on a MOVE on a collection with any value but "infinity"."
|
||||
if hdr := r.Header.Get("Depth"); hdr != "" {
|
||||
if parseDepth(hdr) != infiniteDepth {
|
||||
return http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidDepth
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return moveFiles(ctx, h.FileSystem, src, dst, r.Header.Get("Overwrite") == "T")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *Handler) handleLock(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) (retStatus int, retErr error) {
|
||||
duration, err := parseTimeout(r.Header.Get("Timeout"))
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusBadRequest, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
li, status, err := readLockInfo(r.Body)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ctx := getContext(r)
|
||||
token, ld, now, created := "", LockDetails{}, time.Now(), false
|
||||
if li == (lockInfo{}) {
|
||||
// An empty lockInfo means to refresh the lock.
|
||||
ih, ok := parseIfHeader(r.Header.Get("If"))
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidIfHeader
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(ih.lists) == 1 && len(ih.lists[0].conditions) == 1 {
|
||||
token = ih.lists[0].conditions[0].Token
|
||||
}
|
||||
if token == "" {
|
||||
return http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidLockToken
|
||||
}
|
||||
ld, err = h.LockSystem.Refresh(now, token, duration)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if err == ErrNoSuchLock {
|
||||
return http.StatusPreconditionFailed, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Section 9.10.3 says that "If no Depth header is submitted on a LOCK request,
|
||||
// then the request MUST act as if a "Depth:infinity" had been submitted."
|
||||
depth := infiniteDepth
|
||||
if hdr := r.Header.Get("Depth"); hdr != "" {
|
||||
depth = parseDepth(hdr)
|
||||
if depth != 0 && depth != infiniteDepth {
|
||||
// Section 9.10.3 says that "Values other than 0 or infinity must not be
|
||||
// used with the Depth header on a LOCK method".
|
||||
return http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidDepth
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
reqPath, status, err := h.stripPrefix(r.URL.Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
ld = LockDetails{
|
||||
Root: reqPath,
|
||||
Duration: duration,
|
||||
OwnerXML: li.Owner.InnerXML,
|
||||
ZeroDepth: depth == 0,
|
||||
}
|
||||
token, err = h.LockSystem.Create(now, ld)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if err == ErrLocked {
|
||||
return StatusLocked, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer func() {
|
||||
if retErr != nil {
|
||||
h.LockSystem.Unlock(now, token)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}()
|
||||
|
||||
// Create the resource if it didn't previously exist.
|
||||
if _, err := h.FileSystem.Stat(ctx, reqPath); err != nil {
|
||||
f, err := h.FileSystem.OpenFile(ctx, reqPath, os.O_RDWR|os.O_CREATE|os.O_TRUNC, 0666)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
// TODO: detect missing intermediate dirs and return http.StatusConflict?
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
f.Close()
|
||||
created = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#HEADER_Lock-Token says that the
|
||||
// Lock-Token value is a Coded-URL. We add angle brackets.
|
||||
w.Header().Set("Lock-Token", "<"+token+">")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/xml; charset=utf-8")
|
||||
if created {
|
||||
// This is "w.WriteHeader(http.StatusCreated)" and not "return
|
||||
// http.StatusCreated, nil" because we write our own (XML) response to w
|
||||
// and Handler.ServeHTTP would otherwise write "Created".
|
||||
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusCreated)
|
||||
}
|
||||
writeLockInfo(w, token, ld)
|
||||
return 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *Handler) handleUnlock(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) (status int, err error) {
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#HEADER_Lock-Token says that the
|
||||
// Lock-Token value is a Coded-URL. We strip its angle brackets.
|
||||
t := r.Header.Get("Lock-Token")
|
||||
if len(t) < 2 || t[0] != '<' || t[len(t)-1] != '>' {
|
||||
return http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidLockToken
|
||||
}
|
||||
t = t[1 : len(t)-1]
|
||||
|
||||
switch err = h.LockSystem.Unlock(time.Now(), t); err {
|
||||
case nil:
|
||||
return http.StatusNoContent, err
|
||||
case ErrForbidden:
|
||||
return http.StatusForbidden, err
|
||||
case ErrLocked:
|
||||
return StatusLocked, err
|
||||
case ErrNoSuchLock:
|
||||
return http.StatusConflict, err
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *Handler) handlePropfind(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) (status int, err error) {
|
||||
reqPath, status, err := h.stripPrefix(r.URL.Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
ctx := getContext(r)
|
||||
fi, err := h.FileSystem.Stat(ctx, reqPath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
|
||||
return http.StatusNotFound, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return http.StatusMethodNotAllowed, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
depth := infiniteDepth
|
||||
if hdr := r.Header.Get("Depth"); hdr != "" {
|
||||
depth = parseDepth(hdr)
|
||||
if depth == invalidDepth {
|
||||
return http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidDepth
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
pf, status, err := readPropfind(r.Body)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
mw := multistatusWriter{w: w}
|
||||
|
||||
walkFn := func(reqPath string, info os.FileInfo, err error) error {
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
var pstats []Propstat
|
||||
if pf.Propname != nil {
|
||||
pnames, err := propnames(ctx, h.FileSystem, h.LockSystem, reqPath)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
pstat := Propstat{Status: http.StatusOK}
|
||||
for _, xmlname := range pnames {
|
||||
pstat.Props = append(pstat.Props, Property{XMLName: xmlname})
|
||||
}
|
||||
pstats = append(pstats, pstat)
|
||||
} else if pf.Allprop != nil {
|
||||
pstats, err = allprop(ctx, h.FileSystem, h.LockSystem, reqPath, pf.Prop)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
pstats, err = props(ctx, h.FileSystem, h.LockSystem, reqPath, pf.Prop)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return mw.write(makePropstatResponse(path.Join(h.Prefix, reqPath), pstats))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
walkErr := walkFS(ctx, h.FileSystem, depth, reqPath, fi, walkFn)
|
||||
closeErr := mw.close()
|
||||
if walkErr != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, walkErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
if closeErr != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, closeErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (h *Handler) handleProppatch(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) (status int, err error) {
|
||||
reqPath, status, err := h.stripPrefix(r.URL.Path)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
release, status, err := h.confirmLocks(r, reqPath, "")
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
defer release()
|
||||
|
||||
ctx := getContext(r)
|
||||
|
||||
if _, err := h.FileSystem.Stat(ctx, reqPath); err != nil {
|
||||
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
|
||||
return http.StatusNotFound, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return http.StatusMethodNotAllowed, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
patches, status, err := readProppatch(r.Body)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return status, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
pstats, err := patch(ctx, h.FileSystem, h.LockSystem, reqPath, patches)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
mw := multistatusWriter{w: w}
|
||||
writeErr := mw.write(makePropstatResponse(r.URL.Path, pstats))
|
||||
closeErr := mw.close()
|
||||
if writeErr != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, writeErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
if closeErr != nil {
|
||||
return http.StatusInternalServerError, closeErr
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func makePropstatResponse(href string, pstats []Propstat) *response {
|
||||
resp := response{
|
||||
Href: []string{(&url.URL{Path: href}).EscapedPath()},
|
||||
Propstat: make([]propstat, 0, len(pstats)),
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, p := range pstats {
|
||||
var xmlErr *xmlError
|
||||
if p.XMLError != "" {
|
||||
xmlErr = &xmlError{InnerXML: []byte(p.XMLError)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
resp.Propstat = append(resp.Propstat, propstat{
|
||||
Status: fmt.Sprintf("HTTP/1.1 %d %s", p.Status, StatusText(p.Status)),
|
||||
Prop: p.Props,
|
||||
ResponseDescription: p.ResponseDescription,
|
||||
Error: xmlErr,
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
return &resp
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
infiniteDepth = -1
|
||||
invalidDepth = -2
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// parseDepth maps the strings "0", "1" and "infinity" to 0, 1 and
|
||||
// infiniteDepth. Parsing any other string returns invalidDepth.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Different WebDAV methods have further constraints on valid depths:
|
||||
// - PROPFIND has no further restrictions, as per section 9.1.
|
||||
// - COPY accepts only "0" or "infinity", as per section 9.8.3.
|
||||
// - MOVE accepts only "infinity", as per section 9.9.2.
|
||||
// - LOCK accepts only "0" or "infinity", as per section 9.10.3.
|
||||
// These constraints are enforced by the handleXxx methods.
|
||||
func parseDepth(s string) int {
|
||||
switch s {
|
||||
case "0":
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
case "1":
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
case "infinity":
|
||||
return infiniteDepth
|
||||
}
|
||||
return invalidDepth
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#status.code.extensions.to.http11
|
||||
const (
|
||||
StatusMulti = 207
|
||||
StatusUnprocessableEntity = 422
|
||||
StatusLocked = 423
|
||||
StatusFailedDependency = 424
|
||||
StatusInsufficientStorage = 507
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func StatusText(code int) string {
|
||||
switch code {
|
||||
case StatusMulti:
|
||||
return "Multi-Status"
|
||||
case StatusUnprocessableEntity:
|
||||
return "Unprocessable Entity"
|
||||
case StatusLocked:
|
||||
return "Locked"
|
||||
case StatusFailedDependency:
|
||||
return "Failed Dependency"
|
||||
case StatusInsufficientStorage:
|
||||
return "Insufficient Storage"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return http.StatusText(code)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
errDestinationEqualsSource = errors.New("webdav: destination equals source")
|
||||
errDirectoryNotEmpty = errors.New("webdav: directory not empty")
|
||||
errInvalidDepth = errors.New("webdav: invalid depth")
|
||||
errInvalidDestination = errors.New("webdav: invalid destination")
|
||||
errInvalidIfHeader = errors.New("webdav: invalid If header")
|
||||
errInvalidLockInfo = errors.New("webdav: invalid lock info")
|
||||
errInvalidLockToken = errors.New("webdav: invalid lock token")
|
||||
errInvalidPropfind = errors.New("webdav: invalid propfind")
|
||||
errInvalidProppatch = errors.New("webdav: invalid proppatch")
|
||||
errInvalidResponse = errors.New("webdav: invalid response")
|
||||
errInvalidTimeout = errors.New("webdav: invalid timeout")
|
||||
errNoFileSystem = errors.New("webdav: no file system")
|
||||
errNoLockSystem = errors.New("webdav: no lock system")
|
||||
errNotADirectory = errors.New("webdav: not a directory")
|
||||
errPrefixMismatch = errors.New("webdav: prefix mismatch")
|
||||
errRecursionTooDeep = errors.New("webdav: recursion too deep")
|
||||
errUnsupportedLockInfo = errors.New("webdav: unsupported lock info")
|
||||
errUnsupportedMethod = errors.New("webdav: unsupported method")
|
||||
)
|
||||
519
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/xml.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
519
vendor/golang.org/x/net/webdav/xml.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,519 @@
|
||||
// Copyright 2014 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
|
||||
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
|
||||
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
|
||||
|
||||
package webdav
|
||||
|
||||
// The XML encoding is covered by Section 14.
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#xml.element.definitions
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"encoding/xml"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"net/http"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
// As of https://go-review.googlesource.com/#/c/12772/ which was submitted
|
||||
// in July 2015, this package uses an internal fork of the standard
|
||||
// library's encoding/xml package, due to changes in the way namespaces
|
||||
// were encoded. Such changes were introduced in the Go 1.5 cycle, but were
|
||||
// rolled back in response to https://github.com/golang/go/issues/11841
|
||||
//
|
||||
// However, this package's exported API, specifically the Property and
|
||||
// DeadPropsHolder types, need to refer to the standard library's version
|
||||
// of the xml.Name type, as code that imports this package cannot refer to
|
||||
// the internal version.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This file therefore imports both the internal and external versions, as
|
||||
// ixml and xml, and converts between them.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// In the long term, this package should use the standard library's version
|
||||
// only, and the internal fork deleted, once
|
||||
// https://github.com/golang/go/issues/13400 is resolved.
|
||||
ixml "golang.org/x/net/webdav/internal/xml"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#ELEMENT_lockinfo
|
||||
type lockInfo struct {
|
||||
XMLName ixml.Name `xml:"lockinfo"`
|
||||
Exclusive *struct{} `xml:"lockscope>exclusive"`
|
||||
Shared *struct{} `xml:"lockscope>shared"`
|
||||
Write *struct{} `xml:"locktype>write"`
|
||||
Owner owner `xml:"owner"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#ELEMENT_owner
|
||||
type owner struct {
|
||||
InnerXML string `xml:",innerxml"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func readLockInfo(r io.Reader) (li lockInfo, status int, err error) {
|
||||
c := &countingReader{r: r}
|
||||
if err = ixml.NewDecoder(c).Decode(&li); err != nil {
|
||||
if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
if c.n == 0 {
|
||||
// An empty body means to refresh the lock.
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#refreshing-locks
|
||||
return lockInfo{}, 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
err = errInvalidLockInfo
|
||||
}
|
||||
return lockInfo{}, http.StatusBadRequest, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
// We only support exclusive (non-shared) write locks. In practice, these are
|
||||
// the only types of locks that seem to matter.
|
||||
if li.Exclusive == nil || li.Shared != nil || li.Write == nil {
|
||||
return lockInfo{}, http.StatusNotImplemented, errUnsupportedLockInfo
|
||||
}
|
||||
return li, 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type countingReader struct {
|
||||
n int
|
||||
r io.Reader
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c *countingReader) Read(p []byte) (int, error) {
|
||||
n, err := c.r.Read(p)
|
||||
c.n += n
|
||||
return n, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeLockInfo(w io.Writer, token string, ld LockDetails) (int, error) {
|
||||
depth := "infinity"
|
||||
if ld.ZeroDepth {
|
||||
depth = "0"
|
||||
}
|
||||
timeout := ld.Duration / time.Second
|
||||
return fmt.Fprintf(w, "<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"utf-8\"?>\n"+
|
||||
"<D:prop xmlns:D=\"DAV:\"><D:lockdiscovery><D:activelock>\n"+
|
||||
" <D:locktype><D:write/></D:locktype>\n"+
|
||||
" <D:lockscope><D:exclusive/></D:lockscope>\n"+
|
||||
" <D:depth>%s</D:depth>\n"+
|
||||
" <D:owner>%s</D:owner>\n"+
|
||||
" <D:timeout>Second-%d</D:timeout>\n"+
|
||||
" <D:locktoken><D:href>%s</D:href></D:locktoken>\n"+
|
||||
" <D:lockroot><D:href>%s</D:href></D:lockroot>\n"+
|
||||
"</D:activelock></D:lockdiscovery></D:prop>",
|
||||
depth, ld.OwnerXML, timeout, escape(token), escape(ld.Root),
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func escape(s string) string {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
|
||||
switch s[i] {
|
||||
case '"', '&', '\'', '<', '>':
|
||||
b := bytes.NewBuffer(nil)
|
||||
ixml.EscapeText(b, []byte(s))
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Next returns the next token, if any, in the XML stream of d.
|
||||
// RFC 4918 requires to ignore comments, processing instructions
|
||||
// and directives.
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#property_values
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#xml-extensibility
|
||||
func next(d *ixml.Decoder) (ixml.Token, error) {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
t, err := d.Token()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return t, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch t.(type) {
|
||||
case ixml.Comment, ixml.Directive, ixml.ProcInst:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return t, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#ELEMENT_prop (for propfind)
|
||||
type propfindProps []xml.Name
|
||||
|
||||
// UnmarshalXML appends the property names enclosed within start to pn.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It returns an error if start does not contain any properties or if
|
||||
// properties contain values. Character data between properties is ignored.
|
||||
func (pn *propfindProps) UnmarshalXML(d *ixml.Decoder, start ixml.StartElement) error {
|
||||
for {
|
||||
t, err := next(d)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch t.(type) {
|
||||
case ixml.EndElement:
|
||||
if len(*pn) == 0 {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s must not be empty", start.Name.Local)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
case ixml.StartElement:
|
||||
name := t.(ixml.StartElement).Name
|
||||
t, err = next(d)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if _, ok := t.(ixml.EndElement); !ok {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("unexpected token %T", t)
|
||||
}
|
||||
*pn = append(*pn, xml.Name(name))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#ELEMENT_propfind
|
||||
type propfind struct {
|
||||
XMLName ixml.Name `xml:"DAV: propfind"`
|
||||
Allprop *struct{} `xml:"DAV: allprop"`
|
||||
Propname *struct{} `xml:"DAV: propname"`
|
||||
Prop propfindProps `xml:"DAV: prop"`
|
||||
Include propfindProps `xml:"DAV: include"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func readPropfind(r io.Reader) (pf propfind, status int, err error) {
|
||||
c := countingReader{r: r}
|
||||
if err = ixml.NewDecoder(&c).Decode(&pf); err != nil {
|
||||
if err == io.EOF {
|
||||
if c.n == 0 {
|
||||
// An empty body means to propfind allprop.
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#METHOD_PROPFIND
|
||||
return propfind{Allprop: new(struct{})}, 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
err = errInvalidPropfind
|
||||
}
|
||||
return propfind{}, http.StatusBadRequest, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if pf.Allprop == nil && pf.Include != nil {
|
||||
return propfind{}, http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidPropfind
|
||||
}
|
||||
if pf.Allprop != nil && (pf.Prop != nil || pf.Propname != nil) {
|
||||
return propfind{}, http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidPropfind
|
||||
}
|
||||
if pf.Prop != nil && pf.Propname != nil {
|
||||
return propfind{}, http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidPropfind
|
||||
}
|
||||
if pf.Propname == nil && pf.Allprop == nil && pf.Prop == nil {
|
||||
return propfind{}, http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidPropfind
|
||||
}
|
||||
return pf, 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Property represents a single DAV resource property as defined in RFC 4918.
|
||||
// See http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#data.model.for.resource.properties
|
||||
type Property struct {
|
||||
// XMLName is the fully qualified name that identifies this property.
|
||||
XMLName xml.Name
|
||||
|
||||
// Lang is an optional xml:lang attribute.
|
||||
Lang string `xml:"xml:lang,attr,omitempty"`
|
||||
|
||||
// InnerXML contains the XML representation of the property value.
|
||||
// See http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#property_values
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Property values of complex type or mixed-content must have fully
|
||||
// expanded XML namespaces or be self-contained with according
|
||||
// XML namespace declarations. They must not rely on any XML
|
||||
// namespace declarations within the scope of the XML document,
|
||||
// even including the DAV: namespace.
|
||||
InnerXML []byte `xml:",innerxml"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ixmlProperty is the same as the Property type except it holds an ixml.Name
|
||||
// instead of an xml.Name.
|
||||
type ixmlProperty struct {
|
||||
XMLName ixml.Name
|
||||
Lang string `xml:"xml:lang,attr,omitempty"`
|
||||
InnerXML []byte `xml:",innerxml"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#ELEMENT_error
|
||||
// See multistatusWriter for the "D:" namespace prefix.
|
||||
type xmlError struct {
|
||||
XMLName ixml.Name `xml:"D:error"`
|
||||
InnerXML []byte `xml:",innerxml"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#ELEMENT_propstat
|
||||
// See multistatusWriter for the "D:" namespace prefix.
|
||||
type propstat struct {
|
||||
Prop []Property `xml:"D:prop>_ignored_"`
|
||||
Status string `xml:"D:status"`
|
||||
Error *xmlError `xml:"D:error"`
|
||||
ResponseDescription string `xml:"D:responsedescription,omitempty"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ixmlPropstat is the same as the propstat type except it holds an ixml.Name
|
||||
// instead of an xml.Name.
|
||||
type ixmlPropstat struct {
|
||||
Prop []ixmlProperty `xml:"D:prop>_ignored_"`
|
||||
Status string `xml:"D:status"`
|
||||
Error *xmlError `xml:"D:error"`
|
||||
ResponseDescription string `xml:"D:responsedescription,omitempty"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MarshalXML prepends the "D:" namespace prefix on properties in the DAV: namespace
|
||||
// before encoding. See multistatusWriter.
|
||||
func (ps propstat) MarshalXML(e *ixml.Encoder, start ixml.StartElement) error {
|
||||
// Convert from a propstat to an ixmlPropstat.
|
||||
ixmlPs := ixmlPropstat{
|
||||
Prop: make([]ixmlProperty, len(ps.Prop)),
|
||||
Status: ps.Status,
|
||||
Error: ps.Error,
|
||||
ResponseDescription: ps.ResponseDescription,
|
||||
}
|
||||
for k, prop := range ps.Prop {
|
||||
ixmlPs.Prop[k] = ixmlProperty{
|
||||
XMLName: ixml.Name(prop.XMLName),
|
||||
Lang: prop.Lang,
|
||||
InnerXML: prop.InnerXML,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for k, prop := range ixmlPs.Prop {
|
||||
if prop.XMLName.Space == "DAV:" {
|
||||
prop.XMLName = ixml.Name{Space: "", Local: "D:" + prop.XMLName.Local}
|
||||
ixmlPs.Prop[k] = prop
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Distinct type to avoid infinite recursion of MarshalXML.
|
||||
type newpropstat ixmlPropstat
|
||||
return e.EncodeElement(newpropstat(ixmlPs), start)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#ELEMENT_response
|
||||
// See multistatusWriter for the "D:" namespace prefix.
|
||||
type response struct {
|
||||
XMLName ixml.Name `xml:"D:response"`
|
||||
Href []string `xml:"D:href"`
|
||||
Propstat []propstat `xml:"D:propstat"`
|
||||
Status string `xml:"D:status,omitempty"`
|
||||
Error *xmlError `xml:"D:error"`
|
||||
ResponseDescription string `xml:"D:responsedescription,omitempty"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MultistatusWriter marshals one or more Responses into a XML
|
||||
// multistatus response.
|
||||
// See http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#ELEMENT_multistatus
|
||||
// TODO(rsto, mpl): As a workaround, the "D:" namespace prefix, defined as
|
||||
// "DAV:" on this element, is prepended on the nested response, as well as on all
|
||||
// its nested elements. All property names in the DAV: namespace are prefixed as
|
||||
// well. This is because some versions of Mini-Redirector (on windows 7) ignore
|
||||
// elements with a default namespace (no prefixed namespace). A less intrusive fix
|
||||
// should be possible after golang.org/cl/11074. See https://golang.org/issue/11177
|
||||
type multistatusWriter struct {
|
||||
// ResponseDescription contains the optional responsedescription
|
||||
// of the multistatus XML element. Only the latest content before
|
||||
// close will be emitted. Empty response descriptions are not
|
||||
// written.
|
||||
responseDescription string
|
||||
|
||||
w http.ResponseWriter
|
||||
enc *ixml.Encoder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write validates and emits a DAV response as part of a multistatus response
|
||||
// element.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It sets the HTTP status code of its underlying http.ResponseWriter to 207
|
||||
// (Multi-Status) and populates the Content-Type header. If r is the
|
||||
// first, valid response to be written, Write prepends the XML representation
|
||||
// of r with a multistatus tag. Callers must call close after the last response
|
||||
// has been written.
|
||||
func (w *multistatusWriter) write(r *response) error {
|
||||
switch len(r.Href) {
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
return errInvalidResponse
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
if len(r.Propstat) > 0 != (r.Status == "") {
|
||||
return errInvalidResponse
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if len(r.Propstat) > 0 || r.Status == "" {
|
||||
return errInvalidResponse
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
err := w.writeHeader()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
return w.enc.Encode(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// writeHeader writes a XML multistatus start element on w's underlying
|
||||
// http.ResponseWriter and returns the result of the write operation.
|
||||
// After the first write attempt, writeHeader becomes a no-op.
|
||||
func (w *multistatusWriter) writeHeader() error {
|
||||
if w.enc != nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.w.Header().Add("Content-Type", "text/xml; charset=utf-8")
|
||||
w.w.WriteHeader(StatusMulti)
|
||||
_, err := fmt.Fprintf(w.w, `<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>`)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
w.enc = ixml.NewEncoder(w.w)
|
||||
return w.enc.EncodeToken(ixml.StartElement{
|
||||
Name: ixml.Name{
|
||||
Space: "DAV:",
|
||||
Local: "multistatus",
|
||||
},
|
||||
Attr: []ixml.Attr{{
|
||||
Name: ixml.Name{Space: "xmlns", Local: "D"},
|
||||
Value: "DAV:",
|
||||
}},
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Close completes the marshalling of the multistatus response. It returns
|
||||
// an error if the multistatus response could not be completed. If both the
|
||||
// return value and field enc of w are nil, then no multistatus response has
|
||||
// been written.
|
||||
func (w *multistatusWriter) close() error {
|
||||
if w.enc == nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
var end []ixml.Token
|
||||
if w.responseDescription != "" {
|
||||
name := ixml.Name{Space: "DAV:", Local: "responsedescription"}
|
||||
end = append(end,
|
||||
ixml.StartElement{Name: name},
|
||||
ixml.CharData(w.responseDescription),
|
||||
ixml.EndElement{Name: name},
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
end = append(end, ixml.EndElement{
|
||||
Name: ixml.Name{Space: "DAV:", Local: "multistatus"},
|
||||
})
|
||||
for _, t := range end {
|
||||
err := w.enc.EncodeToken(t)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return w.enc.Flush()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var xmlLangName = ixml.Name{Space: "http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace", Local: "lang"}
|
||||
|
||||
func xmlLang(s ixml.StartElement, d string) string {
|
||||
for _, attr := range s.Attr {
|
||||
if attr.Name == xmlLangName {
|
||||
return attr.Value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return d
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type xmlValue []byte
|
||||
|
||||
func (v *xmlValue) UnmarshalXML(d *ixml.Decoder, start ixml.StartElement) error {
|
||||
// The XML value of a property can be arbitrary, mixed-content XML.
|
||||
// To make sure that the unmarshalled value contains all required
|
||||
// namespaces, we encode all the property value XML tokens into a
|
||||
// buffer. This forces the encoder to redeclare any used namespaces.
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
e := ixml.NewEncoder(&b)
|
||||
for {
|
||||
t, err := next(d)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
if e, ok := t.(ixml.EndElement); ok && e.Name == start.Name {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if err = e.EncodeToken(t); err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
err := e.Flush()
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
*v = b.Bytes()
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#ELEMENT_prop (for proppatch)
|
||||
type proppatchProps []Property
|
||||
|
||||
// UnmarshalXML appends the property names and values enclosed within start
|
||||
// to ps.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// An xml:lang attribute that is defined either on the DAV:prop or property
|
||||
// name XML element is propagated to the property's Lang field.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// UnmarshalXML returns an error if start does not contain any properties or if
|
||||
// property values contain syntactically incorrect XML.
|
||||
func (ps *proppatchProps) UnmarshalXML(d *ixml.Decoder, start ixml.StartElement) error {
|
||||
lang := xmlLang(start, "")
|
||||
for {
|
||||
t, err := next(d)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch elem := t.(type) {
|
||||
case ixml.EndElement:
|
||||
if len(*ps) == 0 {
|
||||
return fmt.Errorf("%s must not be empty", start.Name.Local)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
case ixml.StartElement:
|
||||
p := Property{
|
||||
XMLName: xml.Name(t.(ixml.StartElement).Name),
|
||||
Lang: xmlLang(t.(ixml.StartElement), lang),
|
||||
}
|
||||
err = d.DecodeElement(((*xmlValue)(&p.InnerXML)), &elem)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return err
|
||||
}
|
||||
*ps = append(*ps, p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#ELEMENT_set
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#ELEMENT_remove
|
||||
type setRemove struct {
|
||||
XMLName ixml.Name
|
||||
Lang string `xml:"xml:lang,attr,omitempty"`
|
||||
Prop proppatchProps `xml:"DAV: prop"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://www.webdav.org/specs/rfc4918.html#ELEMENT_propertyupdate
|
||||
type propertyupdate struct {
|
||||
XMLName ixml.Name `xml:"DAV: propertyupdate"`
|
||||
Lang string `xml:"xml:lang,attr,omitempty"`
|
||||
SetRemove []setRemove `xml:",any"`
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func readProppatch(r io.Reader) (patches []Proppatch, status int, err error) {
|
||||
var pu propertyupdate
|
||||
if err = ixml.NewDecoder(r).Decode(&pu); err != nil {
|
||||
return nil, http.StatusBadRequest, err
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, op := range pu.SetRemove {
|
||||
remove := false
|
||||
switch op.XMLName {
|
||||
case ixml.Name{Space: "DAV:", Local: "set"}:
|
||||
// No-op.
|
||||
case ixml.Name{Space: "DAV:", Local: "remove"}:
|
||||
for _, p := range op.Prop {
|
||||
if len(p.InnerXML) > 0 {
|
||||
return nil, http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidProppatch
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
remove = true
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return nil, http.StatusBadRequest, errInvalidProppatch
|
||||
}
|
||||
patches = append(patches, Proppatch{Remove: remove, Props: op.Prop})
|
||||
}
|
||||
return patches, 0, nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
28
vendor/modules.txt
vendored
28
vendor/modules.txt
vendored
@ -2,6 +2,9 @@
|
||||
github.com/PuerkitoBio/purell
|
||||
# github.com/PuerkitoBio/urlesc v0.0.0-20170810143723-de5bf2ad4578
|
||||
github.com/PuerkitoBio/urlesc
|
||||
# github.com/alecthomas/template v0.0.0-20160405071501-a0175ee3bccc
|
||||
github.com/alecthomas/template
|
||||
github.com/alecthomas/template/parse
|
||||
# github.com/asaskevich/govalidator v0.0.0-20180720115003-f9ffefc3facf
|
||||
github.com/asaskevich/govalidator
|
||||
# github.com/client9/misspell v0.3.4
|
||||
@ -18,6 +21,8 @@ github.com/fzipp/gocyclo
|
||||
# github.com/garyburd/redigo v1.6.0
|
||||
github.com/garyburd/redigo/redis
|
||||
github.com/garyburd/redigo/internal
|
||||
# github.com/ghodss/yaml v1.0.0
|
||||
github.com/ghodss/yaml
|
||||
# github.com/globalsign/mgo v0.0.0-20180905125535-1ca0a4f7cbcb
|
||||
github.com/globalsign/mgo/bson
|
||||
github.com/globalsign/mgo/internal/json
|
||||
@ -119,6 +124,8 @@ github.com/mitchellh/mapstructure
|
||||
github.com/op/go-logging
|
||||
# github.com/pelletier/go-toml v1.2.0
|
||||
github.com/pelletier/go-toml
|
||||
# github.com/pkg/errors v0.8.0
|
||||
github.com/pkg/errors
|
||||
# github.com/pmezard/go-difflib v1.0.0
|
||||
github.com/pmezard/go-difflib/difflib
|
||||
# github.com/spf13/afero v1.1.2
|
||||
@ -134,8 +141,18 @@ github.com/spf13/pflag
|
||||
github.com/spf13/viper
|
||||
# github.com/stretchr/testify v1.2.2
|
||||
github.com/stretchr/testify/assert
|
||||
# github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger v0.0.0-20180315045949-97f46bb9e5a5
|
||||
github.com/swaggo/echo-swagger
|
||||
# github.com/swaggo/files v0.0.0-20180215091130-49c8a91ea3fa
|
||||
github.com/swaggo/files
|
||||
# github.com/swaggo/swag v1.3.3-0.20181109030545-8f09470d62b2
|
||||
github.com/swaggo/swag/cmd/swag
|
||||
github.com/swaggo/swag
|
||||
github.com/swaggo/swag/gen
|
||||
# github.com/toqueteos/webbrowser v1.1.0
|
||||
github.com/toqueteos/webbrowser
|
||||
# github.com/urfave/cli v1.20.0
|
||||
github.com/urfave/cli
|
||||
# github.com/valyala/bytebufferpool v1.0.0
|
||||
github.com/valyala/bytebufferpool
|
||||
# github.com/valyala/fasttemplate v0.0.0-20170224212429-dcecefd839c4
|
||||
@ -149,6 +166,9 @@ golang.org/x/crypto/acme
|
||||
golang.org/x/lint/golint
|
||||
golang.org/x/lint
|
||||
# golang.org/x/net v0.0.0-20181005035420-146acd28ed58
|
||||
golang.org/x/net/webdav
|
||||
golang.org/x/net/context
|
||||
golang.org/x/net/webdav/internal/xml
|
||||
golang.org/x/net/idna
|
||||
# golang.org/x/sys v0.0.0-20180906133057-8cf3aee42992
|
||||
golang.org/x/sys/unix
|
||||
@ -159,14 +179,14 @@ golang.org/x/text/width
|
||||
golang.org/x/text/secure/bidirule
|
||||
golang.org/x/text/unicode/bidi
|
||||
# golang.org/x/tools v0.0.0-20181026183834-f60e5f99f081
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/go/loader
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/go/ast/astutil
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/go/gcexportdata
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/go/internal/gcimporter
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/imports
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/go/loader
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/internal/gopathwalk
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/go/buildutil
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/go/internal/cgo
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/go/internal/gcimporter
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/imports
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/internal/gopathwalk
|
||||
golang.org/x/tools/internal/fastwalk
|
||||
# gopkg.in/alexcesaro/quotedprintable.v3 v3.0.0-20150716171945-2caba252f4dc
|
||||
gopkg.in/alexcesaro/quotedprintable.v3
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user